Exploring The Potential Of Solar Energy: Benefits And Considerations
Solar energy has emerged as a promising renewable energy source that has the potential to reduce reliance on fossil fuels. This article explores the benefits and considerations of expanding solar energy. We will provide an overview of how solar energy works, discuss the main advantages solar offers such as cost savings and job growth, examine challenges facing the solar industry, review potential solutions, analyze the future outlook for solar, suggest ways individuals can support solar expansion, and provide a conclusion on the viability of solar energy.
Overview of Solar Energy
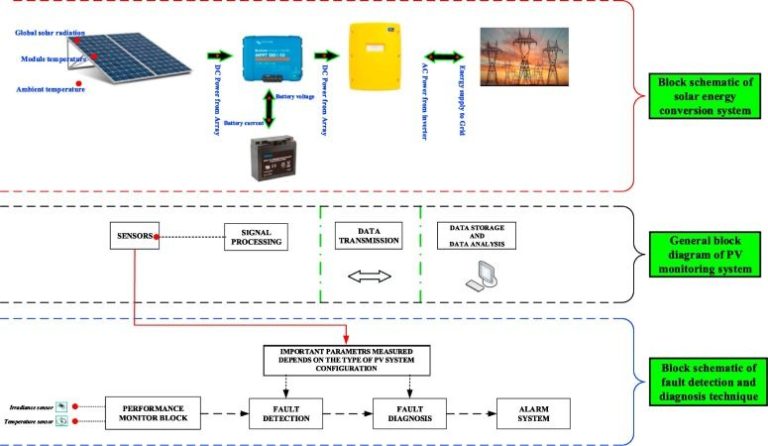
Solar energy refers to harnessing the sun’s rays to generate electricity or heat. It is a renewable source of energy that relies on the sun shining onto photovoltaic panels or solar thermal collectors to produce power.
The concept of utilizing the sun’s energy dates back over 2000 years to when ancient societies used sunlight to light fires. In 1839, French physicist Edmond Becquerel discovered the photovoltaic effect, whereby electricity can be generated from sunlight. The first photovoltaic module was built in 1954 at Bell Labs. Since then, solar technology has advanced considerably with photovoltaic panels becoming a mainstream method to produce renewable electricity around the world.
Solar energy works because photons from sunlight knock electrons free from atoms, creating electricity. Solar panels are made up of many solar cells containing photovoltaic materials, most commonly silicon. As sunlight hits the cells, the excited electrons generate a current. This electricity can then be used directly for heating or lighting or fed into batteries for later use. Solar thermal collectors concentrate sunlight to heat fluids which are used to provide hot water or turn generators.
Solar Energy Benefits
One of the main benefits of solar energy is that it is clean and renewable. Unlike fossil fuels such as coal and oil which produce harmful emissions, solar energy does not generate pollution or greenhouse gases. Relying more on solar energy can significantly reduce a region’s carbon footprint.
Solar is also a renewable energy source. It is virtually limitless, unlike fossil fuels which are finite. The sun continuously provides an enormous amount of energy in the form of sunlight and heat. We would never run out of solar power the way oil and gas reserves can be depleted.
Transitioning to more solar energy reduces dependence on fossil fuels. Rather than importing coal, oil, and natural gas, regions can become more energy independent by harnessing the power of the sun. This provides greater energy security and insulation against price shocks.
Increasing solar capacity also reduces overall emissions. With fewer fossil fuels being burned, there are lower levels of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide as well as other pollutants emitted. This creates cleaner air and a healthier environment.
Cost Savings from Solar Energy
One of the biggest benefits of solar energy for homeowners and businesses is the cost savings compared to traditional electricity. Installing solar panels allows users to generate their own electricity, reducing or even eliminating monthly electricity bills. The sun provides free renewable energy, so once the solar panel system is installed, the main costs are just maintenance and repairs over the 20-30 year lifetime of the system.
After the initial investment, which can often be offset by rebates and tax credits, solar energy requires very minimal maintenance costs. Solar panels have no moving parts and are designed to withstand extreme weather. Overall maintenance costs are estimated to be around $100-$150 per year for a typical residential solar system. This covers things like cleaning the panels, checking connections, and monitoring performance. By comparison, maintenance costs for utility-scale solar farms are around $20-$30 per kilowatt of capacity per year.
With solar energy eliminating or greatly reducing electricity bills over decades of operation, the lifetime savings from solar can be substantial for households and businesses. Solar helps lock in low energy prices over the long-term, providing stability and reducing exposure to potentially rising electricity rates from utilities.
Job Creation
Renewable energy, especially solar power, employs more people per unit of electricity generated compared to fossil fuels like coal, oil or gas. Unlike fossil fuels, solar energy requires a large workforce for manufacturing, installation, and maintenance. Building out solar capacity creates 3-4 times more jobs per dollar invested than fossil fuel power plants.
Utility scale and residential solar projects drive economic growth and jobs in local communities. Solar energy creates jobs across diverse industries like construction, engineering, manufacturing, sales, and administration. Siting solar farms and plants in rural areas boosts economic activity and incomes in struggling communities. Home solar adds jobs to local roofer and electrician workforces. Solar projects require ongoing operations and maintenance, providing stable long-term employment.
A study by the Solar Foundation found that jobs in the solar industry grew 167% from 2010 to 2019 across the U.S., ten times faster than overall job growth. Another report estimated that between 2012 – 2019, the solar industry created 93,000 jobs, adding $11.8 billion to the U.S. economy. States with solar-friendly policies see the most solar job growth. As solar continues to expand into new markets, it will spur further local job creation and promote community revitalization.
Solar Energy Challenges
While solar energy offers many benefits, there are some challenges that need to be addressed for it to reach its full potential.
One major challenge is the high upfront cost of installing solar panels and related infrastructure. Solar panels, inverters, batteries, wiring and labor can cost tens of thousands of dollars for a residential system and millions of dollars for a large commercial or utility-scale system. This poses a financial barrier for many homeowners, businesses and utilities that would like to adopt solar power.
Another challenge is that solar energy availability depends on having sufficient sunlight. Solar panels do not work well on cloudy or stormy days, at night, or in areas that receive fewer hours of direct sunlight each day. This limits solar energy more in some regions than others.
Solar power also requires a lot of land area for solar farms to produce energy at scale. Empty land near transmission infrastructure is not always readily available, and land costs can also add to the expense of developing utility-scale solar.Rooftop solar on homes overcomes this challenge for distributed generation, but not when centralized solar generation is needed.
Solutions to Challenges
Advancements in solar technology and government incentives are helping address the challenges facing wider solar adoption. Companies are developing new materials and manufacturing processes to lower the costs of solar panels, while increasing their efficiency. This is making solar power more cost competitive with fossil fuels.
Governments around the world are also implementing supportive policies and incentives. Tax credits, rebates, andother financial incentives are making it more affordable for homes and businesses to install solar systems. Many governments have implemented renewable energy standards that require a certain percentage of electricity to come from solar and other renewables.
Regulatory changes are also speeding up the permitting and installation process for solar projects. Overall, these types of government incentives, along with innovative technologies, are key to overcoming past barriers and accelerating the solar energy transition.
Future Outlook for Solar
The future looks bright for solar energy. Experts predict strong growth in solar capacity and generation over the next decade.
Global solar capacity is expected to more than double between 2022 and 2027, reaching over 1,300 gigawatts. In the United States, solar capacity could triple in the next 10 years.
Driving this growth is the continuing cost declines for solar panels, making solar power more affordable and competitive. Emerging solar technologies like perovskite solar cells and solar windows also have potential to further reduce costs.

Favorable government policies will support solar expansion. Many countries have targets to significantly increase renewable energy. In the U.S., the Inflation Reduction Act extends tax credits for solar projects.
With such robust growth forecasts, solar is positioned to become a major electricity source worldwide. Solar farms will likely become commonplace. Homes and businesses with solar panels will contribute power to the grid. Exciting innovations will unlock new applications.
The future is bright for solar power. With costs falling and supportive policies, solar energy has tremendous potential for continued expansion andmass adoption. The growth outlook is bullish.
Ways to Support Solar
There are several ways individuals and businesses can support the adoption of solar energy. The most direct way is to install solar panels on your home or business. The upfront cost can be high, but solar panels can pay for themselves in energy savings over time. There are also leasing and financing options to help spread out the cost. Once panels are installed, make sure they are properly maintained.
You can also invest in solar by putting money into solar companies, funds, or crowdfunding projects. This provides capital for solar expansion. Investing allows you to support the industry financially without installing panels yourself.
Additionally, you can advocate for policies that enable solar adoption. This includes supporting renewable energy tax credits, net metering laws, streamlined solar permitting, and programs that allow shared community solar. Contacting local, state, and national representatives is an important way to voice your support for solar-friendly policies.
With growing public support, the right investments, and smart policies, solar energy can continue expanding and providing clean, renewable power around the world.
Conclusion
In summary, solar energy shows immense promise as a renewable, clean energy source but still faces challenges around upfront costs and integration with existing infrastructure. The benefits are clear – solar can reduce electricity bills, create jobs, improve public health through reduced pollution, and help fight climate change. However, costs remain high compared to fossil fuels, and solar intermittency requires storage solutions and grid upgrades.
Despite these hurdles, solar capacity and efficiency continues to grow rapidly. With the right policies, incentives, R&D funding, and public engagement, solar energy can play a major role in building a sustainable energy future. But continued effort is needed. Individuals can help by installing solar at home, pressuring representatives to enact solar-friendly policies, and supporting organizations accelerating the transition. The potential is clear – with dedication and innovation, solar energy can brighten our future.