Do Solar Powered Generators Really Work?

Introduction
Solar generators are portable systems that use solar panels to convert sunlight into electricity that can then be stored in batteries for later use. They are designed to provide backup power for off-grid use cases such as camping, power outages, or locations without access to the electrical grid. Solar generators allow users to harness the power of the sun to generate their own electricity for a variety of modern devices and appliances.
Unlike a traditional gasoline generator, a solar generator relies on renewable solar energy rather than fossil fuels. This makes them an eco-friendly and sustainable option for generating electricity. Solar generators vary greatly in size and power output capabilities, from small portable models that can charge smartphones and laptops to large systems that can power an entire home.
How Solar Generators Work
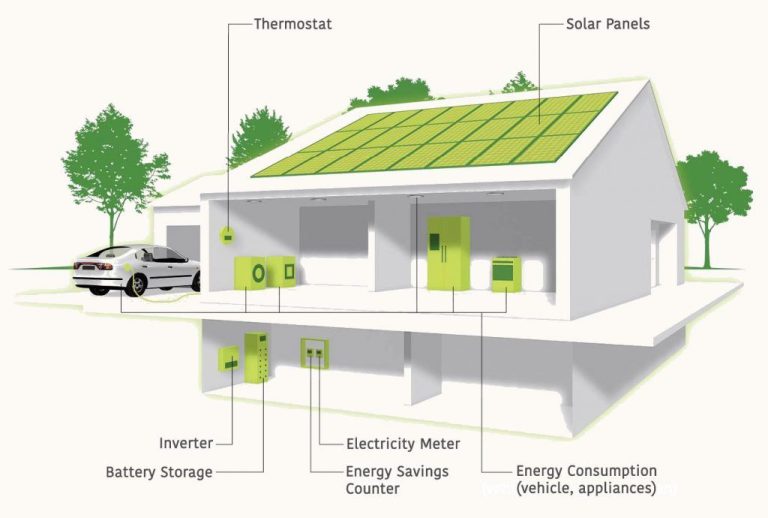
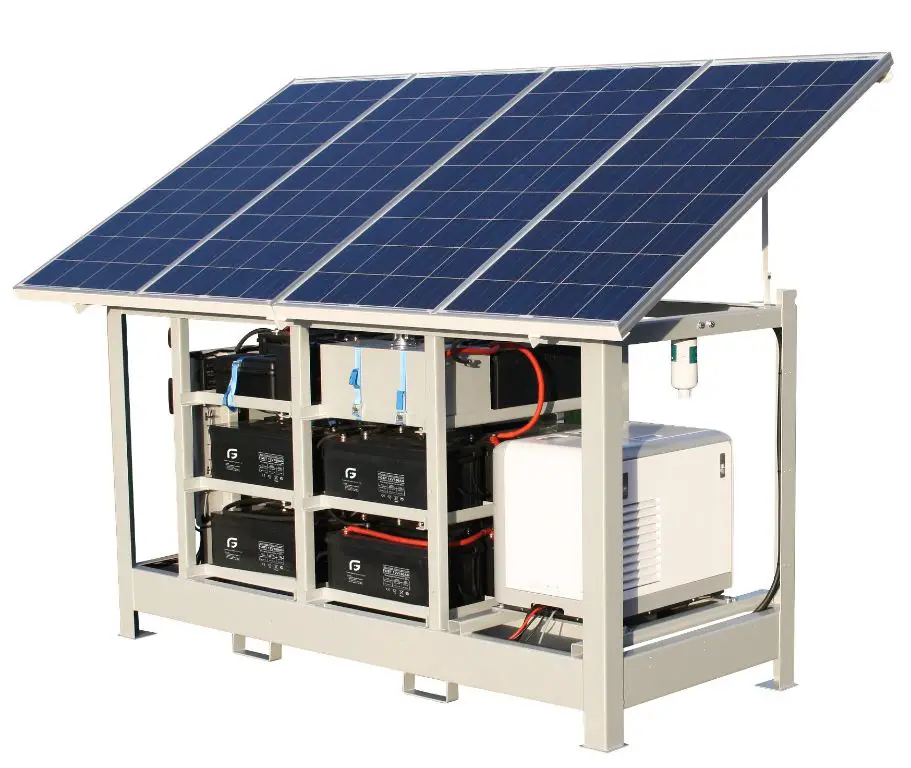
Solar generators are made up of four main components that work together to capture, store, and deliver solar energy for powering devices and appliances:1
- Solar panels – These capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. The more solar panels connected, the more power can be generated.
- Charge controller – This regulates the voltage and current coming from the solar panels going into the batteries. It prevents overcharging and damage to the batteries.
- Battery bank – Deep cycle batteries store the energy from the solar panels for use when needed. More and larger batteries provide increased storage capacity.
- Inverter – An inverter converts the DC electricity from the batteries into alternating current (AC) that powers appliances, tools, and devices.
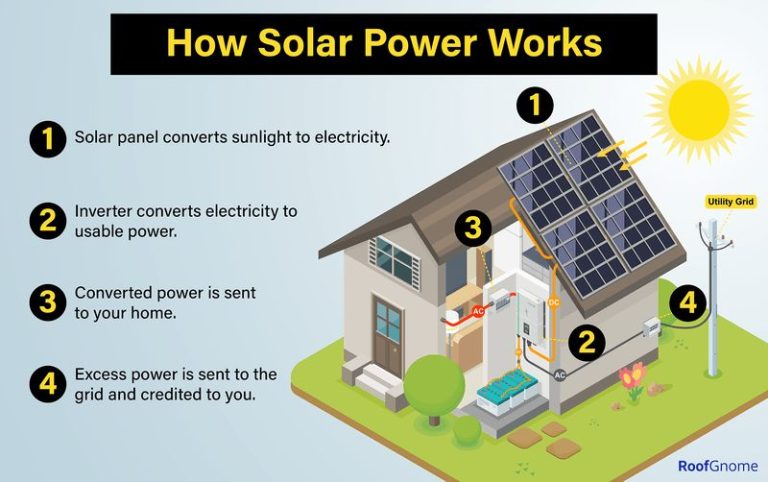
The solar panels charge the batteries during daylight hours. The stored energy in the batteries can then be accessed as needed by plugging devices into the AC outlets on the power station unit. This allows solar energy to be used even when the sun isn’t shining.2
Power Output Capabilities
The power output rating of a solar generator indicates how much wattage it can supply to run appliances and devices. This is an important specification to consider when choosing a solar generator.
Small solar generators usually range from 300-1000 watts. They are best for powering smaller electronics like phones, laptops, and lights. For example, the Anker 521 PowerHouse 200 can supply 200 watts continuously and 400 watts at peak (1).
Medium solar generators from 1000-2000 watts can handle larger appliances like mini-fridges, CPAP machines, and portable AC units for short periods. The EcoFlow DELTA 1300, for instance, has a 1200W rated power and can surge to 1800W (2).
Large solar generators above 2000 watts are suitable for high-draw appliances like full-size refrigerators, electric stoves, and RV air conditioners. The EcoFlow DELTA Max has 2016W rated power and can surge to 3600W (3).
When selecting a solar generator, it’s important to add up the surge wattage of the devices you plan to power and choose a generator with at least that much output capacity.
Advantages of Solar Generators
Some of the main advantages of using solar generators are that they provide clean, renewable power from the sun, reduce reliance on the electrical grid, and offer portable, modular setups. Solar generators convert sunlight into electricity through built-in solar panels. This makes them a sustainable green energy source, producing no emissions or pollution (Source). Unlike fuel generators, solar generators don’t require ongoing purchases of gasoline or propane.
Solar generators can operate independently of the electrical grid. This makes them ideal for emergency power, camping, off-grid living, and other applications where grid electricity is inaccessible. Their portable, compact designs with multiple charging options provide flexible power generation you can take anywhere. Modular solar generators allow users to connect additional solar panels for increased energy production (Source). With sufficient solar input, they can match or even surpass the capabilities of gas generators without noise, fumes or environmental impact.
Limitations of Solar Generators
While solar generators offer many benefits, they do come with some limitations that should be considered before purchasing.
The biggest limitation is that solar generators are dependent on sunlight to recharge (1). Unlike gas generators, solar generators will not work at night or on very cloudy, stormy days when sunlight is minimal. This makes solar generators less reliable for emergency backup power unless paired with battery storage capacity to get through extended periods of overcast weather.
Solar generators also have a high upfront cost compared to gas generators (2). The batteries, solar panels, charge controllers and inverters required contribute to a steep initial investment that can range from $500 up to $5000 depending on power output and capacity.
In addition, the battery capacity in solar generators is limited compared to fuel tanks for gas generators (3). The batteries may only supply power for a few hours up to a couple days, depending on the solar generator’s wattage and battery size. This makes sizing the solar generator appropriately for your expected power needs very important.
While solar generators have limitations, they can still provide renewable, silent and emissions-free power generation when sized and installed correctly for the given application.
Sizing a Solar Generator
When sizing a solar generator for your home, the two key factors to consider are your household’s power needs and allowing for peak loads and days without sun. To calculate your power needs, you’ll need to tally the wattage requirements of essential appliances you want to run during an outage, such as lights, the refrigerator, phone and laptop chargers, a small TV, and possibly a small window AC unit. As a rule of thumb, an average American household needs around 2000-5000 watts (2-5 kW) of solar generator capacity.
However, it’s important to not just look at average power needs, but also plan for peak usage times. Devices like air conditioners and electric heaters can spike up power demand substantially, so your solar generator needs extra capacity to handle loads of 5000+ watts. Planning for days with cloud cover is also crucial – most solar experts recommend at least 3-5 days of power storage capacity for outages. Taking all these factors into account, a robust home solar generator system would be in the 10,000+ watt range.
Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation and ongoing maintenance are key to getting the most out of a solar generator system. When positioning the solar panels, it’s important to mount them facing true south if in the northern hemisphere or true north if in the southern hemisphere. The solar panels should be tilted at an angle equal to your latitude to optimize sun exposure throughout the year. Avoid shading from trees, buildings or other obstructions.
Batteries should be stored indoors or in a weatherproof enclosure, away from extreme temperatures. Keep the batteries fully charged when not in use to prevent sulfation. Periodically clean the solar panels with a soft brush and mild detergent to remove any dirt or debris that could impede performance. Inspect wiring connections, fuses and controllers periodically for corrosion or damage. Check that none of the system components are drawing excess current when not in use. Refer to the manufacturer’s maintenance guidelines for additional tips to keep your solar generator operating efficiently for years to come.
Some essential regular maintenance tasks include:
– Cleaning dust and dirt from solar panels (Source)
– Checking battery voltage and refilling battery fluid as needed (Source)
– Inspecting wiring and connections for damage
– Testing inverter, charge controller, and monitoring system operation
– Checking for error codes or fault indicators
– Replacing filters and fans as specified
Case Studies
Solar generators have a wide range of applications for household, RV, and emergency preparedness uses. Here are some real-world examples:
Whole House Solar Generator: One homeowner installed a large-scale solar generator system to meet 100% of their home’s electricity needs. This completely off-grid system uses solar panels, batteries, and a power inverter to power their entire house (Source).
RV Solar Generator: Many RV owners add portable solar generators to their vehicles to provide off-grid power while camping or traveling. These compact units can recharge from solar panels during the day to power lights, appliances, and devices overnight (Source).
Emergency Preparedness: Solar generators can provide backup electricity during power outages from storms or grid failures. They allow users to charge phones, run medical devices, refrigerate food and medications, and power other essentials.
Cost Considerations
The upfront cost of a solar generator can range quite a bit, with lower-capacity models starting around $100 and larger-capacity models going up to several thousand dollars. According to one source, the average cost of a solar generator is around $2,000 (1). This is considerably more expensive than a comparable gas generator, which averages around $1,000 (2). However, solar generators can pay for themselves over time by reducing or even eliminating electricity bills.
When evaluating the costs of a solar generator system, it’s important to consider the total system cost including not just the generator unit but also solar panels and any other accessories or installation expenses. On a lifecycle cost basis though, solar generators can save money compared to grid electricity. One analysis found solar generator systems can have payback periods of 4-6 years, yielding many subsequent years of free power (1). For off-grid applications without access to utility power, the value proposition of solar generators is even stronger given the lack of alternatives beyond gas generators or small solar panel setups.
Overall, while solar generators require greater upfront investment, their ability to produce free renewable electricity over decades of use makes them a worthwhile investment for many homeowners, businesses, and remote installations. Wise consumers should crunch the numbers for their particular situation.
Conclusions
In summary, solar generators can provide clean, quiet, and renewable energy for off-grid uses like RVs, camping, and emergency backup power. Their power output capabilities usually range from 500 watts to 3000 watts, which is enough to power most smaller appliances and electronics. Key advantages are portability, zero fuel costs, and zero emissions. However, solar generators have limitations in terms of powering larger home appliances, reliance on sufficient sunlight, and higher upfront costs compared to gas generators.
The ideal uses for solar generators are for powering devices like phones, laptops, lights, small kitchen appliances, and TVs when you’re off-grid or experiencing a power outage. For uses that demand consistent high power like running central air conditioning, electric ovens, or power tools, solar generators may not be able to meet those energy demands alone. Having realistic expectations about a solar generator’s capabilities for your particular needs is important.
Overall, solar generators can be a worthwhile investment for portable renewable energy depending on your budget and intended application. They are mature products with many benefits, but also limitations to be aware of. For portable off-grid power needs under 3000 watts, solar generators present an eco-friendly and quiet alternative to traditional gas generators.