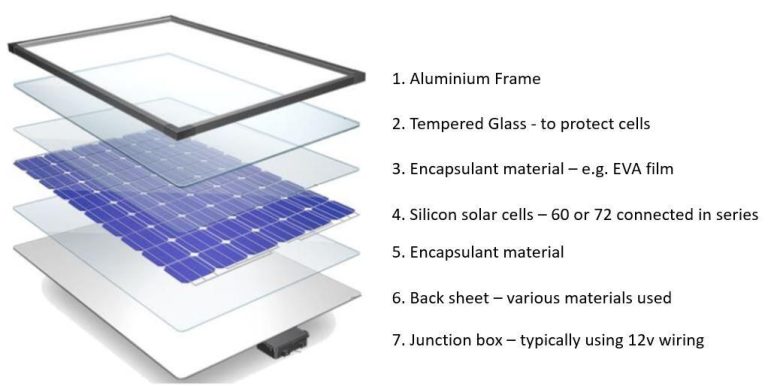
What Can Solar Energy Be Used To Power?
Solar energy is the radiant light and heat from the sun that is harnessed using a range of ever-evolving technologies such as solar heating, photovoltaics, and concentrated solar power. Interest and adoption of solar energy has grown rapidly in recent years, for several key reasons:
– Costs for solar technology, especially solar panels, have fallen dramatically, making solar power increasingly competitive with conventional power sources.
– Solar energy is renewable and unlimited, reducing reliance on finite fossil fuel resources that contribute to climate change.
– Solar power systems can operate decentralized from the grid, providing energy access and independence.
– Advancements in technology, battery storage, and super-efficient solar cells continue to enhance solar capabilities.
– Many governments provide incentives and policies to encourage solar adoption for environmental and strategic energy goals.
Homes
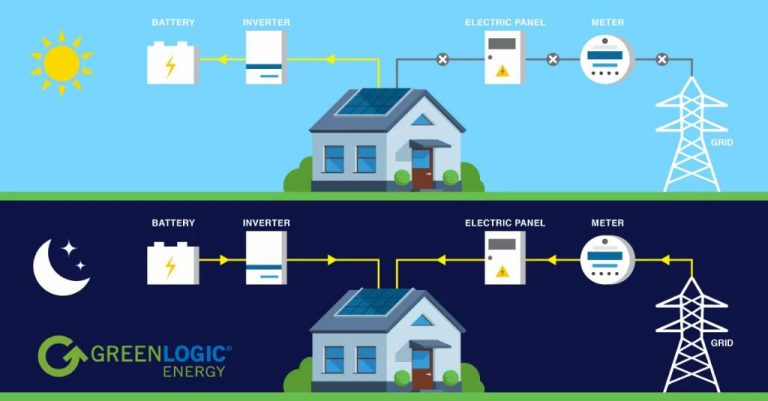
Solar panels on residential homes are one of the most common uses of solar energy. Homeowners can install solar panels on their rooftops or ground-mounted in their yards to generate electricity. The solar panels convert sunlight into direct current electricity, which then goes through an inverter to become alternating current that powers the home’s appliances and devices.
A major benefit for homeowners is net metering. This allows any excess electricity generated by the solar panels to be fed back into the main power grid. The homeowner’s electricity meter essentially runs backwards when they overproduce solar energy, giving them credits on their utility bill. At night or on cloudy days when the home’s solar panels aren’t generating enough, the household simply draws electricity from the grid like normal.
The amount of solar energy produced depends on factors like the number and efficiency rating of the panels, as well as the available sunlight which varies by climate and location. In optimal conditions, rooftop solar panels can provide most or even all of a household’s electricity needs, essentially zeroing out their power bill.
Home solar panel systems do require a significant upfront investment, but government incentives like tax credits help offset the costs. Over the lifespan of the system, homeowners can save substantially on electricity expenses. Going solar also reduces a home’s carbon footprint.
Businesses
Many businesses are turning to solar energy to help reduce their energy costs and become more sustainable. Solar panels can generate electricity to power anything from small shops to large manufacturing facilities. The upfront cost of installing a solar energy system can be high, but the long-term savings are significant. Once the system is paid off, businesses benefit from free electricity generated from the sun.
Commercial solar energy systems can offset 20-100% of a business’s electricity usage, depending on the size of the solar array and the building’s energy consumption. The more energy a business uses, the larger the solar system it will need to see substantial savings. However, even smaller systems can cut costs. Solar works well for powering buildings during peak daylight hours when electricity rates are highest. This helps businesses save on monthly utility bills.
Solar panels can go on rooftops, parking garages, or the ground. Many companies are choosing to install rooftop systems to make use of available space while maximizing solar production. Solar parking canopies are also popular for generating power while providing shade and protection. Some businesses with a lot of unused land are opting for ground-mounted systems. No matter the setup, commercial solar delivers clean, renewable power to the business.
Schools and Government Buildings
Many schools, government facilities, and other institutional buildings are installing solar energy systems. Solar panels can provide clean, renewable electricity to power these large facilities and reduce their dependence on the grid. According to one estimate, nearly 5,000 K-12 schools in the U.S. have gone solar.
There are several reasons why solar power is well-suited for schools and government buildings:
- They usually have large, flat roofs that offer ample space to install a solar array.
- They operate during daylight hours when solar panels are producing the most electricity.
- Installing solar aligns with sustainability and environmental initiatives many schools and government agencies have adopted.
- The long-term cost savings from lower energy bills help free up money for other priorities like education and community services.
Solar installations can serve as living laboratories to educate students about renewable energy. Monitoring solar panel output can also provide real-world data for math and science lessons. Many schools integrate their solar arrays into the curriculum.
Government facilities like libraries, recreation centers, administrative buildings, and public works garages are also adding solar. These installations reduce grid demand and showcase a commitment to clean energy.
Solar Power for Farms
Solar energy is transforming agriculture by providing a clean, renewable source of electricity to power equipment and operations. Farmers are increasingly adopting solar to reduce energy costs, maximize efficiency, and boost sustainability.
Solar panels can be installed on barns, equipment storage facilities, and processing buildings to provide electricity. The open space on farms also allows large solar arrays to be constructed, sometimes covering acres of land. These can provide enough electricity to power all farm operations.
Solar power is used on farms for:
- Pumping water for crop irrigation from wells or ponds.
- Ventilating, heating, and cooling greenhouses and animal barns.
- Refrigerating crops during storage and transport.
- Operating electric fencing around pastures and facilities.
- Charging electric farm vehicles and machinery.
Solar energy lowers costs for farmers by reducing expensive diesel and electricity purchases. It also provides energy security and independence, allowing farms to be self-powered off the grid. With solar, agriculture can be powered sustainably into the future.
Electric Vehicles
Solar energy can be used to power and charge electric vehicles, reducing their carbon footprint significantly. Homeowners with solar panels can install EV charging stations that draw clean energy from the sun. This allows EV owners to fuel their cars with renewable energy rather than reliance on the electric grid, which is often powered by fossil fuels.
Solar-powered charging stations are becoming more commonplace at workplaces, hotels, shopping centers, and other public places. Some electric utilities are also building large solar arrays specifically to power EV charging infrastructure. These solar charging stations give EV drivers more options to “refuel” their vehicles with clean energy.
The synergy between EVs and solar power is clear. As more drivers switch to electric vehicles, solar energy can provide the emissions-free electricity needed to charge their cars and trucks. Studies show solar-charged EVs can reduce lifecycle emissions by up to 75% compared to gas-powered vehicles. With transportation being a major contributor to climate change, solar-powered EVs are one solution to decarbonize the sector.
Utilities
One of the largest uses of solar power is in utility-scale solar farms. These farms have thousands or even millions of solar panels that generate huge amounts of electricity. This power is fed into the electric grid, helping to meet the energy demands of entire regions.
Some of the largest solar farms in the world are over 500 megawatts in capacity. The Topaz Solar Farm in California has over 9 million solar panels and can provide power to over 160,000 homes. Other massive solar farms are located in India, China, the Middle East, and Australia.
Solar farms can generate renewable energy more cheaply than building new fossil fuel power plants. The modular nature of solar panels also allows capacity to be added in phases. Solar farms are increasingly being built instead of coal and natural gas plants.
Utilities like the ability to purchase solar electricity under long-term contracts, providing price certainty even as fuel costs fluctuate. Solar farms can also be built relatively quickly. And the generated power does not create any greenhouse gas emissions.
Large scale solar power is transforming grids around the world. It allows utilities to meet renewable energy targets and reduce dependence on fossil fuels. Farm operators benefit from stable revenues. And electricity customers benefit from clean energy displacing dirty fuels.
Spacecraft and Satellites
Solar panels have become an essential power source for spacecraft, satellites, and space stations. When in orbit, these space vehicles can take advantage of near-continuous sunlight to generate electricity from solar panels. Some key examples include:
- The International Space Station – The ISS has four huge solar array wings covered in solar panels that provide 84-120 kilowatts of power. These wings rotate to stay aligned with the Sun.
- Satellites – Communications, GPS, weather, and many other satellites rely on solar panels for power. Solar arrays can rotate and tilt to track the Sun.
- Space probes and landers -NASA’s Curiosity rover on Mars uses a radioisotope thermoelectric generator for power. But solar panels have powered probes like Juno, New Horizons and Insight during their journeys.
- Future manned missions – NASA’s upcoming Artemis missions to establish a lunar base plan to use solar arrays for power. Solar is vital for enabling long-term exploration and research.
Solar power is ideal for space because of the consistent sunlight in orbit and the lack of atmosphere. Advancements in solar cell efficiency and panel technology have steadily improved the viability of solar energy in space.
Off-grid Uses
Solar energy is also commonly used for off-grid applications where connecting to the electrical grid is not possible or practical. Some examples of off-grid solar use include:
RVs
Many recreational vehicles like campers and motorhomes are equipped with solar panels to provide electricity without being plugged in. The solar panels charge batteries during the day, which then power lights, appliances, and electronics when stationary.
Cabins and cottages
In remote locations like lakes, mountains, and forests, solar power is an ideal way to electrify a secondary home or cabin that is off the grid. Solar panels can supplement or replace generators.
Outdoor equipment
Small solar panels can power or recharge equipment used for camping, hiking, boating and other outdoor activities. This includes lights, small appliances, phones, GPS devices and more.
Solar is a versatile renewable energy source that can provide electricity without access to an electrical grid. For many off-grid applications, solar is the most practical and affordable option.
Conclusion
As we have seen, solar energy can be used to power an incredibly diverse range of applications, from homes and businesses to vehicles, utilities, and even spacecraft. The adoption of solar power continues to grow rapidly around the world, thanks to falling costs and improving technology. In the future, we can expect solar to play an even greater role in powering our modern lifestyles in a clean and sustainable way.
Solar energy offers many advantages over traditional fossil fuel-based power sources. It is renewable, abundant, and emits no greenhouse gases. Solar also provides energy independence and security, since the fuel source, sunlight, is available everywhere. With solar costs declining and efficiency increasing, it is now cost-competitive with conventional power sources for a widening range of uses.
Governments, businesses, and homeowners are all recognizing the environmental and economic benefits of “going solar.” As more capacity comes online, economies of scale will further reduce costs. Supportive policies, like renewable portfolio standards and net metering, are accelerating growth. Technological improvements, like smart grids and energy storage, will enable higher solar penetration. The future is bright for this clean, versatile renewable energy source.