Does Solar Energy Have A Good Future?

Solar energy has tremendous potential as a renewable, clean source of electricity. With concerns about climate change and rising energy costs, solar power offers a promising solution. This article examines the future prospects for solar energy due to key trends like improving technology, declining costs, and growing adoption.
Thesis statement: Solar energy has a bright future due to improving technology, declining costs, and growing adoption. While there are still challenges, the overall trends point to solar becoming a major energy source worldwide within the next few decades.
Brief History of Solar Power
The first solar cell was invented in 1883 by Charles Fritts, who coated selenium with a thin layer of gold to form the junctions and convert sunlight into electricity at less than 1% efficiency (Source: https://ae-solar.com/history-of-solar-module/). However, solar technology did not see widespread commercial use until the invention of the silicon solar cell by Russell Ohl in 1939, which led to more efficient solar panels (Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solar_panel).
The modern solar panel was created in 1954 when researchers at Bell Laboratories accidentally discovered that silicon doped with certain impurities was very sensitive to light. This led to the production of the first practical photovoltaic cells with 6% efficiency (Source: https://www.smithsonianmag.com/sponsored/brief-history-solar-panels-180972006/). Through the space programs in the 1960s, photovoltaics gained recognition as a power source for satellites and other space vehicles.
However, it wasn’t until the energy crisis in the 1970s that people began widely adopting solar for terrestrial uses. The first commercially available photovoltaic modules came on the market in 1972. With government subsidies, solar panels were installed in everything from private residences to lighthouses off the New England coast.
Current State of Solar Technology
There are two main types of solar technology that are used to convert sunlight into electricity – photovoltaic (PV) panels and concentrated solar power (CSP).
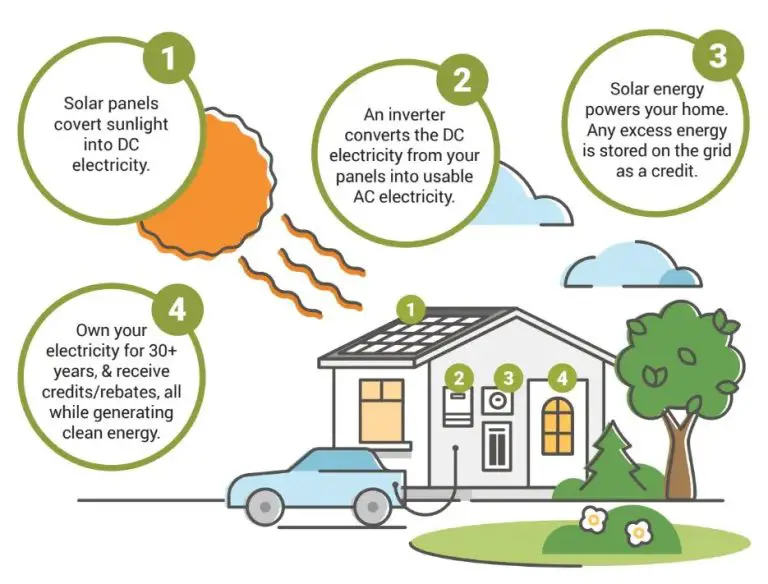
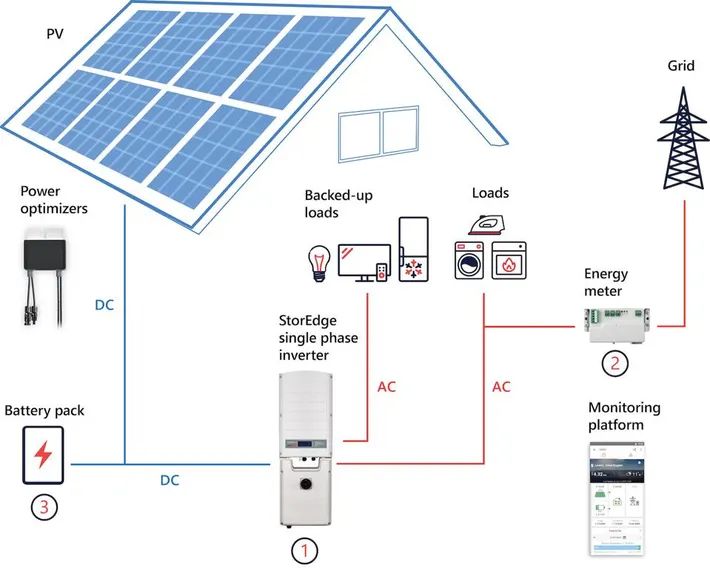
PV panels, also known as solar panels, are made up of solar cells containing photovoltaic material, most commonly silicon. When sunlight hits the panels, photons excite electrons in the solar cells, causing electricity to flow. This electricity is known as direct current (DC) power and must be converted into alternating current (AC) power using inverters before it can be used (1).
CSP systems use mirrors to concentrate sunlight onto a receiver containing a heat transfer fluid. The high temperatures generated turn a turbine to produce electricity. There are different types of CSP technologies like parabolic troughs, solar towers, and solar dishes (2).
PV panels are the most common solar technology today, accounting for over 90% of global solar photovoltaic capacity. Their modular nature allows them to be installed on rooftops of homes and businesses or ground-mounted over large areas. PV system components like modules and inverters have also improved in performance and declined in costs over the years (2).
Sources:
(1) https://www.energy.gov/eere/solar/how-does-solar-work
(2) https://www.energy.gov/eere/solar/solar-photovoltaic-technology-basics
Declining Costs
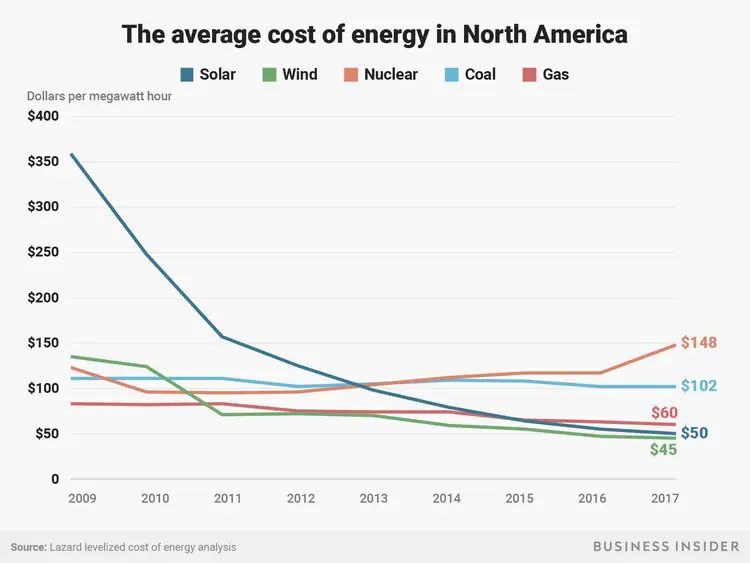
The cost of solar panels and installation has been steadily declining over the past decade. According to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), the average price of solar panels dropped by 70% between 2009 to 2019. Documenting a Decade of Cost Declines for PV Systems. This downward trend is expected to continue as technology improves and economies of scale further reduce manufacturing and installation costs.
The declining prices make solar energy more financially viable for homeowners and businesses. Many experts predict the cost of solar will drop an additional 40% by 2035. This gives solar power the potential to compete straight-up with fossil fuels across many markets in the coming years. As prices drop, solar adoption rates continue to climb year after year.
Solar Adoption Trends
Solar power adoption has been growing rapidly worldwide over the past decade. According to the Pew Research Center, the share of homeowners in the U.S. with rooftop solar panels increased from 4% in 2016 to 11% in 2022 (1). In terms of global markets, China continues to lead in total solar installations, followed by the United States and India. Europe has also seen substantial growth, with Germany and Italy among the top markets.
Residential solar adoption varies significantly by country. In the UK, around 4% of homes have rooftop solar panels, while in Australia over 20% of households generate solar power (2). Factors driving adoption include declining costs, supportive government policies, and increased environmental awareness. With continued advancements in solar technology and battery storage, the solar industry is projected to experience strong growth worldwide in the coming decades.
Government Support
The government provides significant incentives and support for solar power at both the federal and state levels. This includes tax credits, cash rebates, solar renewable energy certificates (SRECs), and supportive policies and regulations.
At the federal level, homeowners can claim a 26% tax credit in 2023 for installing a residential solar system, dropping to 22% in 2024 and beyond. There is no cap on the credit amount. Businesses can claim a 10% credit with no maximum. Homeowner’s Guide to the Federal Tax Credit for Solar.
Many states offer additional tax credits and cash rebates beyond the federal incentives. For example, New York offers a 25% tax credit up to $5,000. Massachusetts provides a base incentive of up to $1.20/Watt. Some utilities also give cash rebates for solar installations. SRECs can provide additional income from selling excess solar power back to the grid. Federal Solar Tax Credit Guide For 2024.
Supportive policies like renewable portfolio standards, net metering, and streamlined permitting have also boosted solar adoption. The federal Solar Investment Tax Credit has been a major driver of growth since it was enacted in 2006.
Environmental Benefits of Solar Energy
One of the biggest benefits of solar energy is its minimal impact on the environment. Unlike fossil fuels like coal and natural gas, solar energy production does not generate air pollution or greenhouse gases. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, generating electricity from solar power instead of fossil fuels can reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 80% per kilowatt hour. Solar energy technologies help mitigate climate change by displacing electricity generation from fossil fuel sources.
In addition, solar energy does not create pollution like sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, mercury, and particulates that damage the air and environment with fossil fuel energy production. The EnergySage notes that if we generated just 20% of U.S. electricity from solar energy instead of fossil fuels, we could prevent over 450 million metric tons of carbon dioxide emissions per year. Solar power is a clean energy source that is critical for reducing greenhouse gases and slowing climate change. With environmental benefits like minimal emissions and air pollution, solar energy can have a profoundly positive impact.
Challenges Facing Solar
While solar power offers many benefits, it also faces some key challenges that need to be addressed for it to reach its full potential. Three major challenges facing solar power are intermittency, storage, and grid integration.
Intermittency refers to the fact that solar energy is only produced when the sun is shining. At night or on cloudy days, solar panel output drops significantly. This intermittency makes it difficult to rely solely on solar power around the clock. Solutions like energy storage and interconnecting solar with other energy sources can help address intermittency.
Energy storage is still expensive compared to other energy sources. Storing surplus solar energy for use when the sun isn’t shining remains costly. Battery storage technology is improving but has yet to reach price parity with fossil fuels in most cases. Reducing storage costs through research and development will help make solar power more viable.
Integrating a large amount of solar power into the existing electric grid also poses challenges. The grid was designed for centralized power plants, not distributed rooftop solar arrays. Upgrading the grid with smart inverters, demand response technology, and energy storage will facilitate grid integration of solar power.
Despite these challenges, many experts argue they can be addressed through technological improvements, supportive policies, and market solutions. With the right strategies, solar power can play an expanding role in the global renewable energy mix.
Future Advancements
There are ongoing efforts to improve the efficiency and lower the costs of both existing and new solar technologies (https://energy.mit.edu/research/future-solar-energy/). For existing commercial photovoltaic solar panels, researchers are working on improving the efficiency of energy conversion by using new materials and novel cell designs.
Emerging solar technologies that show promise for potential future commercialization include perovskite solar cells, organic photovoltaics, quantum dot photovoltaics, and concentrator photovoltaics. Perovskite solar cells in particular have seen rapid increases in efficiency over the past decade and may be poised to challenge silicon-based solar panels in the future (https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-023-03714-y).
There are also early stage research efforts into more revolutionary and speculative technologies like solar paints, solar windows, orbital solar arrays, and artificial photosynthesis that aim to make solar energy ubiquitous across society and infrastructure.
Overall, solar technology has a bright future as efficiency improvements, cost declines, and new innovations continue to enhance solar photovoltaics’ competitiveness over other energy sources.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the outlook for solar energy is overwhelmingly positive. While solar currently accounts for only a small fraction of global energy production, we’ve seen remarkable growth in solar adoption over the past decade. Costs continue to fall dramatically, and solar technology is rapidly advancing and improving. With supportive government policies and increased investment, solar appears poised to become a major pillar of the global energy mix. The environmental and sustainability benefits of solar give it a unique edge over fossil fuels. Although some challenges remain, such as grid integration and storage, the overall trajectory suggests solar power will play an increasingly prominent role in the future as we transition to clean and renewable sources of energy.