Is Solar Energy Facts For Students
What is solar energy?
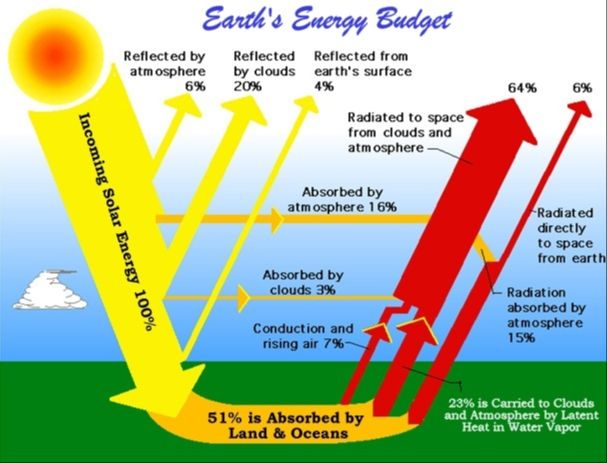
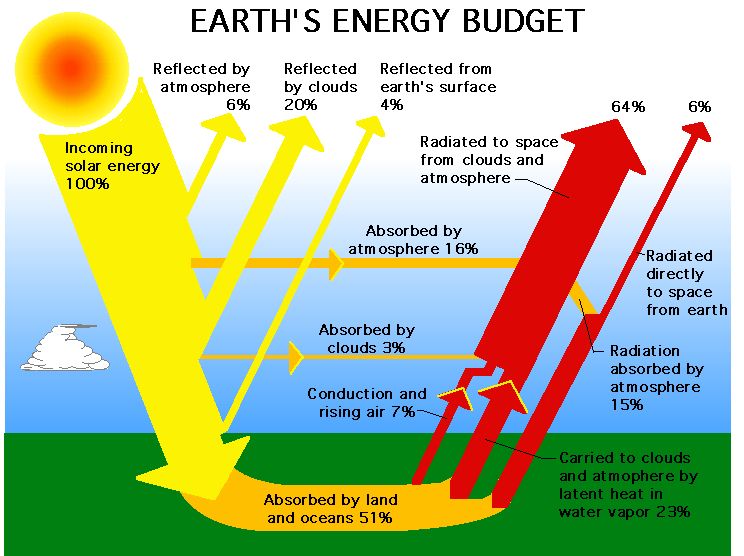
Solar energy is radiant energy from the sun that is converted into thermal or electrical energy. The sun produce energy through a process called nuclear fusion, in which hydrogen atoms fuse together to create helium. This fusion process releases enormous amounts of energy in the form of photons or light particles (SolarPowerConference, 2022).
Some key facts about solar energy:
- Solar energy is a renewable energy source, meaning it cannot be depleted and is constantly replenished.
- The amount of solar energy that hits the Earth’s surface in one hour could power the world for a year (SolarPowerConference, 2022).
- Solar energy can be converted into electricity using photovoltaic solar panels or concentrated solar power plants.
- Solar energy is considered a green energy source because it does not produce pollution or greenhouse gases.
- Solar power is used worldwide, from small scale residential systems to large utility-scale solar farms.
The formal definition of solar energy is radiant energy emitted by the sun that can be converted into other forms of energy, like heat or electricity. Solar energy is essential to almost all life on Earth, as it powers photosynthesis in plants and helps maintain Earth’s climate. Harnessing solar power is one way to produce renewable energy without harmful byproducts.
Benefits of solar energy
Solar energy is a renewable energy source. Unlike fossil fuels such as coal, oil and natural gas that are finite resources, solar energy is abundantly available and does not produce greenhouse gas emissions when converted into useful forms of energy.
Using solar energy reduces reliance on fossil fuels. Fossil fuels are non-renewable energy sources that will eventually dwindle as demand increases. Switching to solar energy reduces dependence on fossil fuels and conserves these limited resources for future generations.
Solar energy helps reduce air pollution as it does not emit pollutants like nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide and particulate matter into the atmosphere during energy production, which can lead to acid rain, smog and respiratory problems. In contrast, burning fossil fuels releases large amounts of harmful pollutants.
Solar energy can help reduce electricity bills with minimal maintenance costs. Although installing solar panels has an upfront cost, over the system’s lifespan the free and abundant sunlight converts to electricity savings. Many schools have seen significant cost savings after switching to solar power. For example, some schools are eligible for solar grants to make the switch even more cost-effective.
How solar panels work
Solar panels work through the photovoltaic effect, which is the process of converting photons from sunlight into electricity. Solar cells inside solar panels are made up of semi-conductor materials like silicon. When sunlight hits the solar cell, the photons are absorbed by the semi-conductor material which causes electrons to become energized and move freely.
The solar cell has electric fields built into it which act like a one-way street to provide a direction for the electrons to flow. Metal conductive plates on the cell collect the electrons at the front and back, creating an electrical current. Wires connect the front and back plates to allow the current to flow from the cell into an external circuit.
So in summary, the photovoltaic effect causes solar cells to convert photons from sunlight into electricity through energizing electrons and using electric fields to make them flow in one direction to produce a current. This electricity generated can then be used to power electrical devices and equipment.
Source: How solar panels work simply how does …
Types of solar power systems
There are three main types of solar power systems:
Photovoltaics
Photovoltaic (PV) systems use solar panels made up of solar cells to convert sunlight directly into electricity. The solar cells are made of semi-conducting materials like silicon that absorb photons from sunlight and release electrons, generating an electric current. PV systems come in different sizes, from small rooftop systems for homes to large utility-scale solar farms. They require little maintenance and have a long lifespan. (Sunation, 2022)
Solar heating and cooling
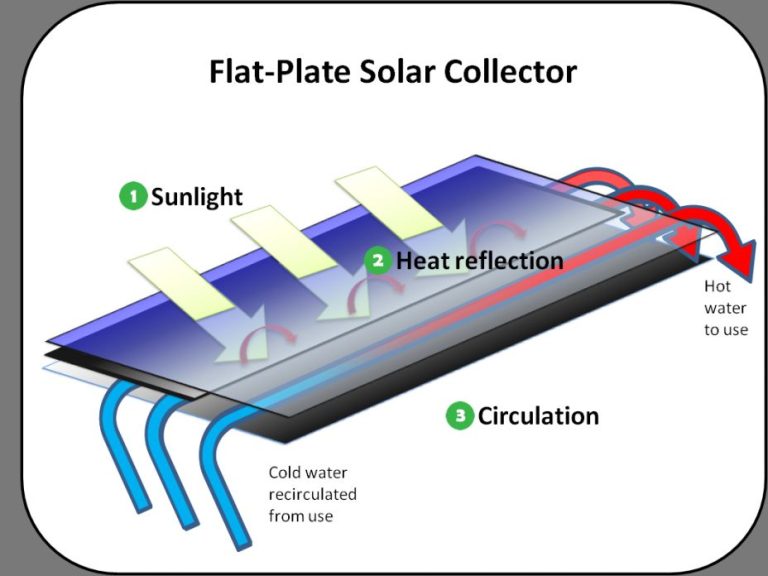
Solar heating systems use solar thermal collectors to absorb heat from the sun and transfer it to water or air. The heated fluid can then be used for hot water, space heating, and even absorption cooling. Solar collectors come in various forms like flat plates, evacuated tubes, unglazed, and concentrating. Solar heating is often used for residential water and space heating as well as heating pools. (Avaada, 2022)
Concentrated solar power
Concentrated solar power (CSP) systems use mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a receiver containing a heat transfer fluid. The concentrated heat is used to drive a heat engine like a steam turbine connected to an electrical generator. CSP allows energy storage by heating molten salts to produce steam on demand. CSP plants provide utility-scale power and are suitable for regions with high direct solar radiation. Major CSP technologies include parabolic troughs, power towers, and dish/engines.
Interesting solar energy facts
Solar energy has enormous potential as an energy source. Some interesting facts about solar energy capacity and statistics:
The amount of solar energy that hits the Earth’s surface in one hour could power the entire world for a year (Source: https://easyscienceforkids.com/solar-energy-facts-for-kids-video/).
Just 0.1% of the Earth’s land area covered in solar panels could power the entire world (Source: https://freedomsolarpower.com/blog/teaching-solar-power-to-the-next-generation).
The solar energy industry in the United States grew by over 10,000% in the last decade (Source: https://easyscienceforkids.com/solar-energy-for-kids-video/).
Solar panels get more efficient each year – most panels today are 15-20% efficient at converting sunlight to electricity.
California has over 20 gigawatts of installed solar capacity, more than any other U.S. state.
Developing countries are installing solar power faster than developed nations – the top countries for new solar in 2018 were China, India, and Japan.
History of solar energy
The history of harnessing solar energy dates back to the 7th century B.C.E, when magnifying glasses were used to concentrate the sun’s rays to make fire. Some key events and figures in the early development of solar technology include:
In the 3rd century B.C.E, the Greeks and Romans used passive solar energy in the designs of their architecture. Buildings were oriented to maximize sunlight exposure.
In 1839, French physicist Edmond Becquerel first discovered the photovoltaic effect while experimenting with electrolytic cells.
In 1904, Albert Einstein published a paper explaining the photoelectric effect, for which he later won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1921.
In 1918, American inventor Maria Telkes began experimenting with the concept of storing solar energy in chemical salts, leading to the first solar-powered heating system.
The 1950s and 1960s saw major advances, including the invention of the first practical solar cell by Bell Labs in 1954. The space industry drove much of the early development of solar technology.
Solar Energy Challenges
While solar energy has many benefits, it also comes with some challenges that need to be addressed for it to reach its full potential. Some of the main challenges with solar power include:
Intermittency: The amount of sunlight that hits the earth varies depending on the time of day, weather, and seasons. This means solar power generation can be intermittent and inconsistent. Solar only generates power when the sun is shining, so storage solutions or backup power is needed for times when sunlight is limited. https://www.constellation.com/energy-101/energy-innovation/solar-energy-pros-and-cons.html
Storage: Since solar power can’t be generated at night, effective energy storage solutions are important for solar to reach its potential. Developing efficient and cost-effective storage is still a challenge. Batteries can store solar energy for use when the sun isn’t shining, but they add significant cost. New storage technologies like pumped hydro and thermal storage are being explored.
High costs: While solar costs have dropped dramatically over the last decade, the upfront installation costs for solar remain high for many homeowners and businesses. Solar arrays require a significant initial investment that can deter adoption. Loans, tax credits and rebates can help alleviate costs, but overall affordability is still a challenge.
Solar Energy Future
The future of solar energy looks very promising. Solar power is currently the fastest growing energy source worldwide, with an average annual growth of over 20% over the last decade 1. This growth is expected to continue as solar technology improves and costs continue to fall.
One key area of improvement is solar cell efficiency. Current commercial solar cells convert 15-20% of sunlight into electricity, but researchers are working on new materials and designs to increase this efficiency, with some prototype solar cells already achieving over 40% efficiency 1. Higher efficiency means more electricity generated from the same sized solar panel.
There are also new solar technologies being developed, like organic solar cells that can be printed or painted onto surfaces, and solar windows that generate electricity. These innovations could greatly expand where and how solar power is used.
Solar power is projected to continue its rapid growth over the next decade. Total global solar capacity is forecast to triple by 2030, with some projections estimating solar will provide up to 20% of global electricity by 2030 and as much as 50% by 2050 1. With improving technology and economies of scale driving down costs, the future is looking very sunny for solar energy.
Solar energy in schools
Solar energy is becoming an increasingly popular topic in school curriculums, with many schools incorporating solar energy projects and lessons into science, technology, engineering, and math classes. Solar energy offers hands-on learning opportunities for students to understand renewable energy concepts. Many schools are also installing solar panels to generate electricity and reduce energy costs while providing real-world examples of solar technology.
There are many great solar energy activities and projects for middle school and high school students. Building solar ovens, solar cars, or model solar houses allows students to apply their knowledge of solar energy. Analyzing data from school solar panel systems also reinforces graphing, data analysis, and critical thinking skills. Student-run solar energy clubs and competitions are another engaging way to get students interested in solar power.
Learning about solar energy and sustainability can inspire students to pursue careers in the solar industry and related STEM fields. As solar jobs are projected to grow over the next decade, students can gain valuable skills for entering the renewable energy workforce. From solar panel installers to sales representatives to engineers, there are diverse career paths students can explore through solar energy education.
With plenty of free online resources, grants, and hands-on projects available, integrating solar energy into school curriculums has never been more accessible. Solar energy offers a real-world topic to energize STEM education and inspire the next generation of renewable energy professionals.
Solar Energy Careers
The solar energy industry offers various career opportunities for high school students interested in working with renewable energy. Some of the careers available in this field include:
Solar Installers and Technicians
Solar installers and technicians are responsible for installing, maintaining, and repairing solar energy systems like solar panels and batteries. Students interested in hands-on technical work might enjoy becoming a solar installer. Training programs and certifications are available through community colleges, technical schools, and industry associations like the North American Board of Certified Energy Practitioners (NABCEP). The median pay for solar installers is over $42,000 per year.
Project Managers
Solar project managers oversee the development and construction of solar installations. They manage teams, budgets, timelines, permitting, and other aspects of solar projects. Students with organizational skills and an interest in solar may enjoy becoming a solar project manager. Project managers need at least a bachelor’s degree, with majors like engineering, construction management, or business. The median salary for solar project managers is approximately $86,000 annually.
Sales and Marketing Professionals
Salespeople work selling solar systems to homeowners and businesses. Marketing professionals help solar companies attract customers and promote their products and services. Students with marketing, business, and communication skills may enjoy solar sales and marketing roles. Coursework in marketing, communications, and business is helpful. The median pay for sales reps in renewable energy is around $48,000 per year.