Why Are Alternate Forms Of Energy Important?
Fossil Fuels Are Finite
Fossil fuels like oil, natural gas, and coal are non-renewable resources that formed when prehistoric plants and animals died and were gradually buried by layers of rock. Over millions of years, the organic matter was transformed into fossil fuels by exposure to heat and pressure under the earth’s surface. Fossil fuels cannot be replenished on human timescales and will eventually run out.
Fossil fuels took millions of years to form, yet we are depleting them at a far more rapid pace. At current global consumption rates, experts estimate that the world’s oil reserves may run out in 50 years, natural gas in 52 years, and coal in 113 years. Some countries have already reached peak production and are experiencing declines in their domestic supply. With finite reserves and growing energy demands, reliance on fossil fuels is unsustainable in the long run.
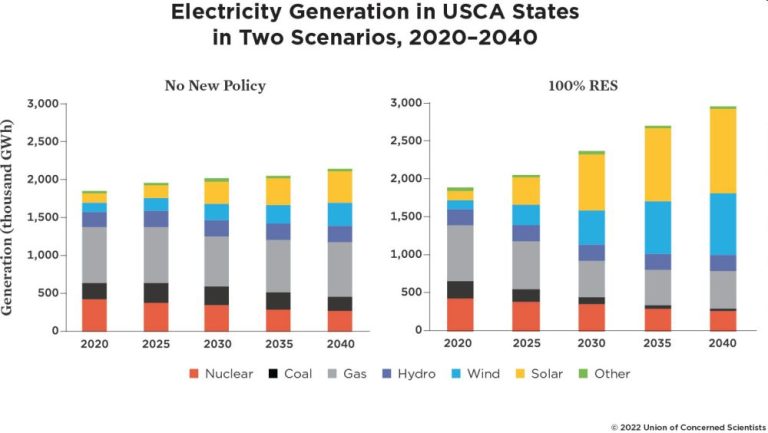
While new discoveries or advanced recovery techniques may extend timelines, fossil fuels remain nonrenewable resources. Sufficient oil, coal and natural gas may not exist to sustain the world’s future energy needs. Transitioning to renewable energy sources that can be continually replenished, such as solar, wind and hydropower, will be essential for long-term energy security and environmental stability.
Environmental Damage of Fossil Fuels
The extraction, processing and burning of fossil fuels like oil, coal, and natural gas have enormous environmental consequences. Burning fossil fuels produces billions of tons of greenhouse gas emissions every year such as carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide. These emissions lead to global warming and climate change, dangerously heating up the planet.
Fossil fuel extraction and transportation can lead to disastrous oil spills in oceans, contaminating marine ecosystems and leading to the deaths of fish, mammals and seabirds. Mining for coal destroys forests and releases toxic mining byproducts into rivers and lakes. Burning coal produces hazardous air pollutants like sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides and particulate matter that contribute to acid rain and respiratory illnesses in people.
The use of fossil fuels is one of the biggest threats to the natural world. Transitioning to clean, renewable energy alternatives like solar, wind and geothermal can help mitigate climate change and pollution caused by our reliance on fossil fuels for energy.
Climate Change
The burning of fossil fuels like coal, oil and natural gas releases large amounts of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane act like a blanket, trapping heat from the sun and causing global temperatures to rise. This leads to climate change effects like melting glaciers, rising sea levels, more extreme weather events, droughts and heat waves.
Since the Industrial Revolution began in the mid-1800s, the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has increased by over 40%. More than half of this increase has occurred since the 1970s as the use of fossil fuels has rapidly accelerated. The release of greenhouse gases from human activities is the primary cause of global warming. According to NASA, 97% of climate scientists agree that climate change trends are extremely likely due to human activities.
Transitioning away from fossil fuels to cleaner forms of energy like solar, wind and geothermal would significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and help mitigate climate change. This is critical for protecting communities around the world from devastating impacts.
Energy Independence
Reliance on imported fossil fuels leaves countries vulnerable to unpredictable price fluctuations and supply disruptions caused by political unrest, trade disputes or natural disasters. Transitioning to renewable energy sources produced domestically can provide greater energy independence and security. With locally generated wind, solar, geothermal and biofuels, nations do not have to worry about fuel imports if conflicts or disasters cut off supply chains. Energy independence also reduces the strategic and economic leverage held by oil and gas exporters.
For example, the European Union imports over 50% of its energy needs, leaving it exposed to supply squeezes like those arising from the Russia-Ukraine war. In contrast, Denmark generates over 40% of its electricity from wind power. This domestic capacity buffers it from global price shocks and supply shortages. The U.S. has vast solar, wind, geothermal and biomass resources that if tapped, could eliminate imports from unstable regions and the associated national security risks and trade deficits. Investing more heavily in renewable power would provide America with a reliable domestic energy supply while also creating jobs and keeping money in the local economy.
Job Creation
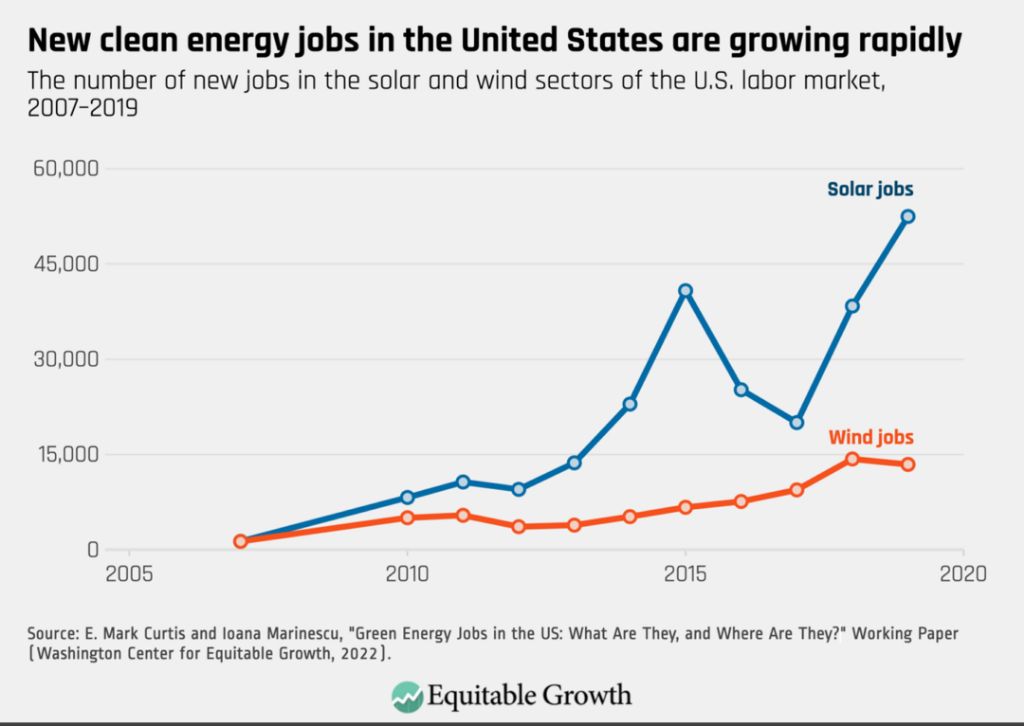
The renewable energy industry is a significant creator of jobs as we transition away from fossil fuels. Per unit of energy produced, renewable sources like wind, solar, and geothermal create more jobs than coal, oil, or natural gas. This is because renewable energy tends to be more labor-intensive to build, operate, and maintain whereas fossil fuel extraction is highly automated.
According to the International Renewable Energy Agency, the renewable energy sector employed 11 million people globally in 2018. With the right policies and investments, they estimate renewable energy could employ over 42 million people by 2050. The vast majority of these jobs provide good wages and benefits too.
In the US, the number of jobs in solar and wind has grown rapidly, reaching over 500,000 in 2019 according to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics. The solar industry alone accounted for over 250,000 jobs. Renewables employ around 3 times more people than the fossil fuel industry per unit of energy generated.
Investing in renewable energy is clearly a great way to create large numbers of stable, well-paying jobs, especially in manufacturing, construction, maintenance and other skilled trades. This helps local economies and provides employment opportunities at all skill levels.
Cost Savings from Renewable Energy
Renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and geothermal can provide significant long-term cost savings compared to fossil fuels. While the upfront costs of building renewable energy facilities are still higher than conventional power plants, the “fuel” costs for renewables are negligible. The sun, wind, and earth’s internal heat are free, while coal, oil, and natural gas must be continuously mined, drilled, transported, and purchased.
Once a renewable power plant is constructed, the marginal cost of producing an additional unit of electricity is close to zero. In contrast, fossil fuel prices can be extremely volatile and are subject to complex geopolitical factors. The costs of renewable energy are much more stable and predictable over time. This helps consumers and businesses better forecast and budget their energy expenses.
As renewable energy technologies mature and production scales up, the upfront capital costs continue to fall. And unlike finite fossil fuel reserves which will become more expensive over time as supplies deplete, the cost of renewables will only go down as efficiency improves. Within the next few years, building new renewable energy is projected to be cheaper than operating existing fossil fuel generators in most markets.
The proven cost savings delivered by renewable energy will only grow over time. Locking in renewable energy today can serve as a long-term hedge against fossil fuel price volatility. That’s why many corporations are rapidly signing long-term power purchase agreements with renewable energy projects – to lock in lower, more predictable electricity costs for decades to come.
Technology Improvements
Renewable energy technologies have seen major innovations and improvements in efficiency and cost over the past decade. For example, solar photovoltaic panels are now over 50% cheaper per watt and have conversion efficiencies exceeding 20%. Wind turbines have grown enormously in size, with rotor diameters now exceeding 120 meters and nameplate capacities over 10 megawatts. This has significantly lowered the cost per kWh of wind energy. Geothermal power plants now utilize enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) and improved drilling technologies to access geothermal resources previously out of reach.
These technology improvements have made alternate forms of energy much more cost competitive with fossil fuels. With continued investments in R&D and economies of scale, costs are projected to decrease further. Advancements in energy storage, smart grids, and other complementary technologies will also aid in the integration of higher shares of renewables onto the electric grid.
Government Support and Incentives
Governments around the world are providing incentives and implementing policies to encourage the development and adoption of renewable energy sources.
In the United States, federal tax credits lower the cost of installation for renewable energy systems like solar panels and wind turbines for homeowners and businesses. Many states also offer additional incentives like rebates and property tax exemptions for renewable energy investments.
The federal government also provides grants, loans, and other funding for renewable energy research and development projects. The Department of Energy has loan guarantee programs to support early-stage renewable energy projects that have difficulty obtaining private financing.
At the state level, Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS) require electric utilities to source a certain percentage of their electricity from renewable sources. As of 2019, 29 states and Washington D.C. had mandatory RPS policies.
Internationally, over 100 countries now have renewable energy targets and policies in place. The European Union has set ambitious goals to source 32% of all energy from renewables by 2030. Countries like Germany, Spain, and Denmark lead in wind power capacity after years of sustained policy support.
Government incentives and long-term policy visions have been integral in driving the rapid growth of renewable energy worldwide.
Corporate Sustainability
Many corporations are increasingly committing to using renewable energy as part of their sustainability goals. For example, Google has pledged to power its operations entirely with clean energy and has signed contracts to purchase over 2.6 gigawatts of renewable energy. Apple has also made significant investments in renewable energy, with over 130 manufacturing partners committed to using clean power across 25 countries. Major companies like Walmart, Amazon, Microsoft, IKEA, and others have pledged to dramatically increase their use of renewables as well.
There are several motivations behind this corporate support for renewables. Using clean energy helps these large companies reduce their carbon footprints and meet ambitious greenhouse gas reduction targets. It also allows them to brand themselves as environmentally friendly and appeal to eco-conscious consumers. Additionally, signing long-term contracts for renewables helps provide financial stability to the renewable energy industry and stimulates further development. As more corporations commit to clean energy, it will drive additional demand and investment in renewables.
Public Opinion
Public support for expanding renewable energy has grown substantially over the past decade. According to a 2021 Pew Research Center survey, 77% of U.S. adults favor expanding solar panel farms, up from 65% in 2016. Similarly, 71% favor more wind turbine farms, compared to 61% in 2016. Gallup polls also show strong public preference for prioritizing renewables over fossil fuels – their 2021 survey found that 60% of Americans prioritize development of alternative energy over oil, gas and coal.
This growth in public opinion is likely driven by increased awareness of climate change and other environmental impacts of fossil fuels. The rapidly falling costs of wind and solar power have also boosted public support. Policies that promote renewable energy enjoy bipartisan appeal, with a majority of Democrats, Independents and Republicans in favor.