How Is Solar Energy Useful To The Life On Earth?
Solar energy is the radiant energy emitted by the sun in the form of electromagnetic waves. The sun produces energy through nuclear fusion reactions at its core, converting hydrogen into helium and releasing enormous amounts of energy in the process. This energy radiates outward from the sun in all directions in the form of photons or light particles.
The sun provides the ultimate source of energy that drives life on Earth. Sunlight is essential for photosynthesis, which allows plants to convert the sun’s energy into chemical energy they can use. Nearly all life on Earth depends either directly or indirectly on this process to obtain energy. The sun also impacts climate and seasons on Earth through the uneven heating of the planet’s surface. Overall, the sun’s light and heat make life as we know it possible on our planet.
Source: https://www.nationalgeographic.org/encyclopedia/sun/
Photosynthesis
Solar energy is essential for the process of photosynthesis in plants. Through photosynthesis, plants use the energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose (food) and oxygen [1]. This process allows plants to trap light energy and convert it into chemical energy that they can use as fuel [2]. Photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts, which contain the green pigment chlorophyll that captures the sunlight. When light is absorbed by chlorophyll, it excites electrons which provides energy to power the synthesis of glucose from CO2 and H2O. The glucose produced through photosynthesis provides food not just for the plant itself, but also for other living organisms that depend on plants for nourishment – from herbivores that eat plants to omnivores and carnivores that eat herbivores [3]. In this way, the solar energy captured through photosynthesis becomes the basis of many food chains and webs, supporting a wide diversity of life.
Climate Regulation
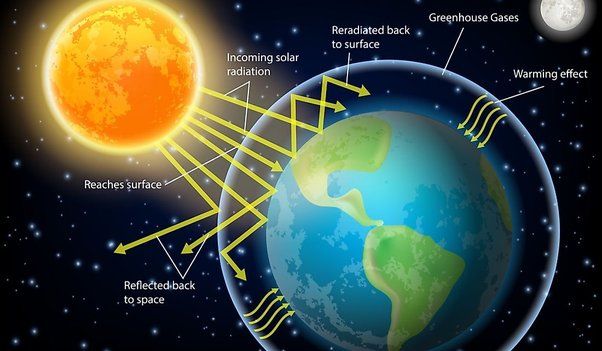
The sun’s solar radiation is the key driver of climate and weather on Earth. As NASA explains, “The Sun powers life on Earth; it helps keep the planet warm enough for us to survive. It also influences Earth’s climate: We know subtle changes in Earth’s orbit around the Sun are responsible for the comings and goings of the past ice ages” (NASA). Different regions on Earth receive different amounts of incoming solar radiation based on their latitude and geographic location. Areas at lower latitudes near the equator receive more direct sunlight than polar regions. This differential heating drives weather patterns and climate zones around the globe.
While the Sun influences Earth’s climate, it is not responsible for the warming trend observed in recent decades. As NASA states, “We know subtle changes in Earth’s orbit around the Sun are responsible for the comings and goings of the past ice ages. But the warming we’ve seen over the last few decades is too rapid to be linked to changes in Earth’s orbit, and too large to be caused by solar activity” (NASA). The primary driver of recent global temperature rise is increased greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide from human activities.
Light
Sunlight provides the light and warmth that is vital to almost all life on Earth (Mead, 2008). The sun emits electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which allows plants, animals, and humans to see. Without light from the sun, the world would be enveloped in darkness.
The visible light provided by the sun enables photosynthesis in plants and phytoplankton. During photosynthesis, plants use the energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. Photosynthesis provides the basic food source for nearly all life on Earth (Mead, 2008).
Sunlight also provides the warmth that maintains temperatures on Earth in a habitable range for life. The greenhouse effect helps trap some of the sun’s warmth in the atmosphere. Sunlight has helped shape ecosystems and climates that have fostered the evolution of biodiversity over billions of years.
Vitamin D
Sunlight exposure allows many organisms, including humans, to produce vitamin D, which is essential for bone health and calcium absorption (1). When skin is exposed to UVB rays from sunlight, it synthesizes vitamin D from cholesterol in the skin (2). Spending just 10-30 minutes in midday sunlight a few times per week allows the body to produce adequate vitamin D (3). One study found that 20-30 minutes of sun twice weekly on the face and arms can achieve serum vitamin D levels of 30 ng/ml (1). Vitamin D from sunlight has been shown to reduce risk of multiple sclerosis, heart disease, flu, depression, and many types of cancer. However, excessive sunlight increases risk of skin cancer, so moderation is key.
Circadian Rhythms
Sunlight plays a critical role in regulating circadian rhythms, the internal clocks that dictate sleep-wake cycles and other biological processes in humans, animals, and plants. Exposure to sunlight, especially bright morning light, helps synchronize our circadian rhythms to Earth’s 24-hour day-night cycle (1). Sunlight suppresses the production of melatonin, a hormone that promotes sleep, and increases cortisol levels, which boosts alertness and wakefulness (2).
In humans, light enters the eyes and signals the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), the brain’s master clock, to align to a 24-hour schedule. When our exposure to sunlight is disrupted, such as in night shift work or jet lag, it can desynchronize the SCN and disrupt healthy sleep-wake patterns. Morning sunlight is especially important for setting circadian rhythm. Studies show that bright light exposure in the morning improves sleep quality and duration at night (3).
Plants and animals also rely on sunlight cues to set their internal clocks. Photosynthetic cycles in plants follow natural daylight patterns. In animals, sunlight impacts feeding schedules, mating, hibernation, and migration behaviors. When circadian rhythms are misaligned in humans and other species, it can have detrimental health effects.
Solar Power
Solar power harnesses energy from the sun and converts it into electricity. It is considered a renewable energy source because the sun’s energy is virtually limitless and solar technologies produce no greenhouse gas emissions during operation (NationalGrid). There are two main technologies used to convert sunlight into electricity:
Photovoltaic (PV) panels consist of solar cells made from materials like silicon that convert sunlight directly into electricity. Arrays of PV panels are mounted together to provide power for homes, businesses, and utilities (Energy.gov).
Concentrated solar power (CSP) systems use mirrors to focus sunlight onto a receiver containing a heat-transfer fluid. The heated fluid is used to drive a turbine to generate electricity (Energy.gov). CSP allows for the sun’s energy to be stored so it can continue producing electricity even when the sun isn’t shining.
Solar power offers several advantages as a renewable energy source. It produces no air pollution, greenhouse gases, or radioactive waste. Solar technologies require little maintenance and have lifespan of 20-30 years. And the sun’s energy is free and available almost everywhere. The main limitations are solar’s intermittent nature and relatively high upfront costs of installation (Energy.gov). But prices continue to fall as technology improves.
Food Chains
Solar energy from the Sun supports entire food chains and ecosystems by providing the original source of energy that producers like plants and algae convert into food. Producers are able to harness the Sun’s energy through the process of photosynthesis to produce carbohydrates that support their growth and development. This stored chemical energy is then passed on to primary and secondary consumers when they eat plants or other organisms, supporting the next trophic levels in a food chain or web. Without the constant supply of solar energy from the Sun reaching Earth, food chains would collapse and ecosystems would drastically change. As the National Geographic explains, “Without sunlight, plants wouldn’t be able to undergo photosynthesis and there would be no energy captured from sunlight for the primary consumers who eat the plants.”
Evolution
One of the most important roles of solar energy for life on Earth is that it likely influenced the evolution of life, according to some evolutionary biologists. Many scientists have theorized that life evolved to utilize solar energy in the most efficient way possible. 1
The evolution of photosynthesis demonstrates this theory. Photosynthesis is the process that plants use to convert sunlight into usable chemical energy. Scientists believe ancient plants evolved to absorb the specific wavelengths of light emitted by the sun. This allowed plants to maximize energy production. The evolution of chlorophyll, the green photosynthetic pigment in most plants, is likely due to its ability to most efficiently absorb the blue and red wavelengths that are most plentiful in sunlight. 1
In a similar way, studies show that many animals have evolved to make the most of solar energy. Some desert animal species are light in color to stay cool by reflecting sunlight. Butterflies warm their flight muscles using concentrated solar energy. The evolution of the eye is also linked to utilizing solar energy. Overall, the theory suggests that many evolutionary adaptations allow organisms to capitalize on solar energy from the sun. 1
Conclusion
In conclusion, solar energy is critically important to sustaining life on Earth. Through photosynthesis, solar energy powers almost all lifeforms and food chains. The sun helps regulate Earth’s climate and weather patterns, providing the right conditions for life. Solar energy gives plants the light they need for growth and supplies animals and humans with vitamin D. Our circadian rhythms are tied to sunlight cycles that keep our biological clocks in sync. Solar power offers a renewable and sustainable energy source that could meet the world’s electricity needs. The sun has driven evolution for billions of years, shaping the planet’s ecosystems. Without the constant stream of solar energy, life as we know it simply could not exist on Earth.
As this overview has shown, the sun enables and sustains all forms of life. Solar energy is the ultimate renewable resource that has given rise to life on our planet. As we work to transition to clean energy and protect our environment, harnessing the power of the sun provides an essential path forward for humanity.