What Are The Examples Of Energy Transformation In Daily Life Activities?
Energy transformation refers to the process of changing energy from one form to another. Some common examples of energy transformations that happen regularly in our daily lives include converting chemical energy from food into kinetic energy through digestion and movement, using electricity to power appliances and devices, and harnessing the kinetic energy of moving wind or water for renewable power generation. The goal of this article is to provide clear illustrations of energy transformation that occur frequently in everyday activities, in order to demonstrate how this important physics concept applies to real-world situations.
Eating and Digesting Food
When we eat food, it contains stored chemical energy. As we digest the food, this chemical energy is transformed into other forms of energy to power our daily activities. For example, the chemical energy in food is converted into mechanical energy that allows our muscles to move. The conversion happens through metabolic processes that break down nutrients from the food we eat into molecules that can be used for energy production.
The chemical energy in carbohydrates, fats, and proteins gets transformed into a molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP provides the immediate source of energy for muscle contraction and other mechanical work inside the body. Without the chemical energy in food to produce ATP, our muscles would not be able to function.
The chemical energy in food also gets converted into thermal energy that helps maintain our body temperature. The metabolic processes that break down food generate heat as a byproduct. This heat energy helps maintain our normal body temperature of 98.6°F (37°C). The transformation of chemical energy from food into thermal energy is essential for regulating body temperature.
In summary, the chemical energy stored in the food we eat transforms into both mechanical energy to enable muscle movement and thermal energy to maintain ideal body temperature. Without these energy transformations, our bodies would not be able to function properly on a daily basis.
Using Electrical Appliances
Another common example of energy transformation in our daily lives is the use of electrical appliances. Electrical energy, which comes from power plants and travels through transmission lines into our homes and businesses, is transformed into various other forms of energy to perform useful work.
For example, a lightbulb transforms electrical energy into light and heat energy. Similarly, a refrigerator converts electrical energy into a cooling effect, while a blender transforms electrical energy into rotational kinetic energy to spin the blades. Televisions and speakers change electrical current into sound waves and radio waves. Electric heaters and stoves produce heat, while electric motors and engines generate motion.
In each case, the electrical energy flowing from the outlet is transformed into other types of energy based on the specific function of the appliance. So even though the initial source is electrical, that energy gets converted into light, sound, heat, motion, etc. to power the different gadgets and devices we use every day.
Combustion Engines
One of the most common examples of energy transformation that we encounter daily is the internal combustion engine in vehicles like cars and motorcycles. In this engine, chemical energy stored in the fuel is converted into mechanical energy that powers the engine, and waste heat energy that is released into the environment.
Specifically, the process begins when fuel (typically gasoline) and air are drawn into the engine cylinder. There the fuel/air mixture is compressed and ignited by a spark plug. This causes combustion – a chemical reaction between the fuel and oxygen in the air.
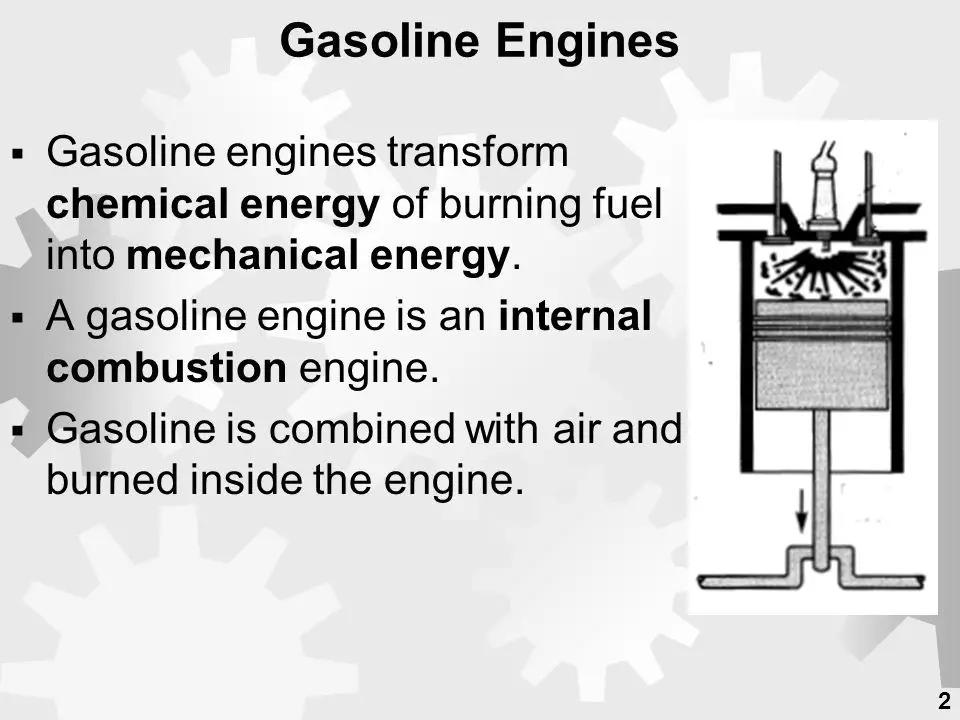
The rapid expansion of gases from this combustion applies force to the piston, making it move. The piston’s linear motion is transformed into rotational motion thanks to the crankshaft and connecting rod, which together deliver the engine’s power. The combustion also generates a tremendous amount of heat which is carried away by the exhaust gases.
So in summary, the chemical potential energy locked inside the gasoline is converted into useful mechanical energy to move the vehicle, with heat as a byproduct. This makes combustion engines an excellent example of energy transforming from one form to another in our daily lives.
Friction from Movement
A common example of energy transformation that happens daily is when mechanical energy transforms into thermal energy through friction. Friction is the resistance two surfaces encounter when moving against each other. The rubbing and sliding of these surfaces converts mechanical energy into heat, displaying energy transformation.
For instance, when brakes are applied in a moving vehicle, the brake pads rub against the wheel rims converting the vehicle’s kinetic energy into heat. The vehicle slows down as mechanical energy is lost, but thermal energy is gained in the process. The brake pads and wheel rims become hot from the friction. This is an important energy transformation that allows vehicles to stop safely.
Similarly, when a person goes for a run or walk, their feet repeatedly hit the ground. The friction between their shoes and the surface leads to heating of the soles. The mechanical energy from the person’s motion transforms into thermal energy through this friction. This is why vigorous exercise leads to an increase in body temperature.
Friction from movement facilitates many everyday activities, while also producing thermal energy as a useful byproduct. Identifying and understanding this energy transformation helps appreciate the role friction plays in daily life.
Solar Energy
Solar energy refers to the light and heat that comes from the sun. The sun emits an enormous amount of radiant energy, which travels to Earth in the form of electromagnetic radiation. When this radiant light energy reaches Earth, it can be transformed into other useful forms of energy like heat and electricity.
One example of solar energy being transformed is through the photoelectric effect. Solar panels contain special materials that absorb photons from sunlight and release electrons, generating an electric current that can be used as electricity. So radiant light energy from the sun gets transformed directly into electrical energy.
Another example is solar thermal collectors that absorb heat from sunlight. The sun’s thermal radiation hits the collector surface, which absorbs the heat and transfers it to a liquid like water or anti-freeze. This heated liquid is then circulated to warm swimming pools, homes, and businesses. So radiant light energy from the sun is transformed into thermal energy or heat.
Solar energy is considered a renewable source of energy because the sun will continue radiating light and heat for billions of years. Transforming solar energy into electricity and heat does not generate any toxic waste or emissions either. The development and usage of solar energy helps reduce reliance on finite fossil fuel reserves that pollute the environment when burned.
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to create their own food. This process converts radiant light energy from the sun into chemical energy that is stored in the bonds of glucose molecules.
During photosynthesis, plants absorb sunlight using chlorophyll in their leaves. The chlorophyll absorbs the light energy and uses it to drive a series of chemical reactions. Carbon dioxide from the air passes through small pores in the plant’s leaves and reacts with water absorbed from the soil by the plant’s roots. The chlorophyll provides the energy needed to combine the carbon dioxide and water into glucose, a simple sugar. Oxygen is produced as a byproduct of photosynthesis and is released into the air.
The glucose molecules produced through photosynthesis contain the chemical energy that powers almost all life on Earth. Plants use this glucose to produce energy, grow, and reproduce. Animals that eat plants digest the glucose molecules to extract energy. The chemical energy derived from photosynthesis is passed along the food chain, powering herbivores, omnivores, and carnivores. This makes photosynthesis one of the most important examples of converting radiant light energy into usable chemical energy on our planet.
Hydroelectric Power
One of the most common examples of energy transformation that we rely on daily is hydroelectric power. At hydroelectric dams, the potential energy stored in elevated water is transformed into electricity. Here’s how it works:
1. Water from a river or reservoir flows through an intake at the top of the dam.
2. The force of gravity causes the water to fall through pipes or tunnels inside the dam.
3. The moving water spins turbines located at the bottom of the dam.
4. The motion of the turbines turns electromagnets within a generator, producing an electric current.
5. The electricity is then transported via power lines to homes and businesses in need of power.
The higher the dam and more water pressure, the more potential energy is available to be transformed into electrical energy. Dams transform the powerful potential energy of immense quantities of water into a manageable and useful form of energy for human consumption.
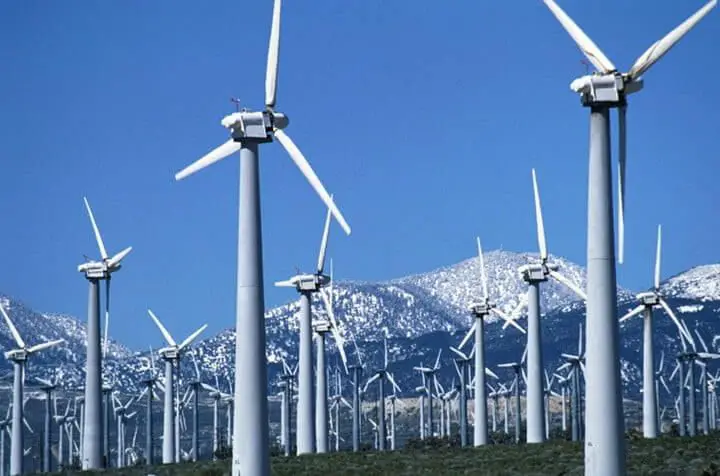
Wind Turbines
Wind turbines are a great example of energy transformation. The kinetic energy from the movement of air is transformed into mechanical energy as the wind spins the blades of the wind turbine. This rotational kinetic energy is then converted into electrical energy through the generator in the turbine. The generator contains magnets that rotate past copper wire coils, inducing an electric current that can be transmitted and used as electricity.
So in summary, the natural kinetic energy of the wind is transformed into rotational kinetic energy to spin the turbine, which is then converted into electrical energy for human use and consumption. This demonstrates a clean, renewable energy source taking natural forms of energy like wind and transforming them into usable electricity.
Conclusion
In our everyday lives, we witness and utilize energy transformation in many common activities without even realizing it. From the food we eat at breakfast to the car ride to work, energy is constantly being converted from one form into another.
When we eat food, chemical energy stored in the bonds of the food molecules is released and converted into thermal energy and kinetic energy that allows our bodies to function and move. The appliances we use in our homes, like lights, televisions, and computers plug into and convert electrical energy into light, sound, and digital operations. The gasoline that fuels cars and other engines is ignited in a combustion reaction that releases heat energy which is transformed into mechanical energy that propels the engine’s moving parts.
Even simple actions like walking or rubbing your hands together demonstrate energy transformation at work through friction converting kinetic energy into thermal energy. Nature also harnesses energy conversion through photosynthesis in plants, solar panels, hydroelectric dams, and wind turbines.
Being aware of the many examples of energy transformation we utilize everyday highlights that energy is an essential driver of life and productivity. Appreciating how energy moves between different states provides a deeper understanding of our world and universe.