How Much Energy In The World Is Solar?
Solar power has experienced exponential growth over the last decade and is poised to play an increasingly significant role in the global energy landscape. The declining costs of solar photovoltaics (PV), favorable government policies, and the urgent need to transition to clean energy have all contributed to solar becoming one of the fastest growing renewable energy sources worldwide. Solar Industry Research Data | SEIA reports that solar has seen an average annual growth rate of 24% in the past 10 years. With such rapid expansion, there is growing interest in understanding the current and future scale of solar energy globally.
Current Share of Solar
Solar photovoltaics (PV) accounted for around 4.5% of total global electricity generation in 2022, up from 3.6% in 2021, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA). The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) reports that PV’s global share rose from around 3.6% in 2021 to 4.5% in 2022 (NREL). Globally, the combined share of wind and solar in electricity production increased by 1.5 percentage points in 2022 to over 12%, with solar making up a significant portion of that growth according to Enerdata (Enerdata). While solar currently accounts for a relatively small percentage of total global energy production, it has been experiencing rapid growth over the past decade.
Solar Energy Capacity
The total installed solar capacity worldwide was around 809 gigawatts (GW) by the end of 2021. This is up from around 760 GW at the end of 2020, representing an increase of over 6%.
To put this in perspective, just 10 years ago in 2011, global solar capacity stood at only around 70 GW. So installed solar capacity has increased more than 10-fold over the past decade thanks to plunging costs and supportive policies.
In terms of electricity generation, solar currently accounts for around 4% of global electricity demand. But solar’s share is rising each year and is projected to reach 20% by 2030.
The countries with the most installed solar capacity are China, the United States, Japan, Germany, and India. These top five countries account for over 70% of global solar capacity.
China leads the world by far, with over 305 GW of installed capacity. The U.S. ranks second with around 122 GW. Japan, Germany, and India have between 65-100 GW of installed solar capacity each.
Countries Leading in Solar
China has emerged as the global leader in total installed solar capacity. According to Wikipedia, China had about 390 GW of solar capacity in 2022, accounting for nearly two-fifths of total global solar capacity [1]. The United States ranks second with 168 GW of solar capacity. Other major countries with significant solar capacity include Japan, Germany, India, Italy, Australia, Spain and South Korea.
The top 5 countries by total installed solar capacity in 2023 are:
- China – 430 GW [2]
- United States – 168 GW
- Japan – 98 GW
- Germany – 70 GW
- India – 60 GW
China’s lead is massive, with over double the solar capacity of the second ranked nation. The country has invested heavily in solar energy and established itself as the dominant global force in solar panel manufacturing and deployment.
Growth of Solar
Solar energy has experienced massive growth in the United States over the past decade. According to the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA), solar has grown at an average annual rate of 24% since 2000. In the last 10 years alone, solar energy capacity has nearly tripled in the U.S. (Solar Industry Research Data | SEIA)
The SEIA reported that the U.S. solar market size was just 2.6 gigawatts of installed capacity in 2010. By 2020, that number had jumped to 108.7 gigawatts, representing a 43% increase over just the past decade. Much of this rapid growth can be attributed to the continuously decreasing costs of solar technology and installation. (The Past Decade of Solar)
According to Environment America, the amount of solar energy produced in the U.S. has increased nearly 12 times over between 2013 to 2022. In 2013, there was enough solar capacity to power 1.6 million American homes. By 2022, solar energy production provided power for 19 million homes. (Wind & solar energy tripled in U.S. over past decade)
Projected Future Growth
Solar energy is projected to experience rapid growth in the coming decades. According to the Solar Futures Study by the U.S. Department of Energy, solar power is predicted to grow from 3% of U.S. electricity today to 40% by 2035 and 45% by 2050, accounting for 1,600 gigawatts. The International Energy Agency (IEA) also sees great potential for solar, estimating it could provide over 11% of global electricity by 2050. The average cost of generating solar electricity is expected to decrease by 60% from 2020 to 2050, further driving growth.
By 2050, the IEA predicts solar photovoltaics (PV) could provide up to 25% of global electricity generation. The continued decline in solar PV costs along with supportive policies and technological advances will enable this high growth trajectory. While challenges remain, solar power is poised to become the dominant source of global electricity by mid-century.
Cost of Solar
The cost of solar panels and solar energy has decreased significantly over the past decade, making solar power more economically viable and affordable. According to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), between 2010 and 2020, the cost of utility-scale solar photovoltaic (PV) systems declined by 70%1. The average price of a residential solar system in the U.S. fell from around $50,000 in 2010 to around $20,000 in 20202.
Several factors have driven down the cost of solar panels and systems over the past decade. Improvements in solar panel efficiency, manufacturing innovations, economies of scale, and competitive global supply chains have all contributed to reducing hardware costs. In addition, lower “soft costs” like permitting, installation labor, supply chain costs, and financing have helped drive down the total installed price of solar PV systems in the U.S.
With ongoing technology improvements and market growth, analysts predict solar PV prices will continue to decrease at a steady pace. One projection estimates an average annual reduction in solar panel pricing of around 20% over the next 5 years3. As prices fall further, solar power is expected to be increasingly adopted worldwide.
Challenges for Solar
While solar energy has many benefits, it also has some unique challenges. Three main challenges for solar energy are intermittency, storage, and grid integration.
Intermittency refers to the fact that solar energy production depends on sunlight, which varies throughout the day and year. Solar panels do not produce energy at night, and energy production can be impacted by weather conditions like clouds or storms. This intermittent generation profile creates challenges for matching supply with electricity demand.
Energy storage is important for addressing solar intermittency so that excess daytime solar electricity can be stored and used at night. However, at scale, cost-effective energy storage for solar remains a key obstacle. Battery storage can be expensive and most storage used today relies on other technologies like pumped hydro or compressed air which have geographic constraints.
Grid integration and management also poses challenges due to the variable and decentralized nature of solar energy. Significant solar energy penetration requires grids and utilities to have advanced monitoring and control capabilities to balance generation and load. Without proper integration, reliability and power quality could suffer.
Ongoing technological improvements, market designs, and grid modernization initiatives aim to help address these solar integration and grid management challenges. However solving the issues of intermittency, storage and grid integration remain critical for solar to supply a major share of electricity.
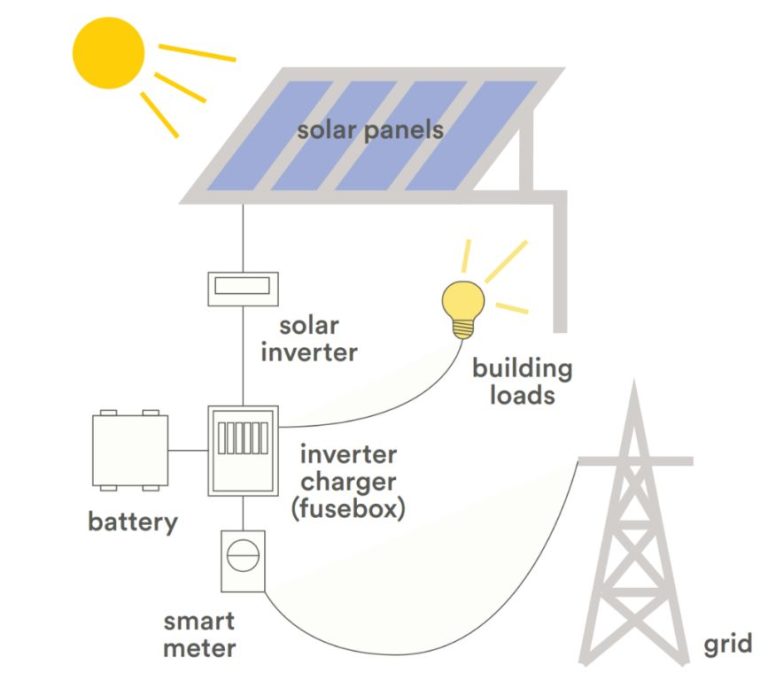
Solar Energy Storage
One of the biggest developments in solar technology has been in the area of energy storage, particularly battery storage. As solar power grows, the ability to store the energy produced by solar panels for use when the sun isn’t shining is critical. There have been significant improvements in battery technology in recent years that are making solar energy storage more affordable and efficient.
Lithium-ion batteries have become the dominant battery technology for home solar storage systems. Compared to traditional lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion batteries have a longer lifespan, degrade slower, are lighter, and have a higher energy density so more power can be stored in less space (Greener Ideal, 2023). Tesla’s Powerwall home battery and the LG Chem RESU system are two popular lithium-ion solar batteries on the market.
Battery costs have also declined dramatically, with the cost of lithium-ion batteries dropping nearly 90% in the last decade (8m Solar, 2023). This makes adding battery storage to home solar systems much more cost effective. Some projections estimate lithium-ion solar battery costs could fall by another 50-75% by 2030.
New battery chemistries like lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries are also being adopted for solar storage. LFP batteries have a longer cycle life, better performance in hotter environments, and reduced risk of overheating compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries (Blue Raven Solar, 2023). Improved battery management systems, inverters, and charge controllers have also helped advance solar storage.
Conclusion
Solar energy is poised for massive growth and has the potential to become a major component of the global energy landscape. According to projections, solar capacity could grow from around 600 GW in 2019 to over 8,500 GW by 2050, accounting for nearly 30% of total global electricity generation. Factors driving this growth include rapidly falling costs, supportive government policies, and improvements in energy storage and grid integration technologies. While there are still challenges around intermittency and grid integration at high solar penetration levels, solutions such as demand response, energy storage, and smart grids can help overcome these. With continued innovation and investment, solar is well on its way to transform how energy is generated and consumed around the world.