How Big Is The Recs Market?
Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs), also known as green certificates or green tags, are a market-based instrument that represent and provide proof of renewable energy generation. One REC is issued for each megawatt-hour (MWh) of electricity generated and delivered to the grid from a renewable energy resource such as solar, wind, geothermal or hydropower.
RECs were created to track renewable energy generation and enable the renewable attributes to be unbundled from the physical electricity. This allows the environmental benefits of renewable energy generation to be sold separately from the underlying electricity. RECs provide a mechanism for companies and individuals to offset their non-renewable electricity use with renewable energy from the grid. The overall purpose is to incentivize and spur development of new renewable energy projects.
This article examines the size and scope of the global market for renewable energy certificates. We will look at regional markets, pricing trends, major companies, and the future outlook and challenges for RECs. The goal is to provide a comprehensive overview of the scale and key dynamics in this rapidly growing eco-commerce market.
History of RECs
Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) first emerged in the late 1990s as a market-based mechanism to promote and track renewable energy generation. The concept was pioneered in the United States as a flexible way for companies to meet state-level renewable portfolio standards (RPS).
RECs allow renewable energy generation to be “unbundled” from the physical electrons produced. For each megawatt-hour (MWh) of renewable electricity generated, a unique REC is created that can be traded separately from the underlying energy. This allows organizations to support renewable energy development even if they are not located near renewable energy projects or connected to a renewable-powered grid.
Through the 2000s, voluntary corporate purchases of RECs expanded rapidly, enabling companies to reduce their carbon footprints and meet sustainability commitments. The growth of RPS programs in states and countries worldwide further increased REC trading volumes as a compliance mechanism. The global market size for RECs has grown exponentially over the past two decades.
Current Global RECs Market Size
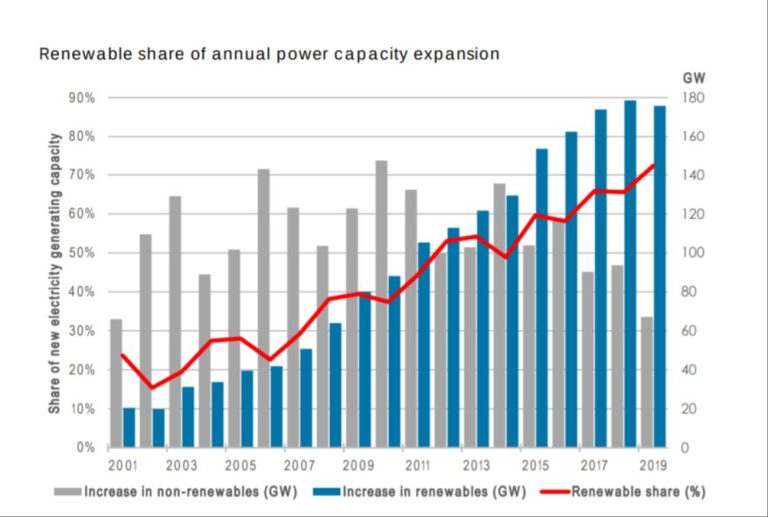
The global market for renewable energy certificates (RECs) has seen significant growth over the past decade, driven by rising demand for clean energy as well as government policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions. According to industry estimates, the total value of the global voluntary RECs market reached $315 million in 2020, more than double the market size of $136 million back in 2010.
In terms of RECs sold annually, the global market traded over 95 million MWh worth of voluntary RECs in 2020. This represents a nearly 50% increase compared to 2014, when approximately 65 million MWh of voluntary RECs were sold worldwide. The United States remains the dominant market for voluntary RECs, accounting for over 80% of global demand. However, emerging markets in Europe and Asia are also contributing to growth. Overall, the rapid expansion of the voluntary RECs market highlights the growing corporate and consumer appetite for renewable energy and carbon offsets around the world.
Regional REC Markets
The RECs market is expanding globally with regional markets emerging around the world. Some of the top regional markets for RECs include:
North America
North America has historically been the largest RECs market. In the United States, RECs are used for compliance with state-level Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS). As of 2022, 30 U.S. states had RPS policies requiring electric utilities to source a portion of their electricity from renewable sources. This creates a significant compliance market for RECs. Major REC suppliers in North America include Green-e, APX, and Brookfield Renewable.
Europe
The European Union has renewable energy targets that have stimulated growth in the RECs market, both for voluntary and compliance purposes. Guarantees of Origin (GOs) serve as the REC tracking system in Europe. The UK, Sweden, Norway, and Austria are major markets for voluntary GO purchases by corporations and individuals. The compliance market is also strong, particularly in Sweden, Italy, Poland, and Belgium.
Australia
Australia has a national Renewable Energy Target scheme which requires electricity retailers to source a percentage of power from renewable sources. This compliance market is the main driver of RECs activity in Australia. Some of the major REC traders in the country include Green Energy Trading, Greenbank Environmental, and Karbone.
Asia Pacific
Countries such as China, India, Japan, and South Korea are quickly growing their renewable energy capacity. REC markets are still emerging in the region but expected to expand significantly. Interest in voluntary REC purchasing is rising among multinational companies based in Asia Pacific. Compliance markets are also developing in South Korea, Japan, and parts of China and India.
Voluntary vs. Compliance RECs
Renewable energy certificates (RECs) are typically divided into two categories: voluntary RECs and compliance RECs. The key difference lies in their purpose.
Voluntary RECs are purchased by individuals, businesses, and organizations that want to offset their electricity use with renewable energy. By purchasing voluntary RECs that are additional to any compliance requirements, buyers are financially enabling the generation of renewable electricity.
Compliance RECs are used by energy suppliers and utilities to comply with renewable portfolio standards and other regulatory policies. These policies require that a certain percentage of electricity sold comes from renewable resources. Compliance RECs provide proof that renewable electricity generation has occurred.
In terms of market size, compliance RECs make up the bulk of the overall RECs market. Compliance needs are driving much of the demand and growth. Voluntary RECs represent a smaller but still significant segment. Many corporations are voluntarily buying RECs as part of their sustainability commitments.
The voluntary RECs market has grown substantially over the past decade, from less than 10 million MWh in 2009 to over 30 million MWh in 2019. However, it is still dwarfed in size by the compliance-driven RECs market. In 2019, over 200 million compliance RECs were retired in the U.S. alone.
Pricing Trends
REC prices have generally been on a downward trend in recent years due to increasing supplies from renewable energy projects coming online. However, there is significant volatility and seasonality in pricing.
Average REC prices have declined from around $15-20/MWh 5-10 years ago to $1-5/MWh today, depending on the region and type of REC. Compliance market RECs tend to trade at higher prices than voluntary market RECs.
There are several factors that drive fluctuations in REC pricing:
-
Rules and regulations – Changes in renewable portfolio standards or carbon policies impact demand and pricing. More ambitious standards drive prices up.
-
Supply and demand – More renewable energy projects coming online increases supply of RECs, pushing prices down. Changes in demand from utilities and corporations impacts prices.
-
Market dynamics – Speculation, lack of transparency, bottlenecks in trading systems, and lack of accurate price signals can distort REC market pricing.
-
Seasonality – REC prices tend to be higher in Q1 and Q2 when RPS compliance deadlines approach, and decline in Q3 and Q4.
These pricing dynamics make REC markets complex to analyze and predict. But overall the trend seems to point to continued declining prices barring major regulatory shifts.
Major Companies in RECs Market
The RECs market is dominated by several key players across the buyer, seller, and broker segments. On the buying side, major corporations with renewable energy commitments drive much of the voluntary demand. This includes tech giants like Google, Apple, and Amazon, who collectively purchased over 7 million RECs in 2021. Retail brands like Walmart, Starbucks, and Target are also top voluntary buyers.
Utilities are the primary compliance buyers, led by firms like Duke Energy, Southern Company, and Xcel Energy. In terms of sellers, major renewable energy developers like NextEra, Invenergy, and EDPR are instrumental in bringing new REC supply to the market. Top brokers and traders like Evolution Markets, APX, and Gatsby make up over 50% of market share for REC transactions and play a critical role connecting buyers and sellers.
The voluntary market is more fragmented with over 150 suppliers offering RECs. However, the top 10 sellers still account for over 60% of transactions. The compliance market is highly concentrated in states like Texas, Illinois, and North Carolina where one or two major utilities often control over 75% of REC purchases.
Future Outlook
The global RECs market is expected to experience steady growth over the next 5-10 years. Several factors point towards a larger, more robust RECs market in the future:
First, many countries have set ambitious renewable energy targets for 2030 and beyond. As governments aim to meet these goals, demand for RECs is likely to increase as a flexible compliance mechanism.
Second, the cost of renewable energy continues to decline, making green power more price competitive with conventional sources. This should spur increased voluntary demand for RECs among corporations, organizations and residential consumers.
Third, new technologies like blockchain and artificial intelligence can help modernize and streamline RECs trading platforms and processes. This has the potential to expand the RECs marketplace by improving accessibility and transparency.
However, the future of RECs will also depend on overcoming ongoing challenges. Continued policy support will be needed to maintain RECs as an attractive compliance tool. And in voluntary markets, consumer education and engagement remains critical for driving participation.
Challenges
The RECs market faces several key challenges that could hinder future growth if not properly addressed:
Declining prices – REC prices have been on a downward trend in recent years due to oversupply in markets like the United States. This reduces revenue potential and makes RECs a less attractive incentive for renewable energy developers.
Policy uncertainty – Changes or repeal of renewable energy policies like renewable portfolio standards creates uncertainty around long-term REC demand. This uncertainty discourages investment in renewable projects.
Fraud – A few cases of REC certificate fraud and double-counting have undermined credibility of REC tracking systems. Stronger verification and enforcement is needed.
Lack of uniformity – Each state or country has different rules and policies for RECs, making trading and tracking across regions complex. Movements toward national or international standards could improve liquidity.
Benefits vs. costs – As the share of renewable energy grows, the marginal benefits of additional REC-driven capacity declines. At some point the costs may begin to outweigh the benefits, requiring rethinking of REC incentive structures.
To address these challenges, policymakers could consider options like setting long-term REC price floors, implementing strong enforcement against fraud, streamlining cross-border REC trading rules, and exploring alternative incentive structures as conditions evolve.
Conclusion
In summary, renewable energy certificates play an important role in renewable energy growth globally. Although the market started small, RECs have expanded significantly, with billions of dollars now traded annually. Key REC markets like Europe, North America, and Australia continue to grow, while emerging markets offer new potential. Both voluntary and compliance REC markets provide incentives to develop more renewable energy projects.
While pricing fluctuates, the overall RECs market outlook remains positive, as more countries and companies set renewable energy targets. However, challenges remain around ensuring robust REC tracking systems, preventing double-counting, and maintaining integrity. The future growth of RECs relies on addressing these issues through regulation and best practices.
Overall, RECs offer a flexible mechanism to accelerate renewable energy deployment worldwide. Their role will likely expand as pressure grows to meet ambitious decarbonization goals. REC markets must continue innovating to enable the transition to a zero-carbon energy system.