What Is A Frameless Solar Panel?
What Are Frameless Solar Panels?
Frameless solar panels are photovoltaic (PV) panels that do not have an aluminum frame around the edges (Green World Investor, 2016). Instead, the solar cells are laminated between sheets of glass or plastic. This frameless design allows the entire surface of the panel to absorb sunlight and generate electricity.
The main components of a frameless solar panel are the front glass layer, the encapsulated solar cells, and the backsheet layer. The glass provides protection and allows light to pass through to the solar cells below. The cells are wired together and laminated between the glass and backsheet using ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA). The backsheet insulates the panel and protects against weather damage.
Compared to traditional framed panels, frameless solar panels have some key advantages:
- Higher efficiency – The lack of framing allows more sunlight to hit the cells (Energy Theory, n.d.). Frameless panels can achieve efficiencies over 20%, while framed are typically 15-18%.
- More aesthetically pleasing – The smooth, glass surface gives a sleek, modern look.
- Lower weight – Without heavy aluminum framing, frameless panels are lighter.
- Reduced soiling – Dirt and debris can slide off the glass more easily.
However, there are some disadvantages to frameless solar panels:
- Less durability – The glass is more prone to cracking without the aluminum frame protection.
- Higher cost – Producing frameless panels requires specialized materials and lamination processes.
- More difficult installation – Framed panels provide rails and clamping points for secure roof mounting.
History and Development
The concept of solar panels has been around for over a century, but the modern silicon photovoltaic (PV) solar panel was first developed in 1954 at Bell Labs. This marked a major advancement in solar technology. Early solar panels, however, had very low efficiency rates of converting sunlight to electricity.
Over the ensuing decades, innovations in materials science and manufacturing have driven steady increases in solar panel efficiency. Some key developments include the invention of the crystalline silicon solar cell in 1960 and the development of thin film solar panels in the 1970s. These helped make solar panels lighter and more flexible.1
Today, typical solar panel efficiency ranges from 15% to 22%. Ongoing research aims to push this even higher through advanced materials like perovskites and quantum dots. Frameless solar panel designs have also emerged as an aesthetic innovation in recent years, delivering high efficiency rates in a sleek, seamless package.
Manufacturing and Materials
Frameless solar panels are manufactured without the aluminum frame found in traditional solar panels. This allows them to be lightweight and low profile. The main structural component is the tempered glass front sheet, usually around 3-4mm thick, which provides rigidity and weather protection without the need for an aluminum frame.
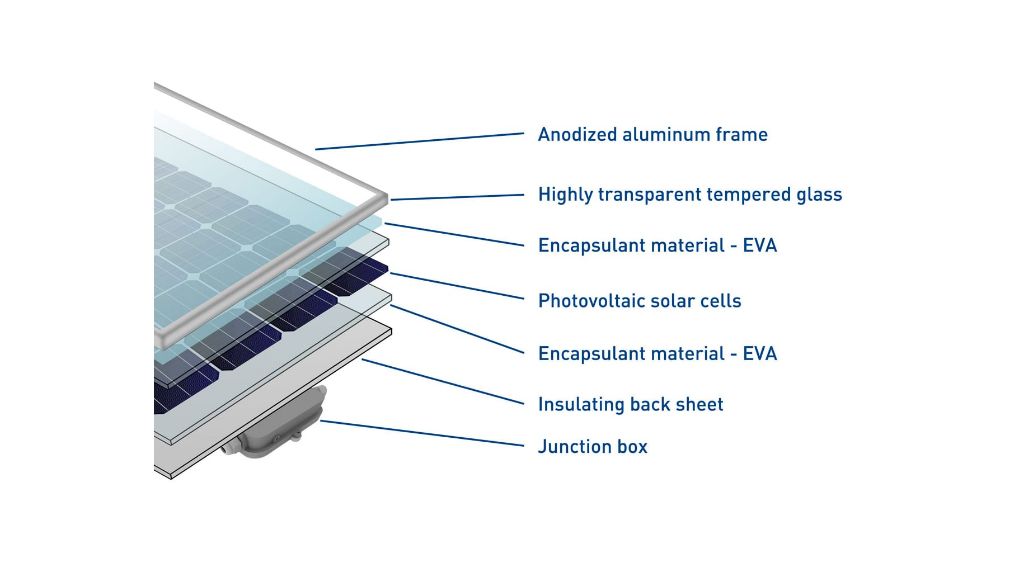
Most frameless solar panels use monocrystalline silicon solar cells encased between the front glass sheet and a polymer backsheet, such as Tedlar or PET. The cells are laminated between these layers using EVA (ethylene vinyl acetate) as an encapsulant.
Some of the major manufacturers producing frameless solar panels include SunPower, LG, Panasonic, Solaria, Silfab Solar, and certain models from JinkoSolar, Trina Solar, and JA Solar. Many frameless panels are produced in China, Taiwan, or Southeast Asia where manufacturing costs can be lower.
Compared to framed panels, frameless models require more precision and quality control during manufacturing to ensure the glass and lamination provide adequate support. The tempered front glass is a key component sourced from specialized suppliers like Eurasia Glass.
Efficiency and Performance
Frameless solar panels are generally just as efficient, if not slightly more efficient, than conventional framed panels. According to Solar Power World, frameless panels see efficiency ranges from 15% to over 22%, which is on par with many framed panels (https://www.solarpowerworldonline.com/2015/01/411-frameless-solar-modules/).
The frameless design allows more sunlight to reach the solar cells from the front and back, boosting energy production. With no framing, there’s also no shadowing or coverings reducing the active solar collection area. This gives frameless panels an edge in low-light conditions where every bit of exposure counts.
In terms of lifespan, frameless panels are expected to last just as long, around 25-30 years, as their framed counterparts. The glass sandwich design protects the solar cells from weathering and degradation over decades of use. Proper installation is important for longevity, but frameless solar itself does not reduce the functional life of the panels (https://ecowowlife.com/frameless-solar-panel/).
Cost Analysis
Frameless solar panels tend to have higher upfront costs compared to framed panels. According to Alibaba, frameless panels can cost 20-30% more than framed panels. This is because frameless panels require more expensive materials and manufacturing techniques to maintain structural integrity without a frame.
However, frameless panels may have lower installation costs. Since they are lighter than framed panels, there are reduced labor and structural costs associated with roof attachments and reinforcements. Frameless panels are also compatible with several mounting systems, providing more flexibility and potential cost savings.
Over their 25+ year lifetime, frameless panels can provide more energy savings compared to framed panels. With higher efficiency and improved performance in high temperatures, frameless panels generate more kilowatt-hours per watt over time. When factoring in performance and durability, most experts estimate frameless panels achieve a better return on investment in the long run.
Installation and Maintenance
Installing frameless solar panels requires some special considerations compared to traditional framed panels. Frameless panels must be mounted using special clips that attach to the panel at specific locations to provide support (Solarbuildermag.com). Pre-assembly and pre-wiring in a controlled environment can help optimize the installation process (Solarpowerworldonline.com).
For maintenance, frameless panels may require more frequent cleaning since the glass surface is exposed without an aluminum frame. Safety considerations are also important since the exposed glass edges may be sharper than framed panels. Installers should wear protective gloves when handling frameless panels.
Overall, with proper planning and protective equipment, frameless solar panels can be safely and effectively installed and maintained. The aesthetic benefits make them an attractive option, as long as the unique requirements are accounted for.
Ideal Applications
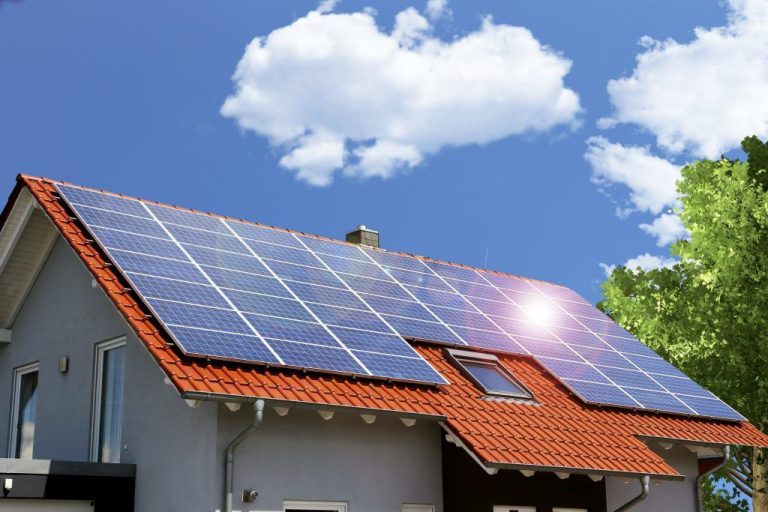
Frameless solar panels are generally well suited for rooftop installations, especially on residential homes. Their sleek aesthetic allows them to blend in seamlessly with modern roof designs (Solar Power World). Without bulky aluminum frames, frameless panels have a lower profile and lighter weight which simplifies logistics for getting them on rooftops.
Pairing frameless solar with home battery storage is another ideal application. Their high efficiency maximizes solar energy generation to charge batteries, while their design creates a streamlined system. Frameless solar panels are also great for carports and pergolas, providing shade while generating power (Green World Investor). Their frameless nature allows them to blend into these structures for clean integration.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of frameless solar panels, like all solar panels, is complex with both benefits and drawbacks. On one hand, solar power generates clean, renewable electricity without emitting greenhouse gases. This helps combat climate change and reduce pollution from fossil fuel sources like coal plants (https://www.ecowatch.com/solar-environmental-impacts.html).
However, manufacturing solar panels has a large carbon footprint. Producing the silicon, metal framing, wires, and glass creates significant CO2 emissions. There is also waste produced when processing silicon and other raw materials (https://energy5.com/the-environmental-impact-of-monocrystalline-polycrystalline-and-thin-film-solar-panels).
When it comes to disposal, most solar panel components are non-toxic and recyclable. But the cost of recycling often outweighs using new materials, so recycling rates are low. This could lead to solar waste building up in landfills. More recycling initiatives and research into more sustainable materials and manufacturing processes can help address these concerns (https://kubyenergy.ca/blog/the-positive-and-negative-environmental-impacts-of-solar-panels).
Overall, most experts agree the environmental benefits of solar power far outweigh the costs. But careful attention must be paid to the sustainability and lifecycle of solar panels to minimize negative impacts.
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the frameless solar panel market is positive, with significant growth potential in emerging markets and the increasing adoption of renewable energy globally. According to Markets and Markets Research, the global frameless solar panel market size is projected to grow from $100.6 billion in 2021 to $221.6 billion in 2028 at a CAGR of 11.7% during the forecast period1. Key factors driving this growth include government incentives and regulations supporting renewable energy adoption, advancements in panel efficiency and performance, and declining costs.
In terms of new technologies, R&D is focused on improving panel efficiency through the use of new materials like perovskites and graphene. Companies are also developing improved mounting and tracking systems to increase energy yield. Frameless solar panels with transparent photovoltaic glass are an emerging innovation with architectural applications. Manufacturers continue to refine production methods to lower costs and retain panel efficiency at larger sizes.
Supportive government policies will be critical for spurring frameless solar panel adoption globally. Many nations have set aggressive carbon reduction and renewable energy targets under the Paris Agreement that will necessitate large-scale PV installations. However, changes in political leadership and policies could impact growth. Overall, the transition to renewable energy appears irreversible, although the rate of adoption may fluctuate.2
Key Takeaways
No longer considered just a newer, thin version of framed solar modules, frameless panels have emerged with distinct benefits that make them an ideal choice for certain applications. Here are the key takeaways on frameless solar panels:
Pros: More lightweight and flexible than framed panels, better performance in high temperatures, easier installation, improved aesthetics.
Cons: Less physically robust than framed, not compatible with all mounting systems, higher price per watt.
Ideal For: New solar installations using frameless-compatible mounting equipment, rooftops, carports, boats/RVs, off-grid setups. Not recommended for retrofitting over old framed panels.
Main Benefits vs Framed: Frameless panels are lighter, more flexible, better performance in heat, streamlined installs, and enhanced aesthetics for seamless integrations.