What Is Solar Energy And Why Is It Important To Life On The Earth?
Solar energy is renewable energy harnessed from the sun. Sunlight is captured and converted into useful forms of energy through a variety of technologies, including solar thermal collectors, photovoltaic panels, concentrating solar power systems, and others. Solar energy is abundant, renewable, and available everywhere the sun shines.
The sun has produced energy for billions of years. Ancient cultures built structures that harnessed the sun for warmth, light, cooking, and more. In the 1800s, the photovoltaic effect was discovered – the phenomenon that certain materials produce small amounts of electricity when exposed to sunlight. Over the next century, scientists and engineers made strides in researching and developing solar technologies.
Solar energy is crucial for nearly all life on Earth. It powers photosynthesis in plants and algae, forming the base of the food chain. It generates warmth, enabling ecosystems and human civilizations to thrive. Solar energy remains the ultimate source of most of our energy, whether extracted directly or embodied in fossil fuels, biofuels, wind, biomass, and hydropower.
How Solar Energy Works
Solar energy works by harnessing the sun’s rays and converting them into usable energy forms like electricity and heat. This happens through one of two main technologies: photovoltaics and solar thermal systems.
Photovoltaic systems directly convert sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. Solar cells made of semiconductor materials absorb photons from sunlight and release electrons, creating an electric current. Multiple solar cells assembled in modules and panels generate solar power that can be used or fed into the grid.
Solar thermal technologies use the sun’s heat for applications like heating water in solar hot water systems or air in solar air heating systems. Concentrated solar thermal plants use mirrors to focus sunlight and generate high temperatures that can drive an engine to produce electricity.
Overall, solar energy works because of the photons in sunlight that can be harnessed in a variety of ways to provide usable energy for human needs. Advances in semiconductor and thermal technologies allow us to capture and utilize the nearly unlimited potential of the sun.
Solar Energy Applications
Solar energy has a wide variety of applications that take advantage of the sun’s abundant renewable power. Here are some of the main uses of solar energy technology today:
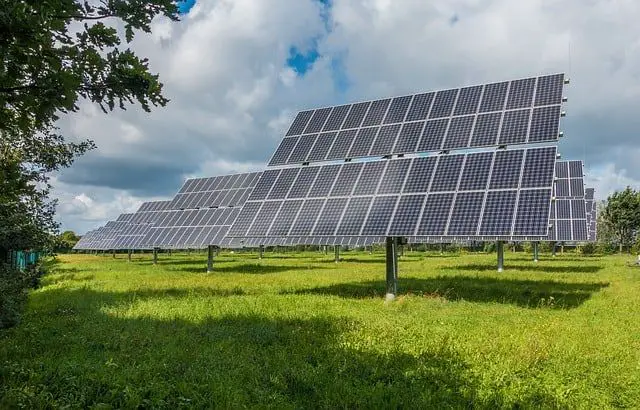
Solar Panels
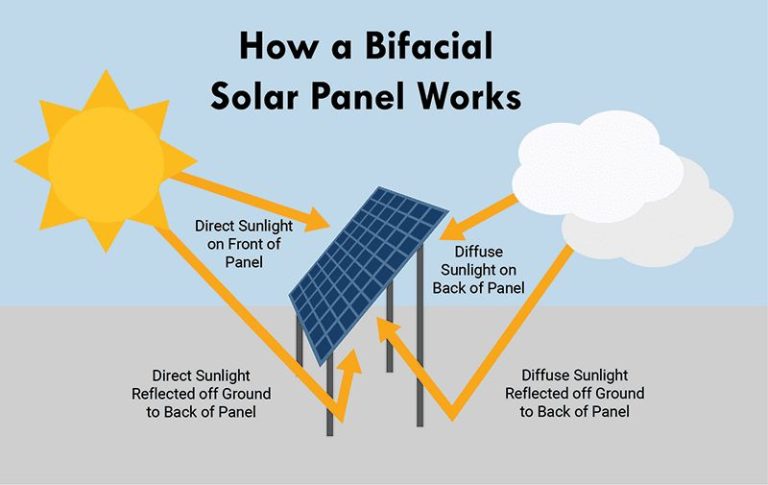
Also known as photovoltaics (PV), solar panels convert sunlight directly into electricity using semiconducting materials. Solar panels on rooftops are the most visible way solar energy is used. Solar PV systems can be small enough to charge a calculator or large enough to power entire buildings.
Solar Water Heating
Solar water heating systems use solar thermal collectors and heat exchangers to heat water. This heated water is then used for residential, commercial, or industrial applications. Solar water heating is one of the most widespread uses of solar energy.
Concentrated Solar Power
Concentrated solar power systems use mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a receiver, generating high temperatures that are used to drive a heat engine/turbine to produce electricity. CSP is another major utility-scale solar power generation technology.
Passive Solar Heating and Lighting
Passive solar building design takes advantage of sunlight’s heating and lighting abilities through orientation, materials, and components like trombe walls and skylights. It does not involve active mechanical systems or appliances.
Advantages of Solar Power
One of the biggest advantages of solar power is that it is a renewable energy source. Solar energy is constantly replenished by the sun and will be available as long as the sun shines. This makes solar a reliable and sustainable long-term energy solution.
Solar power also reduces dependence on fossil fuels like coal, oil and natural gas. These fossil fuel sources are finite and will eventually run out or become too environmentally damaging to retrieve. Solar provides an alternative that can supplement or replace fossil fuels, giving us greater energy independence and security.
In addition, solar energy has minimal emissions and carbon footprint compared to traditional energy sources. Solar panels generate electricity without releasing greenhouse gases or other pollutants into the atmosphere. Widespread adoption of solar could significantly reduce air pollution and carbon emissions that contribute to climate change.
There are also cost savings associated with solar power. While installation costs can be high upfront, solar panels have very low maintenance expenses and the cost of solar electricity itself is free after installation. Many homeowners see a return on investment within just a few years of installing a system. In the long run, the cost predictability of solar contrasts very positively with the volatile prices of fossil fuels.
Disadvantages of Solar Power
While solar power certainly has many benefits, there are some drawbacks to consider as well:
Intermittent power – The amount of electricity generated by solar panels fluctuates throughout the day depending on how much sunlight they receive. This can make it challenging to match energy supply with energy demand. Solar only produces power when the sun is shining so energy storage solutions are often needed.
High upfront costs – Installing a residential or commercial solar array requires a big upfront investment. While solar panels can pay for themselves over time, the initial cost can be prohibitive for some homeowners and businesses.
Land use requirements – Solar farms require significant land area to generate utility-scale amounts of electricity. This can raise concerns about land usage and environmental impact.
Storage issues – Solar energy must be used right away or stored in batteries to be used later. Affordable and efficient energy storage technology is still being developed.
Solar Energy Storage
Solar energy often produces its maximum power output during the middle of the day, when the sun is at its peak intensity. However, energy demand may peak in the morning or evening. The ability to store solar energy allows excess solar power generated during peak production to be stored for later use. There are several ways to store solar energy, with batteries, thermal storage, and pumped hydro storage being among the leading options.
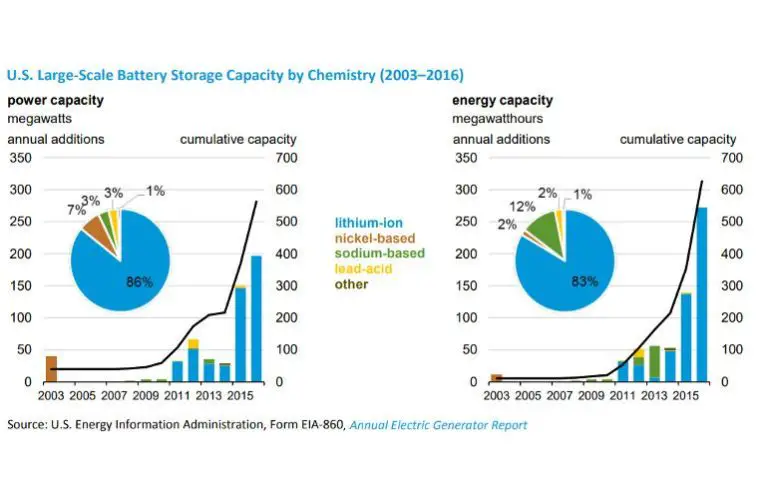
Batteries are one of the most common methods for storing excess solar energy. Excess solar electricity can be used to charge batteries, which can then discharge electricity when needed. Lithium-ion batteries are often used, but research is ongoing into new battery technologies with greater efficiency and storage capacity.
Thermal energy storage allows heat from the sun to be captured and stored for later use. This approach often uses molten salt to store solar heat, which can then heat water to generate steam to drive a turbine and create electricity. The salt allows the heat to be stored for hours or even days.
Pumped hydro storage uses excess electricity to pump water uphill to a reservoir. When electricity demand increases, the water can be released back downhill to power hydroelectric generators. Pumped hydro allows solar power to be stored in bulk and on a large scale.
Solar Power Potential
The amount of solar energy that reaches the Earth’s surface in one hour could meet the world’s energy needs for an entire year. Solar resources are abundant across the globe but they are more concentrated in certain areas. The sunniest regions are located between 15 and 40 degrees latitude north and south of the equator. These areas receive at least 2,000 kWh/m2 per year of solar radiation. Parts of the southwestern United States, South America, North Africa, the Middle East, India, and Australia have some of the highest solar potential in the world.

Global solar photovoltaic capacity has experienced massive growth over the past decade, increasing from 40 gigawatts in 2010 to over 580 gigawatts by the end of 2019. Solar power is now the fastest growing energy source in the world, with an annual average growth of over 40% in recent years. The IEA projections solar capacity to reach over 4,500 gigawatts by 2040 under a sustainable development scenario, supplying up to 13% of global electricity demand. With plummeting costs and supportive policies, the future looks bright for continued expansion of solar energy worldwide.
Top Solar Countries
Here are some of the top countries in the world for installed solar energy capacity:
China
China is the global leader in total installed solar capacity, with over 250 gigawatts as of 2019. The country added an impressive 30 to 40 gigawatts of new solar capacity to its grids yearly since 2017. With its large population and rapidly growing economy, China has made massive investments in renewable energy, including solar power.
United States
The United States has the second-highest installed solar capacity in the world at over 75 gigawatts as of 2019. California leads the nation in deployed solar capacity, followed by states like Texas, Florida and North Carolina. The solar industry employs over 250,000 workers in the U.S. and has expanded as the cost of panels declines.
Japan
Japan had over 56 gigawatts of installed solar capacity by the end of 2019. The country rapidly increased its solar power generation after the Fukushima nuclear disaster in 2011. Japan’s government set ambitious targets and incentives that drove the growth of large-scale solar farms as well as rooftop solar panels.
Germany
Germany is often viewed as a global leader in renewable energy adoption. The country had over 49 gigawatts of solar photovoltaic capacity in 2019. Germany introduced a new renewable energy law in 2000 which kickstarted its solar energy expansion through feed-in tariffs and favorable policies. Today solar PV provides nearly 9% of Germany’s electricity needs.
Solar Energy and the Environment
Solar energy has significant environmental benefits compared to fossil fuel sources. By harnessing power from the sun rather than burning coal, oil, and gas, solar energy systems produce power without contributing to air pollution or global warming. Specifically, solar energy reduces emissions of:
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) – a major greenhouse gas
- Nitrogen oxides (NOx) – causes smog and acid rain
- Sulfur dioxide (SO2) – contributes to acid rain and respiratory problems
- Particulates – impacts human health and contributes to smog
These reductions in emissions and pollution lead to improved public health and lower environmental damage from energy production. Solar panels have no emissions during operation, allowing them to provide clean renewable electricity.
Regarding land use, solar farms do take up significant land area. However, many solar installations can co-exist with other land uses like farming and grazing. And unlike coal mining which can produce land subsidence and permanent scarring, the land used for solar farms can be repurposed or returned to its natural state. With thoughtful siting and dual-use strategies, solar’s environmental footprint can be minimized.
The Future of Solar Energy
As solar technology continues to improve, the future looks bright for solar energy. Some key areas of progress in the coming years are likely to be:
Improving Efficiency and Storage
Research is ongoing into developing more efficient solar photovoltaic cells that are able to convert a greater percentage of sunlight into electricity. Thermal energy storage solutions are also being improved to allow solar thermal plants to provide power 24/7.
Batteries and other storage technologies are becoming cheaper and more efficient. This will allow solar power to be stored when generation exceeds demand and provide electricity at night or on cloudy days.
Projected Growth
Solar power capacity is expected to grow significantly in the coming decades. As costs continue to fall, solar will become increasingly competitive with fossil fuels. Many projections estimate solar could provide 20-50% of global electricity by 2050.
Role in Fighting Climate Change
Solar energy produces no greenhouse gas emissions during operation. Expanding solar power generation can help reduce reliance on fossil fuels and combat climate change. Most scientists agree solar will need to play a major part in decarbonizing the world’s electricity system.