Will Solar Panels Work If Power Goes Out?
Power outages have been on the rise in recent years. According to a 2022 survey, 84% of Americans are concerned about growing power outages, with the frequency increasing from 1.2 to 1.42 events per customer annually (source). At the same time, 39% of Americans falsely believe that home solar panels will still provide power during an outage without a battery backup system (source). This article explores whether solar panels actually work when the power goes out.
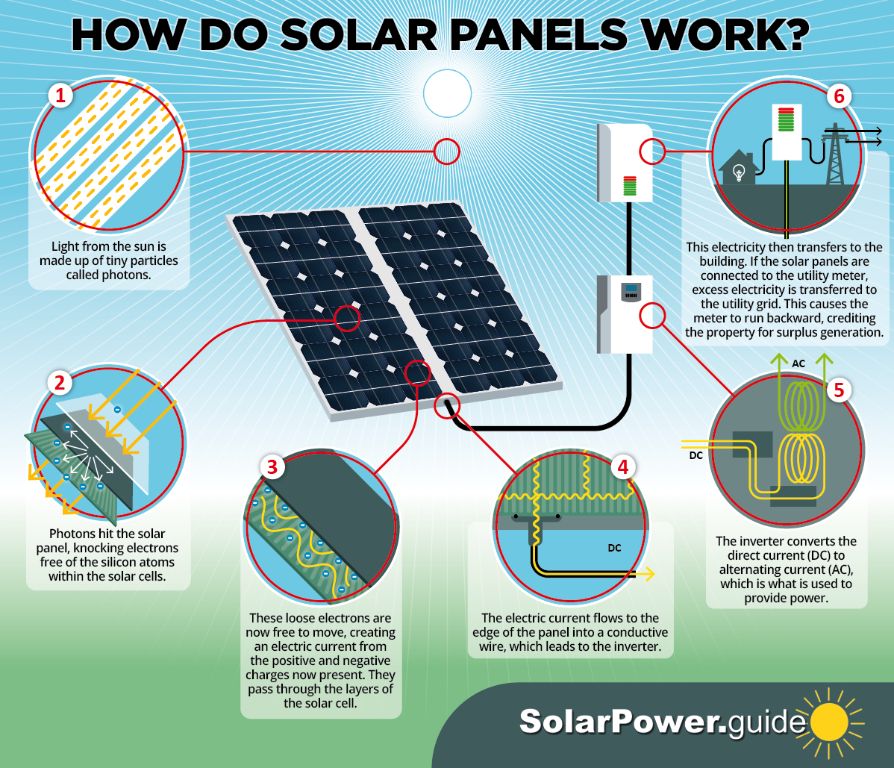
How Solar Panels Work
Solar panels work by converting sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. At an atomic level, solar cells consist of layers of semiconductor material, typically silicon. When sunlight hits the solar panel, the photons from the sunlight excite the electrons in the semiconductor atoms, causing the electrons to break free from their atomic bonds. This process generates an electric current as the freed electrons move through the solar cell. The current is then routed to allow connection to wires and electrical devices (Live Science, 2022).
The photovoltaic effect causes electrons to be knocked loose, allowing electricity to flow when sunlight hits the solar panel. Wires route the current generated by the flow of electrons when they are set free by sunlight photons. This simple process allows solar panels to convert sunlight into usable electricity.
Grid-tied vs Off-grid Solar
The key difference between grid-tied and off-grid solar systems is whether the system is connected to the utility grid or not. Grid-tied solar systems are connected to the existing electrical grid, while off-grid systems operate independently of the grid (Unboundsolar.com, 2022).
Grid-tied systems feed excess solar energy back to the grid, which credits the homeowner’s account. Any additional energy needs are pulled from the grid at night or on cloudy days. This allows grid-tied systems to be smaller and less expensive than off-grid systems because they don’t need large batteries for energy storage (Chintglobal.com, 2022).
Off-grid systems operate independently through solar panels, batteries, and sometimes a backup generator. All power is generated and stored on-site. Off-grid systems require larger solar arrays and battery banks to meet energy needs around the clock. They are popular in remote areas without utility access.
The choice between grid-tied and off-grid depends on factors like utility access, energy goals, and budget. Grid-tied is simpler and more affordable, but off-grid provides independence and backup power.
Solar During Power Outages
During a power outage, most grid-tied solar systems will automatically shut down. This is due to a safety mechanism called “islanding prevention” that is built into grid-tied inverters (the devices that convert the solar panel’s DC power into AC power). Islanding prevention causes the solar system to shut down when it senses the grid is down, to prevent the solar panels from continuing to energize the grid lines during an outage. This is done to protect utility line workers who may be working on those lines and could get electrocuted if the grid is still energized by rooftop solar panels.
So in most cases, grid-tied solar systems will not work at all during an outage. Even though the solar panels may still be producing electricity, that power has nowhere to go since the grid is down. Any excess solar electricity that was being fed back to the grid also stops. The home simply goes dark like any other around it during an outage, even though sunlight is still hitting the solar panels.
References:
How to Use Solar Panels During a Power Outage
Do solar panels work during a power outage?
Adding a Battery Backup
One way to ensure solar panels continue functioning during a power outage is by adding a battery backup system. Battery backups store excess electricity generated by the solar panels and allow the system to operate independently of the grid during an outage (Altestore, Florida Solar Design Group). There are several options for battery backups to pair with solar panels, like lithium-ion batteries or lead-acid batteries. The batteries connect to the solar system and store electricity for later use. During an outage, the battery kicks in automatically to power the home.
Adding battery backup does increase upfront system costs. However, for homeowners who experience frequent outages or want maximum energy resilience, it can provide peace of mind. Battery costs are also dropping steadily, making them more affordable (Solar Independent Power Systems). With smart inverters and proper configuration, a battery-backed solar system can provide vital electricity even when the grid goes down.
Islanding Prevention
Islanding refers to a situation where a solar power system continues to energize a section of the power grid even when there is an outage or disruption on the wider grid. This usually occurs when the solar panels and inverter continue generating and providing power locally, isolated from the rest of the grid. Islanding can be dangerous as it leads to the risk of backfeeding electricity to grid workers trying to fix the issue. It also creates issues when the grid comes back online and grids are trying to sync back up.
To prevent islanding, grid-tied solar systems have anti-islanding mechanisms built into the inverters. These work by constantly monitoring the grid and can automatically shut the system down when irregularities or outages are detected, disconnecting the local solar power system from the grid. This way the solar system cannot operate in island mode and energize small sections of the grid independently.
According to Windurance, anti-islanding mechanisms involve the inverter monitoring grid voltage, frequency, impedance and other parameters. When the inverter detects anomalies or that parameters are outside normal ranges, indicating a grid outage, it will shut itself down within seconds to prevent islanding.
Safety Considerations
When the power goes out, there are important safety issues to consider with solar panels. The electrical grid acts as a circuit breaker for solar systems, so when it goes down, the solar panels may continue producing electricity while the lines are still energized (Solarenergyworld.com, 2023). This can pose a serious hazard to utility workers who may assume the lines are de-energized. There’s also a risk that the solar energy could backfeed into the grid, which can damage equipment when the grid comes back online.
To prevent these dangers, most solar systems connected to the grid (known as grid-tied systems) will automatically shut off when they detect a power outage. This is called “islanding prevention” and is an important safety feature built into inverters, which are required by the National Electrical Code (SolarReviews.com, 2023). So most grid-tied solar systems will not operate at all during an outage.
Off-grid solar systems do not face the same issues, as they are designed to operate independently without sending electricity back to the utility grid. However, it’s still important to take safety precautions and assume all wires are live during an outage (ParadiseSolarEnergy.com, 2023). The solar batteries may continue supplying power even if the grid is down.
In short, grid-tied solar systems will shut down automatically during outages, while off-grid systems may continue working. Either way, exercise caution and treat all wires as potentially live.
Off-Grid Solar Systems
Off-grid solar systems operate completely independent of the utility grid. They utilize solar panels to generate electricity that charges batteries, which then provide power directly to the home or facility. Since they do not connect to the utility grid at all, off-grid systems operate 24/7 and provide electricity day and night, not just when the sun is shining.
In an off-grid solar system, the solar panels charge a bank of batteries either directly or through a charge controller. The charge controller regulates the voltage and current coming from the solar panels to safely charge the batteries. Once charged, the batteries then supply electricity to the home’s electrical system to power lights, appliances, and other electric devices.
Off-grid solar systems include backup power sources like generators or wind turbines for times when solar production is low. The system is designed to fully meet the electrical loads in the home or facility with multiple power sources and battery storage capacity. With the right system design and battery bank, an off-grid solar system can provide electricity reliably over extended periods of time without utility power.
Off-grid solar offers true energy independence and electricity in remote locations where utility power is not available. As solar and battery technology continues improving, off-grid solar systems are becoming a more practical and cost-effective solution for renewable energy.
Future Outlook
There are some promising developments in solar technology that could allow grid-tied solar systems to continue providing power during grid outages in the future. Research is being done on “islandable” inverters that can disconnect a solar system from the grid during outages while still allowing it to generate power. This prevents the safety risk of backflow to utility lines. Microinverters for individual panels rather than central inverters are also making islanding capabilities more feasible.
Additionally, smart inverters with advanced grid support functions are being developed. These can monitor grid voltage and frequency and seamlessly disconnect and reconnect as needed. With smart inverter technology, solar systems may be able to island themselves instantly when the grid goes down.
Improved power electronics in solar systems can also enable integration with home energy storage more easily. Having a battery backup charged by solar panels allows full off-grid usage during outages without compromising safety or grid regulations. With continuing solar tech innovations, the future possibilities for resilient solar power are promising.
Conclusion
In summary, solar panels can provide power during grid outages, but only if the solar system is properly designed and installed for off-grid operation. Grid-tied solar systems will shut down automatically for safety reasons. Adding battery storage creates a solar backup system that can provide essential electricity when the grid is down. While solar panels have limitations, such as not producing power at night or on cloudy days, they can be a valuable source of electricity resilience and energy independence for many homes and businesses. With proper solar system design and energy storage, solar power can keep the lights on even when the grid goes dark.