How Do We Get Energy From The Sun For Kids?
What is solar energy?
Solar energy is the energy from the sun that is captured and converted into electricity or heat. The sun is a powerful star that gives off tremendous amounts of energy in the form of radiation. This solar radiation can be harnessed and turned into useful forms of energy like electricity and heat using solar technologies like solar panels and solar water heaters.
Solar energy is considered a renewable energy source because the sun will continue shining for billions of years. Unlike fossil fuels like coal, oil and natural gas that come in limited supplies and take millions of years to form, we can’t run out of solar energy. The amount of solar radiation that reaches the Earth’s surface every hour is more than the entire world’s energy needs for a whole year!
Solar energy is also one of the cleanest energy sources since it doesn’t create any air or water pollution. Solar panels silently capture the abundant free energy from the sun and convert it into electricity without emitting greenhouse gases or other pollutants.
How does the sun produce energy?
The sun produces energy through a process called nuclear fusion that takes place in its extremely hot core. The sun’s core has temperatures of over 15 million degrees Celsius. At these extreme temperatures, hydrogen atoms move very fast and collide, fusing together to make helium. This nuclear fusion process releases enormous amounts of energy in the form of photons, which are particles of light. The photons generated in the core of the sun take about 100,000 years to slowly move outward until they reach the sun’s surface. The photons then stream out into space in all directions at the speed of light, bringing heat and light to the planets in our solar system.
So in summary, the sun produces energy through nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium at its insanely hot core. This fusion reaction gives off photons, which bring light and heat to Earth and make nearly all energy on our planet possible.
How do solar panels work?
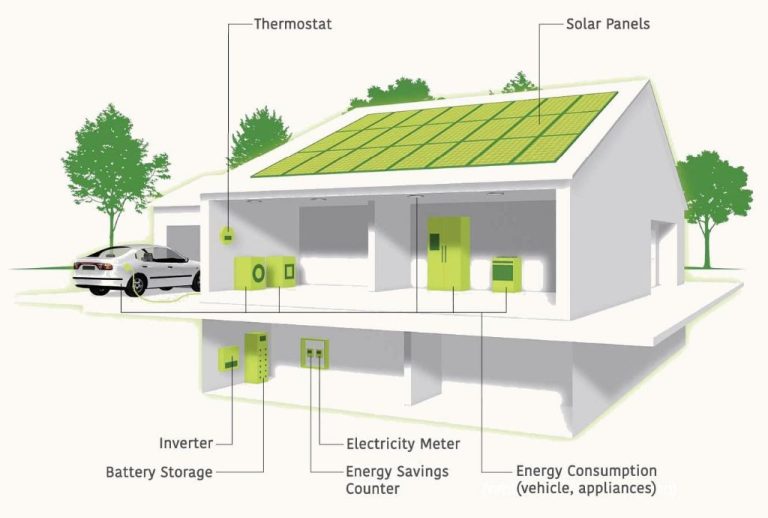
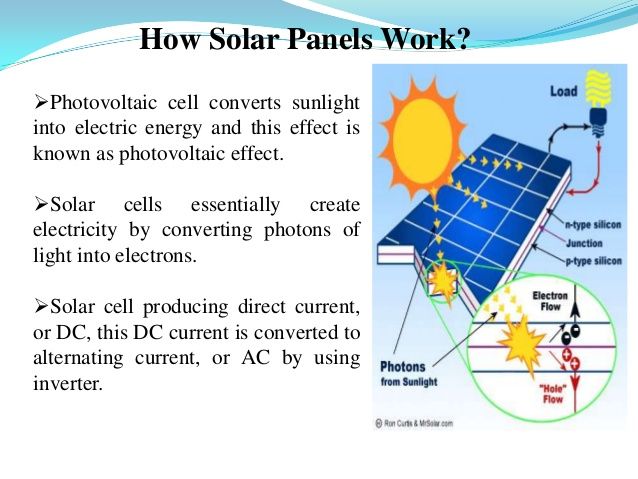
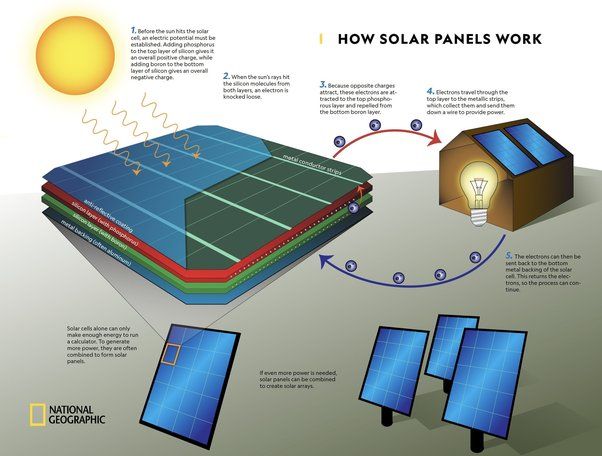
Solar panels contain special cells called photovoltaic cells that convert sunlight into electricity. When sunlight hits these cells, the photons (light particles) are absorbed by the cells’ semiconductor material, such as silicon. This causes electrons to be released from the atoms in the semiconductor. The flow of these electrons produces an electric current, which generates electricity.
The photovoltaic cells are wired together to form modules, which are mounted in arrays on solar panels. The current generated from the solar panels then flows through wires to the inverter, which converts the direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) that can be used to power homes and businesses.
Solar panels are made of photovoltaic cells, which consist of one or two layers of a semiconducting material, usually silicon. When sunlight shines on a solar cell, the energy from the photons of light knocks electrons loose from the atoms of the cell’s semiconductor material. The flow of these electrons generates an electric current that powers devices and lights.
Types of solar power systems

There are a few main types of solar power systems that are used to harness energy from the sun:
Photovoltaics (PV)
Photovoltaic solar panels, or PV panels, are the most common type of solar panels. They are made up of solar cells containing a photovoltaic material that converts sunlight directly into electricity. When sunlight hits the solar cells, electrons are knocked loose and flow into metal conductors to produce electricity.
Concentrated solar power (CSP)
Concentrated solar power systems use lenses or mirrors to focus sunlight onto a small area. The concentrated light is converted into heat, which drives a heat engine connected to an electrical power generator. CSP is generally used for large utility-scale solar power plants.
Passive solar heating and lighting
Passive solar systems take advantage of sunlight without using any mechanical or electrical devices. For example, windows oriented to the south allow sunlight to heat up a building during the day. Overhangs block direct summer sunlight but allow lower winter sunlight to enter. Skylights and light tubes pipe sunlight into building interiors to provide natural lighting.
Storing solar energy
Solar panels produce electricity when the sun is shining, but we also need power when it’s cloudy or dark. That’s why it’s important to store some of the energy collected during the daytime so it can be used at night. There are a few different ways to store solar energy.
Batteries
One way to store solar energy is in batteries. Solar batteries collect extra electricity from solar panels during the day and store it chemically so it can be used when the sun isn’t shining. Batteries for solar power systems are large and high-capacity to hold enough energy for use at night. Popular types of batteries used are lead-acid batteries and lithium-ion batteries.
Pumped hydro storage
Pumped hydro storage uses surplus electricity to pump water uphill to a reservoir. When power is needed, the stored water is released downhill to turn turbines and generate electricity again. This is an affordable way to store large amounts of energy.
Molten salt storage
Some solar power plants use mirrors to concentrate sunlight and heat molten salt. The hot molten salt stores thermal energy so it can used to make steam to drive a turbine and generator even when the sun isn’t shining.
Solar Energy Pros and Cons
Solar energy has some important advantages but also some limitations to consider.
On the pro side, solar power is a renewable resource, meaning it comes from the sun which will continue shining for billions of years. This makes solar an abundant energy source. Solar also does not create any air or water pollution, so it’s much cleaner for the environment than burning fossil fuels.
However, there are also some downsides. The biggest is that installing solar panels can be expensive upfront. Buying and installing a home solar system can cost $10,000-$30,000 depending on the size. Solar panels also produce energy intermittently, only when the sun is out. So solar may need to be combined with batteries or other energy sources for 24/7 power.
Overall, solar power has some clear advantages as a clean, renewable power source. But the high upfront costs mean it may not make sense for everyone. Understanding both the pros and cons helps when considering solar.
Fun facts about solar
Here are some interesting statistics and fun facts about solar energy for kids:
The sun produces enough energy in one second to power the world for 960,000 years! The sun is by far the largest source of energy that we have access to. Solar panels only need to capture a tiny fraction of the sun’s energy to produce enough electricity.
The word “solar” comes from the Latin word “solaris” which means sun. Many words related to the sun have their roots in Latin, including solar system, solar panel, and solar flare.
The first modern solar cell was created in 1883 by Charles Fritts. He coated selenium with a thin layer of gold to form the first semiconductor solar cell. Solar technology has improved greatly since then!
The world’s largest solar power plant is in China. The Tengger Desert Solar Park opened in 2018 and has 1.5 million solar panels! It can generate up to 1,500 megawatts of power.
Solar panels work even on cloudy days. Clouds block some sunlight, but solar panels can still produce 10-25% of their normal power output on overcast days. The sun’s rays are able to pass through clouds.
The space industry relies heavily on solar power. Satellites and spacecraft like the International Space Station use large solar arrays to harness energy. Solar works well in space because there are no clouds!
Solar energy experiments
Solar energy experiments are a fun way for kids to learn about how solar panels work. Here are some hands-on experiments kids can try at home or school:
Building a solar oven
Using a pizza box, aluminum foil, plastic wrap and black construction paper, kids can build their own solar oven. On a sunny day, a solar oven can reach temperatures up to 300°F and be used to cook food like s’mores or hot dogs. Just be sure not to leave a solar oven unattended.
Creating a solar phone charger
With a small solar panel, kids can build their own solar phone charger. A portable solar panel with a USB port can be connected to a phone’s charging cable and placed in direct sunlight to charge a phone’s battery. This demonstrates how solar panels convert sunlight into electricity.
Solar s’mores
Using a solar oven, kids can melt s’mores in the sunlight alone. By heating the graham crackers, chocolate and marshmallows in a solar oven, kids don’t need an alternate energy source like propane to enjoy this tasty summer treat!
Solar energy around the world
Many countries around the world are harnessing the power of the sun through solar energy. Some leaders in solar capacity include:
China – China has the largest installed solar capacity in the world, with over 250 gigawatts as of 2020. Some major solar projects in China include the Longyangxia Dam Solar Park, the largest solar farm in the world.
United States – The United States has over 100 gigawatts of installed solar capacity. The Solar Star project in California is one of the biggest in the country with a 579 megawatt capacity.
Japan – Japan is a global leader in solar power, with over 65 gigawatts of capacity. The country aims to source between 20-22% of its power from renewables including solar by 2030.
Germany – Germany gets over 8% of its electricity from solar, thanks to supportive policies and investments in technology. Major projects include Waldpolenz Solar Park, Germany’s largest.
Some cool, innovative solar projects around the world include:
– The Ivanpah Solar Electric Generating System in California, which is the world’s largest solar thermal power plant.
– The Noor Complex in Morocco, a massive concentrated solar power plant that provides electricity for over a million people.
– Floating solar farms in China, India and other countries that place solar panels on bodies of water.
– The first fully solar-powered airport in India, Cochin International Airport.
– Tesla’s solar roof tiles that convert sunlight into electricity for homes and businesses.
The future of solar
The future looks bright for solar energy! Engineers and scientists are constantly working to improve solar technology. Here are some exciting innovations in the works:
Improving efficiency and storage – New solar cell designs, materials, and manufacturing methods are making solar panels more efficient at converting sunlight into electricity. At the same time, battery storage technology keeps improving to store extra solar power for use at night or on cloudy days. With better efficiency and storage, solar will become an even more cost-effective energy source.
Projections for growth – Solar power is one of the fastest growing energy sources. Solar capacity has doubled in the past few years and is projected to continue this exponential growth. Some experts estimate that by 2050, solar could provide up to 30% of the world’s electricity as adoption increases.
New solar technologies – Researchers are developing solar technologies like transparent solar panels that can be used as windows, solar paint that can turn any surface into a power source, and solar grids that can provide whole neighborhoods with solar power. These innovations could make solar an accessible energy solution for even more people.
With all the progress on better solar technology, decreased costs, and wider implementation, the future is looking sunnier and brighter for solar power!