What Is Solar For Alternative Energy?
Solar energy is the radiant light and heat from the sun that is harnessed using a range of technologies such as photovoltaic panels and concentrated solar power. Solar energy is an increasingly important renewable energy source that has the potential to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and provide clean, sustainable energy for the future. Solar is considered one of the key technologies to enable the transition to a low carbon economy and mitigate climate change.
The development of solar energy has grown exponentially in recent years as costs have come down dramatically and technology has improved. Solar provides an alternative to traditional energy sources that come with environmental impacts and constraints on supply. The production of solar energy can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. It can also provide energy access to remote areas not connected to an electrical grid. This article will provide an overview of how solar energy works, the technologies involved, solar’s benefits and limitations, key developments and policies related to solar, and projections for the future role of solar energy.
How Solar Energy Works
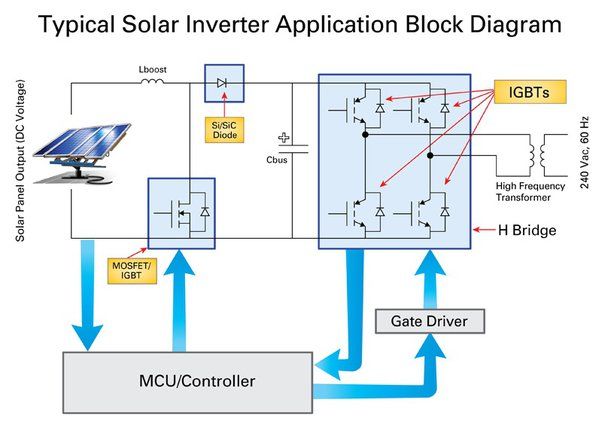
Solar energy systems work by harnessing power from the sun and utilizing it for electricity, heating, cooling, or other energy needs. The key components of solar energy are photovoltaic panels, solar thermal collectors, and concentrated solar power systems.
Photovoltaic panels, also referred to as solar PV, convert sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. When photons from sunlight strike the panel, they excite the electrons in the panel’s semiconducting material, causing electrons to flow and generate electricity. The electricity generated can be used to power homes, buildings or fed into the grid.
Solar thermal collectors, such as solar hot water systems, use sunlight to heat water or a heat-transfer fluid. This captured heat can be used for domestic hot water, heating swimming pools, or other thermal needs. Solar thermal does not convert sunlight into electricity like solar PV.
Concentrated solar power (CSP) systems use mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a receiver. The concentrated light heats the receiver to very high temperatures, which is then used to generate electricity through a steam turbine or heat engine. CSP allows for storage of the heat so power can be produced even when the sun is not shining.
The key difference between solar PV and solar thermal is that PV converts light directly into electricity, while solar thermal captures heat from the sun to produce thermal energy. Solar PV produces electricity, while solar thermal is used for heating applications.
Solar Energy Technology
There are several technologies used to harness energy from the sun for electricity and heating purposes. The main types are:
Photovoltaic Panels
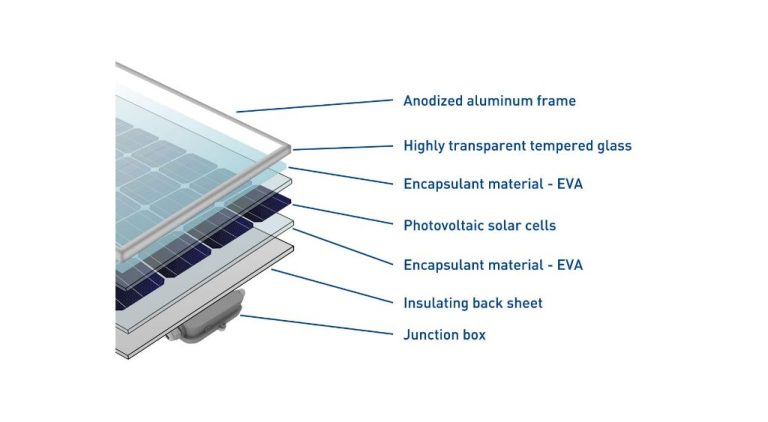
Photovoltaic (PV) panels, also known as solar panels, convert sunlight directly into electricity. They are made up of solar cells, usually silicon, that are sensitive to light. When the solar cells are exposed to sunlight, electrons are knocked loose from the atoms of the semiconductor material, generating a flow of electricity.
Solar Thermal Collectors
Solar thermal collectors, also known as solar hot water panels, absorb heat from the sun to warm water or other fluids. They circulate a liquid through tubes or panels and then use this heated liquid directly or transfer its heat to water in a storage tank.
Solar Water Heaters
Solar water heaters are a type of solar thermal system designed specifically to heat water. They consist of solar thermal collectors and a storage tank. There are active systems with pumps and controls, and passive systems that circulate water naturally.
Concentrated Solar Power
Concentrated solar power (CSP) systems use mirrors or lenses to concentrate a large area of sunlight onto a small area. The focused light is converted into heat, which drives a turbine to generate electricity. CSP systems allow energy storage by heating molten salt to run steam turbines after sunset.
Benefits of Solar
Solar energy offers many benefits that make it an appealing renewable energy source for homes and businesses. Some of the main advantages of solar power include:
Clean, Renewable Source
Solar energy is a clean, renewable source of power that does not produce any direct waste or pollution. Solar panels generate electricity from sunlight without emitting greenhouse gases or other pollutants. This makes solar a sustainable, environmentally friendly energy solution.
Reduces Electricity Bills
Installing solar panels can significantly lower electricity bills, as solar energy directly offsets grid power usage. Many homeowners see their electricity bills drop by 50-90% after going solar. The costs of solar have also fallen dramatically in the past decade, making it more affordable.
Energy Independence
Solar provides energy independence and security, as it allows homes and businesses to generate their own power. This insulating from utility rate hikes and potential grid outages. Relying less on the grid also strengthens personal and national energy security.
Low Maintenance
Once installed, solar panels require very little maintenance over their lifespan of 20-30 years. They have no moving parts and are generally very reliable. This creates very low maintenance costs over the life of a solar system.
Limitations of Solar
While solar energy has many benefits, it also comes with some limitations that need to be considered.
Intermittency
One of the biggest limitations of solar energy is its intermittent nature. Solar panels only produce energy when the sun is shining. At night and on cloudy days, solar panel output drops dramatically or stops completely. This inconsistency makes solar problematic to rely on as a sole energy source. Energy storage solutions like batteries can help mitigate intermittency, but add cost.
High Upfront Costs
The upfront cost of installing solar panels and associated equipment like inverters is quite high for the average homeowner. Though prices have dropped substantially over the years, the upfront investment for a residential solar system can still be daunting. The payback period can take several years to recover the upfront costs through electricity savings.
Land Usage
Utility-scale solar farms require a lot of land space to generate significant capacity. This could potentially require deforestation or use of agricultural land, displacing wildlife habitats and crops. Rooftop solar on homes overcomes the land usage limitation but has capacity constraints based on roof size.
Daylight Dependency
Solar energy can only be generated during daylight hours. In regions farther from the equator, the limited daylight hours in winter can reduce solar output. Solar potential also varies by local climate and cloud cover obscuring the sunlight.
Solar Energy Storage
Solar energy, whether through photovoltaic (PV) panels or solar thermal technology, is an essential renewable source for generating electricity and heat. However, the sun mostly shines during the day, while electricity demand peaks in evening hours. For full utilization of solar power and efficient grid integration, effective energy storage is critical. Several technologies allow storage of solar energy for later use:

Batteries
Batteries are the most common method for storing solar energy. Lithium-ion batteries have emerged as a favorite due to declining costs, long lifetimes, and high-efficiency storage and discharge of electricity. Battery banks co-located with solar arrays store excess daytime solar generation for dispatch at night.
Thermal Storage
Molten salt and other media can store heat efficiently for long durations. In concentrated solar power plants, sunlight heats a transfer fluid that is used to produce steam and generate electricity via a turbine. Excess heat is stored in large insulated tanks and can be drawn upon after sunset.
Pumped Hydro Storage
This mature storage method involves pumping water uphill into a reservoir when solar supply exceeds demand. The water is released to spin hydropower turbines when more electricity is needed. Pumped hydro provides energy storage at a large scale.
Molten Salt Storage
Molten salt is heated to high temperatures by concentrated solar energy during the day. The liquid salt retains the thermal energy for hours in insulated tanks before being used to make steam for electricity generation at night. This provides thermal energy storage with minimal losses.
Solar Energy Policies and Incentives
Governments around the world have implemented various policies and incentives to promote the adoption of solar energy. These programs make installing solar panels more affordable and attractive for homeowners and businesses.
Some of the main solar incentives include:
Tax Credits
Many countries offer tax credits that allow you to deduct a percentage of your solar panel system costs from your taxes. In the United States, there is a federal solar tax credit that allows you to deduct 26% of installation costs from your federal taxes.
Net Metering
Net metering programs allow solar panel owners to get credit for excess electricity they generate but don’t use. This excess electricity goes back into the grid and the owner receives a credit from their utility company. This helps offset the cost of electricity drawn from the grid when solar panels aren’t generating enough.
Feed-in Tariffs
With feed-in tariffs, utility companies are obligated to purchase renewable electricity from solar panel owners at above-market rates. This provides incentive for homeowners and businesses to install solar panels by guaranteeing a return on their investment.
Renewable Portfolio Standards
Many governments require utility companies to source a certain percentage of their electricity from renewable sources like solar. This renewable portfolio standard creates guaranteed demand for solar energy.
Growth of Solar Energy
The solar energy industry has experienced rapid growth in recent years thanks to increasing efficiency, falling costs, and supportive policies. Global solar photovoltaic installations reached over 600 gigawatts in 2019, supplying about 3% of global electricity demand. Projections estimate solar could supply up to 20% of global electricity by 2030 and as much as 49% by 2050.
Solar panel efficiency has steadily increased over the past decades, from around 12% in the 1990s to over 20% for the best commercial panels today. This makes solar a much more viable energy source. Costs have also plummeted, with solar panel prices dropping 90% in the last 10 years. As a result, solar electricity costs have reached parity with fossil fuels in many parts of the world.
With such improvements, solar deployments have skyrocketed. The amount of solar capacity installed globally increases by over 20% annually. The top countries for solar today include China, Japan, Germany, the United States, and India. Solar is now the fastest growing electricity source in the world. Major reports project renewable energy, largely from solar and wind, will supply 30-50% of the world’s electricity by 2050. Some experts believe solarcould realistically provide over 60% of global energy demand in the coming decades.
Major Companies in Solar
The solar energy industry has seen tremendous growth over the past decade, with companies racing to meet the rising demand for solar technology and become leading providers.
Top Solar PV Companies
Some of the major companies involved in solar photovoltaic (PV) panel manufacturing and installation include:
- JinkoSolar – Founded in China, one of the largest solar module manufacturers in the world.
- JA Solar – Another major Chinese solar company focused on manufacturing solar cells and modules.
- Trina Solar – Leading global PV module supplier headquartered in China.
- First Solar – Major U.S. company specializing in thin-film solar modules.
- SunPower – Known for high-efficiency solar panels, headquartered in the U.S.
- SolarWorld – Major German solar PV panel producer with manufacturing in Europe and the U.S.
Top Solar Thermal Companies
Some major players in solar thermal technology and projects include:
- Abengoa Solar – Spanish company building some of the largest concentrated solar power (CSP) plants.
- BrightSource Energy – Develops utility-scale CSP projects, headquartered in the U.S.
- SolarReserve – Builds large CSP plants featuring molten salt storage.
- Aborsun – Leading manufacturer of solar thermal collectors based in China.
Notable Projects
Some groundbreaking solar energy projects demonstrating the technology’s massive potential include:
- Topaz Solar Farm – One of the world’s largest PV power plants, 550MW capacity in California.
- Tengger Desert Solar Park – China’s massive 1,547 MW PV plant, the world’s largest.
- Ivanpah Solar Electric Generating System – Massive 392 MW CSP project in California’s Mojave Desert.
- Noor Ouarzazate CSP complex – Series of CSP plants in Morocco totaling over 500MW capacity.
Future of Solar Energy
The future looks bright for solar energy. As technology continues to improve, solar is expected to play a major role in the world’s energy mix and in combating climate change. Here are some key ways solar is likely to advance in the coming years:
Improving technology: Researchers are working to make solar panels more efficient, longer-lasting and cheaper to manufacture. New materials like perovskites have the potential to dramatically improve solar cell efficiency. Concentrated solar power plants are also becoming more efficient.
Potential applications: Solar electricity generation is likely to explode in growth, especially with improved storage capabilities. New solar technologies and integrated designs allow solar to be installed in more places, powering everything from homes to skyscrapers to vehicles.
Climate change mitigation: As solar power grows more cost-competitive and efficient, it is expected to meet an increasing share of the world’s electricity demand. This growth of renewable solar energy will help reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lessen greenhouse gas emissions.
In summary, solar energy is poised to help create a cleaner, more distributed power grid while meeting the energy needs of the future.