Why Is Solar Energy Considered Renewable Energy Quizizz
Introduction

Renewable energy comes from natural sources that are constantly replenished, such as sunlight, wind, water, plants, and geothermal heat. Nonrenewable energy comes from finite sources that will eventually dwindle as supplies are used up, such as coal, natural gas, oil, and nuclear energy (https://www.un.org/en/climatechange/what-is-renewable-energy). Renewable energy is considered important because it produces much less pollution and greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels, and the resources used are continually replenished (https://www.un.org/en/climatechange/what-is-renewable-energy). Of the various renewable energy sources, this article will focus specifically on solar energy and why it is classified as a renewable resource.
Definition of Solar Energy
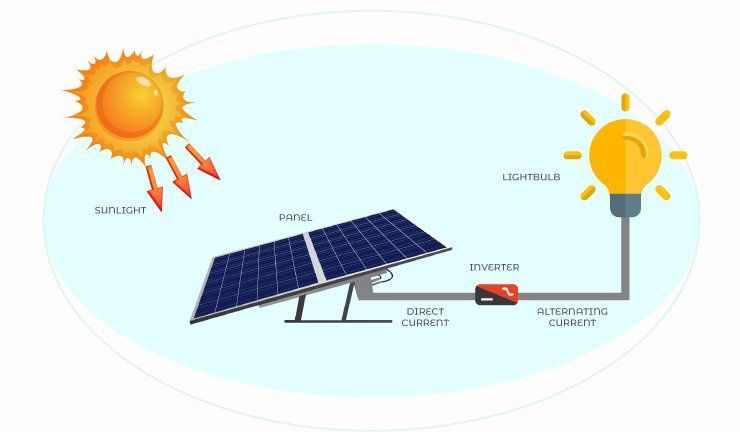
Solar energy is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity or heat. It is considered a renewable energy source because the sun’s energy is virtually limitless and will continue shining for billions of years (1). The process starts with solar panels, which are made up of photovoltaic cells usually arranged in rows and mounted on racks. When sunlight hits the panels, photons excite the electrons in the silicon atoms, causing them to break free and flow as direct current electricity. This electricity is then converted into alternating current and fed into the electrical grid for use or stored in batteries (2). Solar thermal systems work differently by using sunlight to directly heat fluids which can warm water or spaces.
At its core, solar energy relies on a simple process – converting energy from the sun into useful energy on Earth through advanced technology (3). The virtually unlimited supply from the sun means solar can help meet energy needs long into the future in a sustainable way.
Sources:
(1) https://www.nrel.gov/solar/solar-resources.html
(2) https://us.sunpower.com/solar-resources/what-solar-energy-and-how-do-solar-panels-work
(3) https://www.iea.org/reports/solar-pv
Solar Energy is Renewable
Solar energy is considered a renewable energy source because it comes from the sun, which will continue shining for billions of years (see https://www.saveonenergy.com/solar-energy/is-solar-energy-renewable/). The sun produces an enormous amount of energy every day in the form of radiation from nuclear fusion reactions. This solar radiation reaches the Earth continuously and will do so for the lifetime of the sun, making solar energy an essentially inexhaustible resource.
Renewable energy sources are those that can be replenished naturally within a human timescale, like solar, wind, geothermal and hydropower. The fuel for solar power – sunlight – cannot be depleted no matter how much we use it. As long as the sun keeps shining, solar panels can convert sunlight into electricity and thermal energy indefinitely (see https://blog.ecoflow.com/us/why-is-solar-energy-renewable-and-sustainable/). This makes solar a truly renewable energy source unlike fossil fuels which take millions of years to form.
In summary, solar energy is considered renewable because of its origin from the sun, which provides a constant, unlimited supply of solar radiation that will not run out for billions of years. This allows us to utilize solar energy forever with minimal environmental impact.
Solar Energy is Abundant
The potential of solar energy to provide vast amounts of renewable energy is enormous. The sun radiates more energy to the earth in one hour than the world uses in an entire year (MIT News). According to NASA, the sun emits over 340 watts per square meter of energy that reaches the Earth’s atmosphere. Only some of this energy is absorbed and utilized, but it still dwarfs global energy usage. The amount of solar energy striking the Earth in a single day contains twice as much energy as will ever be obtained from all of the Earth’s non-renewable resources of coal, oil, natural gas, and mined uranium combined (Penn State University). Essentially, the potential solar energy available far exceeds global energy demand. Solar energy’s incredible magnitude means it can easily supply all of our energy needs indefinitely.

Solar Energy is Sustainable
Solar energy is considered sustainable because it relies on the unlimited power of the sun, rather than finite fossil fuels that take millions of years to form underground. Unlike coal, oil, and natural gas, the sun’s energy will continue shining indefinitely. Harnessing solar power does not deplete any precious natural resource.
Generating electricity from sunlight also does not create any air or water pollution. Fossil fuel power plants emit greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide as well as smog-forming pollutants such as nitrogen oxides and sulfur dioxide. In contrast, solar panels produce clean, renewable electricity just from exposure to the sun, without emitting any harmful substances. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, solar energy avoids the emission of up to 534 pounds of carbon dioxide per megawatt-hour compared to the U.S. electricity grid average.
By displacing electricity generation from fossil fuels, solar energy can significantly reduce a region’s carbon footprint. Widespread adoption of solar power will be an important strategy for mitigating climate change and transitioning to a low-carbon future. The limitless and non-polluting nature of solar energy makes it one of the most sustainable options among renewable resources.
Solar Technology is Improving
There have been major advances in solar technology in recent years that have dramatically increased the efficiency and lowered the costs of solar panels. Some key improvements include:
Efficiency – The efficiency of solar panels has steadily increased over time. The most common silicon solar panels have gone from around 15% efficiency in the 1990s to over 20% today. New technologies like perovskite solar cells have achieved over 25% efficiency in lab tests. Higher efficiency panels can generate more electricity from the same amount of sunlight, reducing the number of panels needed (Advancements in Solar Panel Technology).
Costs – As manufacturing has scaled up and technology has advanced, the costs of solar panels have plummeted. The average price per watt for solar panels has dropped over 90% since 1977. This makes solar energy much more cost competitive with fossil fuels (5 Advances in Solar).
Storage – Battery storage technology is also improving to allow solar power to be used any time, not just when the sun is shining. Lithium-ion batteries have fallen in price by over 85% in the last decade. New battery chemistries and control systems are enabling longer duration energy storage (The Future of Solar is Bright).
Challenges of Solar
While solar energy has many benefits, it also comes with some limitations that present challenges. Some of the main challenges with solar energy include:
Sunlight availability – Solar panels need direct sunlight to effectively generate electricity. Cloudy days and nighttime reduce energy production. Areas farther from the equator also get fewer daylight hours during the winter months when the sun’s path is lower across the sky.
Energy storage – A key limitation of solar energy is that it can’t be produced at night. Battery storage systems are needed to store and release the energy as needed, but affordable and scalable storage is still a challenge.
Space requirements – Collecting solar energy requires a large surface area facing the sun. Rooftop systems are limited by roof size andrequire additional land for utility-scale solar farms.

Intermittency and variability – Solar output depends on weather and climate conditions, time of day, and season. This variability makes it difficult to integrate solar into the existing electric grid.
Upfront costs – While ongoing costs are low, installing solar panels has high upfront costs. This can be a barrier for widespread adoption, especially in developing areas.
Despite these challenges, innovations in battery storage, smart grids, and solar technology are helping to address some of the limitations of solar power.
Sources:
https://www.greenmatters.com/clean-energy
https://solarpowernerd.com/benefits-of-solar-energy-cars/
Solar Energy Applications
Solar energy has many diverse applications and is used in a variety of ways in our everyday lives (Solar energy applications). The most common uses of solar energy are for generating electricity, providing lighting, heating water, and space heating (Renewable Energy).
Solar photovoltaic (PV) panels convert sunlight directly into electricity. This electricity can be used to power homes, businesses, and the electric grid. Solar PV systems can be small, like rooftop panels on a home, or large solar farms with thousands of panels. The electricity generated from solar PVs is a clean, renewable source of energy (What is the best use for solar power?).
Solar thermal collectors harness heat from the sun to warm water or spaces. Solar water heating systems use solar thermal collectors to heat water for residential, commercial, or industrial uses. Solar space heating systems, like solar air heaters, can supplement a building’s existing heating system. Solar thermal applications offset the need to use electricity or gas for water and space heating.
Concentrated solar power (CSP) plants use mirrors to concentrate sunlight to drive traditional steam turbines and generate electricity on a large scale. CSP plants allow for thermal energy storage, providing electricity even when the sun isn’t shining.
Solar energy is also used for transportation applications. Solar PV cells can recharge batteries in electric vehicles, while concentrated solar thermal plants can also produce solar fuels. Solar lights and road signage are also common solar applications.
Growth of Solar Energy
Solar energy capacity and usage has grown rapidly in recent years. According to the Solar Energy Industries Association, the amount of solar installed in the United States has increased by over 10,000% since 2010, from 1.2 gigawatts to 129 gigawatts today (Solar Decathlon Creating an Ecosystem for Solar Energy Adoption). Globally, solar capacity increased from 40 gigawatts in 2010 to over 600 gigawatts in 2019, an increase of over 1,400% (The Rise of Solar Energy: How Many People are Making the Switch). Some project global solar capacity to reach over 8,500 gigawatts by 2050, enough to power the equivalent of over 1 billion homes.

Solar energy adoption is increasing rapidly not just in places like California and Hawaii, but also in many southern states. Texas, Florida, Georgia, and South Carolina are now amongst the top 10 states for installed solar capacity (Bright Future: Rise of Solar Power in the Southern States). The declining costs of solar technology, favorable policies, and abundant sunshine have made solar an attractive energy option across America.
Conclusion
In conclusion, solar energy is considered a renewable energy source because it comes from the sun, which will continue shining for billions of years to come. Unlike fossil fuels, solar energy is abundant and sustainable. Solar technology is also rapidly improving, making it more efficient and cost-effective. While solar does face some challenges like intermittency and high upfront costs, its many benefits make it an important part of our energy future. As solar technology advances and costs continue to fall, we can expect to see solar energy grow and play a bigger role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change. Solar energy offers a clean, renewable way to produce electricity and heat that can supplement and eventually replace fossil fuels. With further research, investment, and policy support, solar has the potential to become a major pillar of a sustainable energy system.