What Is Natural And Non Natural Resources?
Natural resources are materials or substances that occur naturally and can be used for economic gain. They include minerals, forests, water, fertile land, wildlife, and sources of energy like oil, natural gas, coal, sunlight, wind, and uranium. Natural resources are derived from the environment and are not created by humans.
Non-natural resources refer to materials that do not occur naturally and must be produced or manufactured by humans. Examples include plastics, synthetic fibers, concrete, metals like aluminum, and fuels like gasoline. Non-natural resources require substantial energy and technological processes to be created from raw natural materials. They are made by humans to meet various needs in society.
Examples of Natural Resources
Natural resources are materials that occur in nature without human intervention. Some of the most common natural resources are air, sunlight, water, soil, plants, and animals.
Air is the mixture of gases that surrounds the Earth and that living things breathe. The main gases in air are nitrogen, oxygen, argon and carbon dioxide. Clean air free of pollutants is essential for the health of all organisms.
Sunlight provides light and heat that sustains plant and animal life. Sunlight powers photosynthesis in plants, which produces the oxygen that humans and other animals breathe. It also provides vitamin D in humans.
Water in lakes, rivers, oceans and ice sheets covers most of Earth’s surface. All organisms need water for drinking, transportation, dissolving nutrients, and regulating body temperature. Water shapes the Earth’s surface through flows, glaciers and erosion over time.
Soil consists of a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that provide nutrients, water, and support to plants. Soil allows us to grow crops for food and vegetation. Different types of soil are suitable for different purposes.
Plants convert energy through photosynthesis, provide oxygen and food, and form the foundation of most food chains and webs. They stabilize soils, provide wildlife habitat, and furnish humans with food, fuel, fibers, medicines, and oxygen.
Animals help maintain the balance of natural ecosystems. They pollinate plants, disperse seeds, provide fertilizer, control pests, and form an important part of the food chain. Many animals provide food, clothing, and companionship to humans.
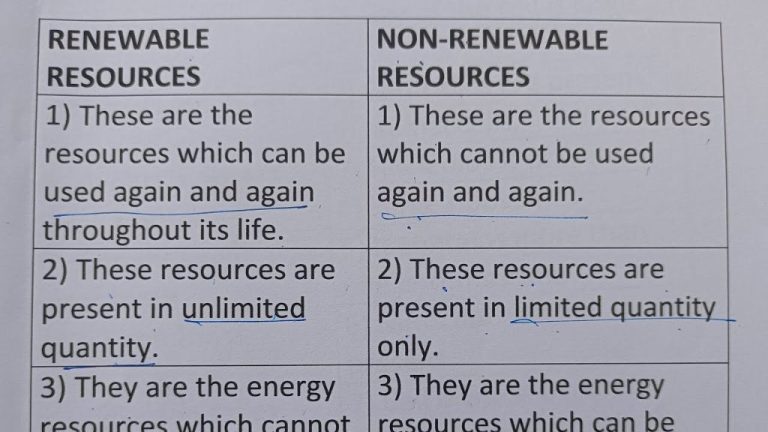
Renewable vs Non-Renewable Natural Resources
Natural resources can be categorized as either renewable or non-renewable based on how they replenish.
Renewable natural resources have the ability to replenish naturally over time. Examples of renewable resources include:
- Solar energy from the sun
- Wind
- Water
- Trees and forests
Renewable resources replenish on human timescales, making them sustainable for continued use and consumption.
Non-renewable natural resources exist in finite quantities and do not replenish over human timescales. Once depleted, they are essentially gone. Examples of non-renewable resources include:
- Fossil fuels like oil, coal, and natural gas
- Metals like gold, silver, copper
- Minerals
Careful management and conservation is crucial for non-renewable resources since they cannot be replaced once extracted and used up.
Importance of Natural Resources
Natural resources are extremely important as they support life, provide for basic needs, and support the economy. Without natural resources, life as we know it would not exist.
The most important function of natural resources is to support life. Things like water, soil, trees, and sunlight provide the basic elements that both plants and animals need to survive. For example, trees produce the oxygen that humans and other animals breathe. Resources like fresh water and fertile soil give plants and crops what they need to grow and produce food. Natural resources quite literally sustain life on Earth.
In addition to supporting life, natural resources provide for many basic human needs. Resources like wood are used for shelter and housing. Fossil fuels like oil and gas are major energy sources for electricity, heating, and transportation. Metals like iron are crucial for infrastructure, machinery, and technology. From the homes we live in to the cars we drive, natural resources enable our modern way of life and standard of living.

Natural resources also power the economy by creating jobs and generating wealth. The extraction, processing, and trade of natural resources employs millions of workers worldwide. Countries with abundant natural resources often have thriving extractive industries that contribute significantly to GDP. Many nations’ economies rely heavily on exporting natural resources like minerals, coal, oil, natural gas, and timber. Overall, natural resources drive economic productivity and growth.
Conservation of Natural Resources
Conservation of natural resources is crucial for maintaining ecological balance and supporting sustainable development. Some key strategies for conserving natural resources include:
Sustainable Use – Using renewable natural resources at a rate where they can replenish themselves. For example, limiting deforestation and managing fisheries sustainably.
Reducing Waste – Decreasing overconsumption and inefficient use of resources. Strategies include reducing food waste, reusing materials, and recycling.
Protecting Ecosystems – Safeguarding habitats like forests, wetlands and coral reefs preserves biodiversity and ecological services.
Setting protected areas, controlling invasive species, and restoring degraded ecosystems are important conservation efforts.
Transitioning to circular economic systems that minimize resource extraction and waste generation can also promote conservation.
Individual actions like reducing energy and water usage, properly disposing waste, and choosing sustainable products and services can support natural resource conservation.
Government regulations, partnerships, and community engagement help drive large-scale conservation success.
Non-Natural Resources
Non-natural resources are materials that are synthesized or manufactured by humans. Unlike natural resources like trees, water, and minerals, non-natural resources do not occur naturally in the environment.
Some examples of non-natural resources include:
- Plastics – Plastics are synthetic materials made from organic polymers like polyethylene, PVC, nylon, etc. Plastics are used ubiquitously in modern society for packaging, containers, electronics, automobiles, and more.
- Synthetic fabrics – Fabrics like polyester, acrylic, spandex, and rayon are made from synthesized polymeric fibers or cellulose. They have properties like stretch, wrinkle resistance, and stain resistance that make them useful for clothing and other textiles.
- Processed fuels – Fuels like gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel are non-natural since they are produced by refining and processing crude oil through fractional distillation.
- Cement – While the limestone used to make cement is natural, the manufacturing process chemically alters it into a new synthetic binding material.
- Synthetic fertilizers – Fertilizers like ammonium nitrate, triple superphosphate, and urea provide essential plant nutrients but are artificially created through chemical processes.
These are just a few examples of the many non-natural resources that modern civilization depends on. Unlike natural resources, non-natural resources can be produced on demand and engineered to have specific desirable properties.
Examples of Non-Natural Resources
Non-natural resources are materials that are produced by humans, rather than occurring naturally in the environment. Some of the most common examples of non-natural resources include:
Plastics
Plastics are synthetic materials made from organic polymers such as polyethylene, PVC, nylon, and polypropylene. Plastics are molded or shaped into countless products that we use every day like containers, toys, electronics, automotive parts, and synthetic clothing.
Synthetic Fabrics
Fabrics like polyester, nylon, acrylic, rayon, and spandex are manufactured using raw materials like petroleum and natural gas. These synthetic fabrics have properties like stretch, wrinkle resistance, stain resistance and waterproofing that make them useful for clothing, furniture, and industrial applications.
Metals
While metals like gold, silver, and copper exist naturally, many of the metals used today are alloys or mixes that are manufactured. Steel, aluminum, titanium, bronze, brass, and stainless steel do not occur naturally and are produced by combining and processing different metal elements in refineries and factories.
Concrete
Concrete is a building material created by mixing cement, aggregate (rock, sand), water, and often additives to form an artificial stone-like material. The cement used in concrete is manufactured from materials like limestone, clay, and iron ore that have been crushed and heated at high temperatures.
Pros and Cons of Non-Natural Resources
Non-natural resources offer many benefits but also have some drawbacks that should be considered. Here are some of the main pros and cons of using non-natural resources:
Pros:
Versatile – Non-natural resources can be transformed into many different materials and products through industrial processes. This makes them extremely versatile in what they can be used for.
Abundant – Many non-natural resources, such as plastics and synthetic fibers, can be produced in large quantities reliably. This makes them more abundant and accessible than scarce natural resources.
Cons:
Pollution – The extraction and processing of non-natural resources often generates significant pollution. Examples include air/water pollution from oil refining and plastic waste.
Non-renewable – Since non-natural resources do not occur naturally, many of them are non-renewable on human timescales. Their supplies are limited and will eventually run out if alternatives are not developed.
Sustainable Use of Non-Natural Resources
Non-natural resources, while extremely useful, need to be used responsibly and sustainably. Here are some ways to ensure the sustainable use of non-natural resources:
Reduce – Decrease our dependence on non-natural resources by cutting back on consumption and waste. Simple everyday actions like turning off lights when not in use, unplugging electronics when not charging, and reducing plastic use can make a meaningful difference.
Reuse – Find ways to reuse items made from non-natural resources instead of throwing them away. Creative ideas like repurposing plastic bottles or containers, donating old electronics, and shopping at secondhand stores prolongs the lifecycle of these resources.
Recycle – Recycling non-natural resources allows their materials to be reprocessed and made into new products. Recycling programs are available in many communities for paper, metals, plastics, electronics and more.
Use Eco-Friendly Materials – Supporting products made from renewable, recycled, or sustainably-sourced materials helps reduce dependence on non-renewable resources. Buying reclaimed wood furniture, recycled paper products, or items with eco-friendly certifications makes a positive impact.
With some mindful effort, we can reduce our consumption, reuse more, recycle diligently, and make choices that reflect the true value of our limited non-natural resources.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it’s clear that both natural and non-natural resources play an important role in our lives. However, they need to be managed carefully to ensure their long-term availability. Natural resources like water, forests, and fossil fuels are limited and can be depleted if overused. At the same time, non-natural resources like plastics and chemicals provide convenience but can harm the environment if not disposed of properly.
The key is finding a balance – using natural resources responsibly and tapping into non-natural resources when they provide a clear benefit. But moderation is important, as is investing in conservation, recycling and renewable energy. With the right balance, we can continue to meet our needs without compromising the planet for future generations.
The sustainable management of both natural and non-natural resources is critical. This requires long-term thinking and responsible actions from governments, businesses and individual citizens. If we work together to protect our shared environment, we can enjoy the benefits of both natural and human-made resources for years to come.