How Do You Pursue A Career In Renewable Energy?

Renewable energy is derived from natural processes and resources that are constantly being replenished, like sunlight, wind, tides, waves, and geothermal heat. The renewable energy industry includes sectors like solar, wind, hydroelectricity, geothermal, and biomass. It is one of the fastest growing sectors today, with the International Renewable Energy Agency estimating that renewable energy jobs could reach 42 million globally by 2050.
Pursuing a career in renewable energy presents a unique opportunity to combat climate change while working in a rapidly expanding industry. The renewable energy sector is projected to grow 5% from 2022-2032, much faster than average job growth in the U.S. economy, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. With climate change being one of the most pressing issues today, a career in renewable energy allows professionals to be at the forefront of developing innovative solutions while contributing to a more sustainable future.
Some of the attractive aspects of a renewable energy career include competitive salaries, skill development in cutting-edge technologies, the chance to work on impactful projects, and flexibility to work in the public and private sectors. Overall, the growth, mission-driven nature, and technical innovation make renewable energy an appealing field to build a long-term career in.
Education Requirements
To pursue a career in renewable energy, there are several educational paths you can take:
Undergraduate Degrees
Many entry-level renewable energy jobs require at least a bachelor’s degree. Common majors include environmental engineering, environmental science, sustainability, energy systems engineering, electrical engineering, and mechanical engineering. Some top programs in renewable energy include Oregon State University, Arizona State University, and Cornell University (source).
Graduate Degrees
For more advanced positions in research, design, or project management, a master’s degree or PhD is often required. Common graduate programs include environmental engineering, sustainable energy systems, energy policy and economics, and renewable energy management (source).
Certifications
Industry certifications can complement formal education and demonstrate specialized skills. Relevant certifications include LEED AP, Certified Energy Manager, NABCEP Solar PV Installer, and Certified Wind Energy Professional (source).
Key Skills Needed
Pursuing a career in renewable energy requires a diverse set of technical, analytical, and interpersonal skills. Here are some of the key skills needed to succeed in this industry:
Technical skills like engineering are essential. Most roles require understanding energy systems, electricity generation, transmission and storage, and being able to design, implement, and maintain renewable energy projects. Knowledge of electrical, mechanical, chemical, civil, and industrial engineering principles is highly valued.
Analytical skills are also important. Conducting energy assessments, evaluating options, optimizing systems, and analyzing data require critical thinking and problem solving abilities. Mathematics, modeling, analysis, and assessment skills allow renewable energy professionals to make sound recommendations.
Additionally, communication and teamwork skills are vital. Renewable energy projects involve many stakeholders and require collaboration across disciplines. Being able to communicate complex technical concepts clearly and work well cross-functionally is critical for success.
Types of Renewable Energy Jobs
There are many career opportunities available within the renewable energy industry. Here are some of the major types of jobs focused on the leading renewable energy sources:
Solar Energy Jobs
Some of the most common solar energy jobs include solar panel installers, solar sales representatives, solar engineers, solar technicians, and solar project managers. These roles involve designing, building, installing, maintaining, and selling solar photovoltaic systems.
Wind Energy Jobs
Wind energy careers consist of jobs like wind turbine technicians, wind energy engineers, wind farm managers, and wind turbine sales representatives. These professionals are involved in developing, operating, and maintaining wind farms and wind turbines.
Geothermal Energy Jobs
Geothermal industry jobs include geothermal technicians, geothermal engineers, geothermal drilling specialists, geothermal sales reps, and geothermal project managers. They work on harnessing heat from under the earth’s surface for power generation.
Hydroelectric Energy Jobs
Hydropower jobs involve operating, maintaining, and building hydroelectric plants and dams. Some common roles are hydroelectric plant technicians, hydroelectric engineers, hydroelectric operations managers, and other specialized technical positions.
Biomass Energy Jobs
The biomass energy sector provides jobs like biomass plant technicians, biomass engineers, biomass procurement managers, and biomass production workers. They work on converting organic matter into energy sources.
Salary and Job Outlook
The renewable energy industry is experiencing rapid growth and job creation. According to the 2023 U.S. Energy and Employment Report, clean energy jobs increased by 9.7% in 2022 to 3.2 million, adding 278,000 net new jobs.[1] This growth outpaced the overall U.S. economy’s job growth rate of 3.8%.
The average salary for renewable energy jobs also remains strong. Solar photovoltaic installers earn an average of $48,490 per year, while wind turbine technicians earn $56,230. More specialized roles like solar engineers and renewable energy engineers earn average salaries of $99,420 and $112,020 per year, respectively.[2]
The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects that solar PV installer jobs will grow by 52% between 2020-2030, adding 25,800 new jobs. Wind turbine technician jobs are expected to increase by 68% in the same period, adding 5,600 jobs.[3] Clearly, the renewable energy industry presents strong job growth and earning potential for those interested in starting a career in this field.
Day-to-Day Responsibilities
The day-to-day responsibilities of jobs in renewable energy vary significantly depending on the specific role. Here is an overview of typical tasks for some common positions:
Engineering roles like wind turbine engineers may spend time designing renewable energy systems, performing complex calculations, running simulations, and testing prototypes. They work on improving efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness of renewable technologies.
Construction managers and technicians are responsible for building, installing, and maintaining renewable energy infrastructure like solar farms and wind turbines. Their daily tasks involve construction planning, sourcing materials, operating heavy machinery, troubleshooting issues, and ensuring projects meet specifications.
Plant operators work hands-on running facilities that generate renewable power. Their duties include monitoring equipment, diagnosing problems, optimizing performance, conducting repairs, and coordinating with maintenance crews. Strict safety protocols are followed.
Project developers handle permitting, siting, financing, and management of renewable energy projects. Typical activities include conducting feasibility studies, obtaining permits, securing financing, negotiating contracts, and coordinating construction and operation teams.
Sales and business development professionals work on marketing renewable energy products and services. They identify business opportunities, contact potential clients, understand needs, promote offerings, negotiate terms, and maintain relationships.
Research scientists and engineers in renewable energy focus on advancing technologies and efficiency. A typical day may involve designing experiments, collecting and analyzing data, modeling systems, writing papers, and reviewing literature.
Challenges and Rewards
Though a career in renewable energy can be very rewarding, it also comes with its fair share of challenges. Many jobs in this industry require hard work, long hours, and dedication. The work is hands-on and can take place outdoors in all weather conditions [1].
However, renewable energy professionals find the work deeply meaningful because they get to be at the forefront of innovative technologies that are rapidly evolving. There’s a sense of purpose in improving the environment and developing more sustainable sources of energy for the future [2].
Workers in this industry have the satisfaction of being part of positive change. While renewable energy careers can be challenging, they provide an opportunity to apply cutting-edge skills to urgent real-world problems.
Getting Your First Job
Internships are a great way to gain experience and get your foot in the door with renewable energy companies. Many firms offer paid internship programs specifically for students interested in energy careers. Look for openings on company websites and job boards. Internships allow you to learn on the job, network with professionals, and develop the skills needed for a full-time renewable energy role.1
Entry-level jobs provide a way to start your renewable energy career after graduation. Common titles include Energy Analyst, Solar Consultant, Wind Technician, and Sustainability Coordinator. Focus on finding openings at renewable energy companies, utilities, engineering firms, and environmental non-profits. Highlight any internship experience, relevant coursework, and skills like data analysis and project management.2
Building experience through volunteering and extracurriculars can also strengthen your renewable energy resume. Look for opportunities to join student organizations and take on leadership roles related to sustainability. Assist professors with renewable energy research projects. Attend industry conferences and events whenever possible.3
Career Advancement
Those working in renewable energy have many opportunities for career advancement. Some ways to move forward in your career include:
Further education – Many roles, especially engineering and project management positions, require or prefer candidates with a master’s degree or other advanced certification. Pursuing an advanced degree in a specialized field like solar engineering or wind turbine design can open up more senior-level roles. Some companies may even provide tuition assistance.
Specialization – Gaining expertise in a specific technology like PV solar, offshore wind, or geothermal systems can make you a more valuable employee. You may be able to specialize by moving between departments or companies.
Leadership roles – With proven experience and expertise, renewable energy professionals can advance to lead teams, departments, or entire organizations and facilities. Leadership roles include project managers, operations managers, and directors.
Future Outlook
A variety of sources make it clear that substantial growth in the renewable energy industry is expected to continue for the foreseeable future. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the share of renewables in global electricity generation is forecast to rise to over 30% in 2024, up from less than 27% in 2019 (IEA, 2023). Total renewable power capacity worldwide is projected to increase more than 60% between 2020 and 2030 (IEA, 2022).
A major driver of continued growth is government incentives and policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions and promoting renewable energy adoption. Many countries have renewable portfolio standards and clean energy policies expected to require hundreds of additional terawatt-hours of clean electricity in the coming years (Deloitte, 2022). Tax credits, rebates, and other financial incentives are also boosting investment and deployment of renewable energy systems.
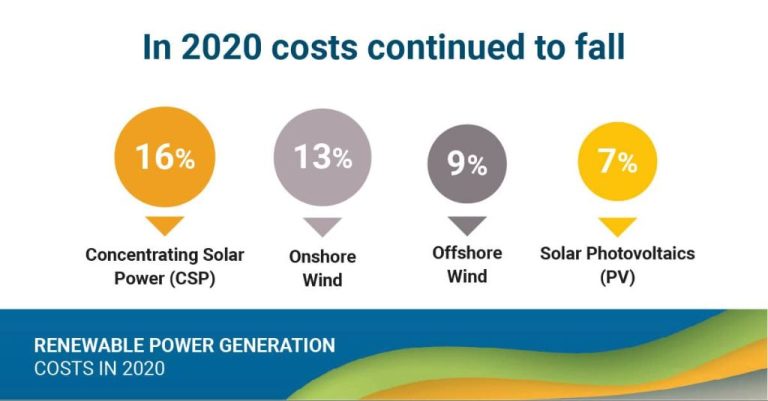
Technological advances and falling costs, especially for solar and wind power, will enable wider adoption of renewables as well. Innovations in areas like energy storage, smart grids, and distributed generation will also support growth. Overall, renewable energy is poised for an increasingly prominent role in meeting the world’s electricity needs going forward.