What Is An Amazing Fact About Energy For Kids?
Energy powers our everyday lives! From the food we eat to the electricity that lights up our homes, we use energy for everything. Some energy facts will absolutely amaze kids and adults alike.
What is Energy?
Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. Energy makes things happen and gets work done. Energy lights up our homes, cooks our food, plays our music, and moves our cars. Energy comes in different forms like heat, light, sound, motion, and more. But they are all related and can be changed from one form to another.
Everything around us has energy. The food we eat, the water we drink, the sunlight that warms us, the electricity that powers our homes – they all provide us with energy. Energy is found everywhere, both natural and man-made, and we use energy every day to live our lives.
Energy comes in many different forms. Some examples are mechanical, thermal, chemical, nuclear and electromagnetic. We use these different forms of energy to do work for us. For instance, we use chemical energy in food to move our bodies. We use electromagnetic energy (electricity) to power our televisions. Energy is the power behind everything we do!
Types of Energy
There are many different types of energy that exist in our world. The most common types that kids learn about in science class are:
- Kinetic Energy – the energy of motion that an object has. For example, a ball rolling down a hill has kinetic energy.
- Potential Energy – the stored energy an object has due to its position or shape. For example, a ball at the top of a hill has potential energy that can turn into kinetic energy as it rolls down.
- Electrical Energy – the energy from the flow of electrons. For example, energy that flows through wires or batteries.
- Heat Energy – the energy that comes from the vibration of atoms and molecules. For example, the energy that allows a pot of water to boil on the stove.
- Light Energy – the energy that comes from electromagnetic waves that we see with our eyes. For example, energy from the sun or a lightbulb.
These are the main types of energy that kids learn about in science class. Understanding the different forms energy can take helps explain how energy flows and changes in our world.
Energy Transformations
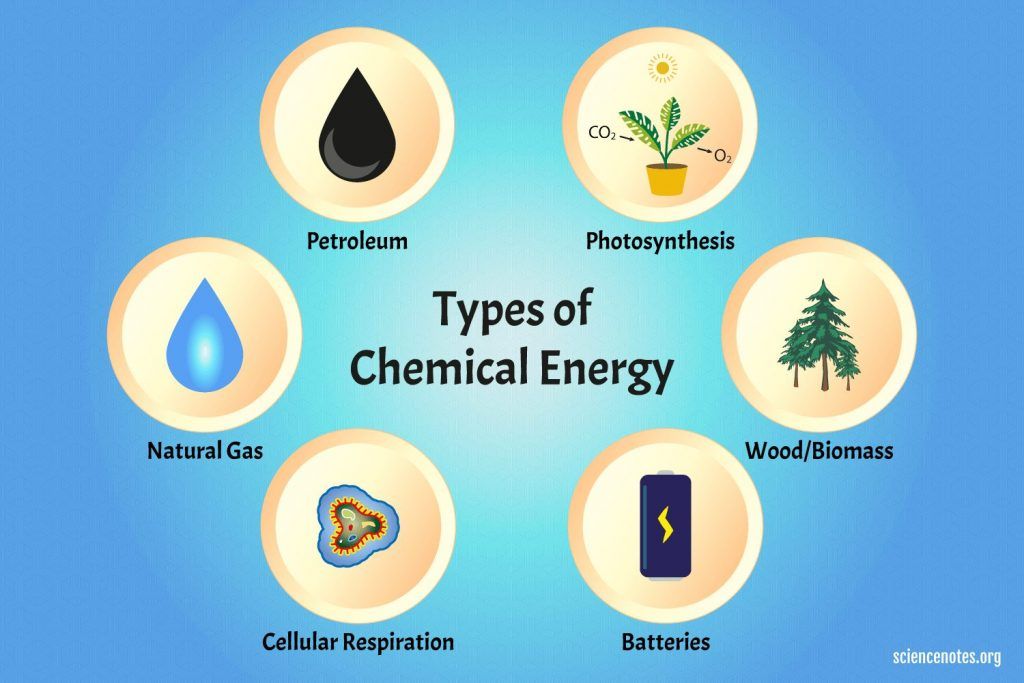
Energy changes from one form to another through energy transformations that happen mostly through chemical reactions or physical changes. Some examples of energy transformations include:
- Chemical energy in a battery changing into light and heat energy from a light bulb.
- Light energy from the sun is absorbed by plants which convert it into chemical energy through photosynthesis.
- The chemical energy in wood, gasoline, or natural gas changing into heat energy when burned.
- The movement of water at a dam turning turbine generators and changing into electrical energy through the use of electromagnets.
These energy transformations show that energy is neither created nor destroyed but rather changes form. Understanding how energy transforms helps explain where our energy comes from and how we utilize it in everyday life.
Renewable vs Non-Renewable
Renewable energy comes from natural sources that are constantly replenished, such as sunlight, wind, water, plants, and geothermal heat. These energy sources are considered renewable because they are naturally replenished within a human’s lifetime. The five major renewable energy sources are:
- Solar energy from the sun
- Wind energy
- Hydropower from flowing water
- Biomass from plants and organic waste
- Geothermal energy from earth’s internal heat
Non-renewable energy comes from sources that will eventually dwindle in supply within a human’s lifetime, such as coal, natural gas, oil, and nuclear fuels. These fuel sources take much longer to replenish naturally compared to the rate at which they are being consumed. That is why they are considered non-renewable.
The key difference is that renewable sources are replenished at a rate comparable to human consumption, while non-renewables are not. This makes renewable sources sustainable over longer periods of time.
Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels are energy sources formed over millions of years from the remains of plants and animals. The three main types of fossil fuels are coal, oil, and natural gas. We dig up fossil fuels and burn them to power things like electricity, vehicles, and manufacturing.
Fossil fuels have helped societies grow and thrive. However, burning fossil fuels releases greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide, that build up in the atmosphere and contribute to climate change. Other problems with fossil fuels include air and water pollution. We also have a limited supply that will eventually run out. Many people think we need to transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources that are cleaner and sustainable.
Solar Energy
Solar energy comes from the powerful rays of the sun that shine down on Earth every day. Solar panels can capture some of this energy and convert it into electricity or heat. How does it actually work?
Solar cells within a solar panel are made up of special materials like silicon that release electrons when they are hit by photons from sunlight. The free electrons are pulled into an electrical circuit and flow out of the panel as an electric current. This current can then be used to power things in homes or businesses.
Some amazing facts about solar power:
- The amount of solar energy that hits the Earth in one hour could power the entire world for a year!
- Solar is now the cheapest form of electrical power in history.
- The first solar cell was invented in 1883 by Charles Fritts.
- Solar panels work even on cloudy days because UV rays can pass through the clouds.
Solar energy is an amazing renewable resource that does not create any pollution. More and more homes and businesses are installing solar panels to take advantage of this clean energy from the powerful sun!
Wind Energy
Wind turbines use giant blades to capture the wind’s energy. As the wind blows over the blades, the turbine spins. This is called the rotor. The spinning rotor spins a generator, which generates electricity. So wind power turns wind energy into electrical energy that we can use.
Here are some fun facts about wind power for kids:
- Some wind turbines are as tall as a 20-story building! Their blades can be over 100 feet long.
- The first wind turbine that could generate electricity was built in 1888 in Scotland.
- There is enough wind energy potential in the U.S. to provide over 10 times the amount of electricity we currently use.
- Floating wind farms can harness stronger wind resources offshore in deep waters.
- Birds and bats can safely fly around wind turbines that are spinning.
So wind power gives us a clean, renewable way to generate electricity from the wind. And there’s a whole lot of wind out there waiting to be used!
Hydroelectricity
Hydroelectric power is a renewable source of energy that uses the power of moving water to generate electricity. Here’s how it works:
1. A dam is built to control the flow of a major river.
2. The dam stores lots of water in a reservoir behind it and controls the water flow.
3. The force of the water being released from the reservoir flows through tunnels in the dam.
4. This flowing water causes the blades of a turbine to spin like a fan.
5. The turbine spins a generator to produce electricity.
Some interesting hydroelectric power facts for kids:
– Hydropower is one of the oldest methods of producing renewable electricity.
– About 16% of the world’s electricity comes from hydropower.
– Hydropower is renewable since it relies on the water cycle caused by the sun.
– Hydropower does not directly produce air pollution or greenhouse gases.
– The speed of the water flow determines how much electricity can be generated.
– China generates the most hydropower in the world.
Energy Conservation
There are lots of simple ways kids can save energy at home and at school every day. Here are some tips:
- Turn off the lights when you leave a room.
- Unplug phone and laptop chargers when not in use to save standby power.
- Take quick 5 minute showers instead of baths to conserve hot water.
- Close doors and windows on cold days to avoid wasting heat or air conditioning.
- Walk or bike for short trips instead of driving to save gas.
- Pack waste-free lunches to conserve disposable packaging.
- Start an energy patrol at school to remind classmates to save power.