How Much Has Solar Energy Growth Worldwide?
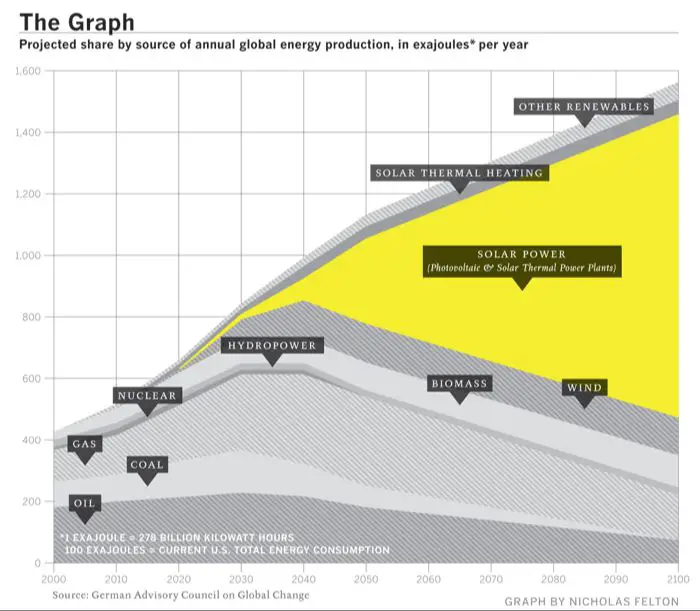
Solar energy capacity worldwide has increased exponentially over the past decade. As the costs of solar technology have rapidly declined and government policies have promoted adoption, solar power generation has expanded from a niche contributor to a mainstream energy source across the globe. This exponential growth is expected to continue as solar energy becomes increasingly cost competitive with fossil fuels, presenting major opportunities along with challenges to integrate this variable renewable resource.
Global Solar Energy Capacity
In the past decade, global solar energy capacity has experienced tremendous growth. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global solar PV capacity reached over 1,185 gigawatts (GW) by the end of 2022, up from only 40 GW in 2010. This represents a nearly 30-fold increase in just over 10 years.
More specifically, global solar capacity was:
- 40 GW in 2010
- 100 GW in 2012
- 177 GW in 2014
- 303 GW in 2016
- 499 GW in 2018
- 652 GW in 2020
- 918 GW in 2021
- 1,185 GW in 2022
This rapid growth has been driven by declining costs, supportive government policies, corporate adoption, and increased demand worldwide. Solar now accounts for over 6% of global electricity generation, up from just 0.1% in 2010. With costs continuing to decrease and climate change concerns rising, solar is projected to grow substantially in the coming decades.
Top Countries by Solar Capacity
China leads the world in total installed solar capacity, with over 390 GW as of 2022, accounting for nearly two-fifths of global solar capacity according to Wikipedia. The United States ranks second in the world with over 130 GW of solar capacity. Japan comes in third with over 75 GW of installed capacity. Other top countries for solar energy include Germany, India, Italy, Australia, Spain and South Korea.
China’s massive investment in solar energy is part of the country’s push to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and combat air pollution in its major cities. The United States has seen enormous growth in solar energy in the past decade, with total capacity tripling since 2014. Major solar incentives and falling costs have made solar power more accessible to American homeowners and businesses. Japan is a global leader in solar panel manufacturing and has aggressively adopted solar power following the 2011 Fukushima nuclear disaster. With abundant sunshine and large investments, countries like Germany, India and others continue to expand their solar energy portfolios.
Solar Energy Cost Decline
The costs of solar panels and installation have dropped dramatically over the last few decades. According to Green World Investor, the price of solar panels has fallen by over 90% since 2009. In India specifically, recent solar power auction bids have fallen to around 3 cents per kilowatt-hour. This makes solar power highly cost competitive with fossil fuels like coal and natural gas.
There are a few key factors driving the continued cost declines:
- Improved solar panel efficiency and manufacturing – panel costs have fallen from $3.50/Watt in 2008 to only $0.25/Watt in 2020.
- Economies of scale – with greater global production volumes, fixed costs are spread over more units.
- Maturing supply chains and industry competition – innovation and economies of scale apply to auxiliary components like inverters and racking systems.

With solar already at grid parity in many regions, some projections forecast costs falling by another 40% or more by 2040. This ongoing decline makes the economics of solar power increasingly compelling worldwide.
Government Policies
Government policies have played a major role in accelerating the adoption of solar energy worldwide. Many national and local governments offer generous subsidies, tax credits, and other incentives to reduce the upfront costs of going solar for homeowners and businesses.
In the United States, the federal government offers a 26% tax credit through 2032 for installing solar panels, which significantly offsets installation costs (https://www.solar.com/learn/solar-rebates-by-state/). Many states such as California also offer additional rebates and incentives on top of the federal credit to make solar even more affordable.
Local governments also provide property tax exemptions in certain counties for homes with solar installations, further enhancing solar savings (https://www.sunternalsolar.com/solar-incentives). The declining costs of solar panels, combined with these generous government subsidies, have been instrumental in the rapid growth of solar adoption, especially in the residential sector.
Governments around the world, from China to Europe, have implemented strong policy support like feed-in tariffs that allow solar system owners to sell excess power back to the grid at above-market rates. These types of forward-thinking policies have catalyzed mass deployment of solar energy globally.
Corporate Solar Adoption
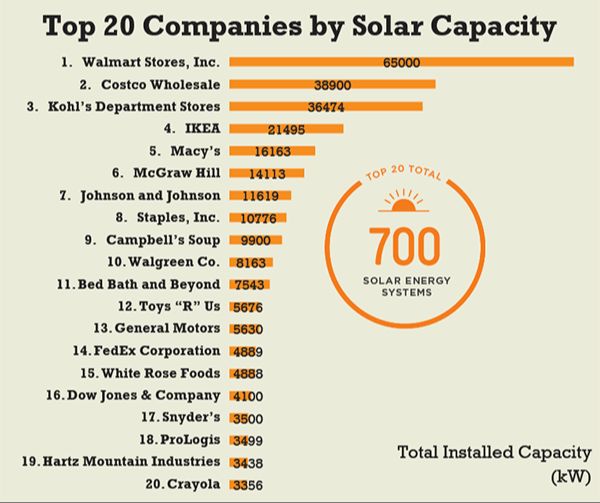
Many major corporations are opting to install solar panels to reduce energy costs and meet sustainability goals. According to Solar Means Business, Now More Than Ever by greenconvergence.com, the top corporate solar users include Target, Walmart, Apple, Amazon, and IKEA with over 200 megawatts (MW) of solar capacity each. Another report states that Lidl recently signed one of the largest solar corporate power purchase agreements in the Netherlands to install solar panels on their buildings.
The benefits of corporate solar include predictable energy costs, reduced carbon emissions, improved brand reputation, and new revenue streams. According to Solar Energy Facts and Stats Every Homeowner Should Know by Forbes, companies like Amazon, Apple, Walmart and Microsoft are utilizing solar energy to power their operations. Solar helps corporations meet renewable energy and carbon reduction goals. Overall, corporate adoption of solar energy continues to grow as prices fall and companies seek clean, renewable power.
Residential Solar
Residential solar, also known as rooftop solar, has seen tremendous growth in recent years as more homeowners install solar panels on their roofs. According to Solar Market Insight Report Q4 2023 (https://www.seia.org/research-resources/solar-market-insight-report-q4-2023), the U.S. residential solar market added over 3 gigawatts (GW) of new capacity in 2021, a record high. There are now over 3 million homes with rooftop solar installations. Falling costs, supportive policies, and innovative financing options have made residential solar more accessible. The outlook for continued growth is positive but faces some headwinds. An analysis by Morgan Stanley predicts more modest single-digit percentage growth in 2022 and 2023 as rising interest rates and policy changes in some markets like California slow adoption.
Solar Job Creation
The growth of the solar industry has led to significant job creation around the world. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, solar industry job growth increased more than 170% across all 50 states, Washington D.C. and Puerto Rico in the past decade (Department of Energy). In 2019 alone, solar industry employment rebounded with a 2.3% increase, adding 5,600 jobs for a total of 249,983 U.S. solar workers (Solar Tribune). However, the COVID-19 pandemic caused major job losses, with projections that the U.S. solar industry could lose 114,000 jobs in 2020 compared to 2019 levels (Union of Concerned Scientists). Overall, the massive growth in solar power generation worldwide has driven increased employment in manufacturing, installation, maintenance, research and other solar-related fields.
Future Solar Growth Projections
Based on research by Deloitte, forecasts for U.S. solar power penetration by 2040 range significantly, from modest levels to exponential growth. However, most industry experts predict substantial expansion of solar energy generation over the next two decades.
According to the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA), annual solar deployment is expected to more than double from 2022 to 2030. SEIA projects solar capacity in the U.S. will reach over 400 gigawatts by 2030.
One Deloitte analysis predicts U.S. solar generation will increase from under 4% of total generation in 2020 to over 20% by 2040. This would require average annual solar capacity additions of 17 gigawatts through 2040.
More optimistic projections estimate solar could provide up to 40% of U.S. electricity by 2035 and 50% by 2040. Realizing these levels of solar penetration will require supportive government policies and rapid declines in solar technology costs.
Major growth drivers for solar include increasingly competitive pricing, improved energy storage capabilities, corporate and residential demand, and state renewable portfolio standards requiring utilities to add renewable energy generation.
Conclusion
In reviewing the exponential growth of solar energy capacity over the past decade, it is clear that solar power is rapidly becoming a mainstream energy source worldwide. Driven by plummeting costs and supportive government policies, solar adoption has soared in many countries. Corporations and homeowners alike are installing solar panels to reduce electricity bills and their carbon footprints. This solar boom has generated hundreds of thousands of new jobs. Based on current growth projections, solar energy has a very bright future ahead, with some estimates suggesting it could provide over 20% of global electricity by 2030. The outlook for solar power is overwhelmingly positive as costs continue to fall andclimate change concerns accelerate the transition to renewable energy.