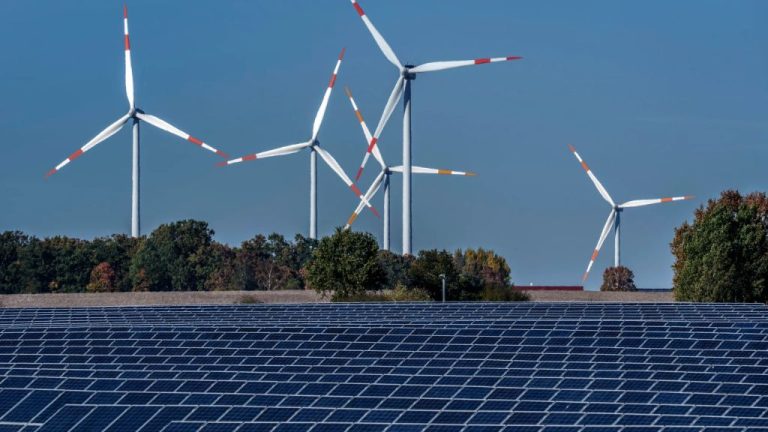
Why Is Renewable Energy Important For The Future?

Renewable energy comes from natural sources or processes that are constantly replenished, such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves, and geothermal heat. Some examples of renewable energy sources include solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal, and biomass. There is an urgent need to transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources for several important reasons:
First, renewable energy helps reduce dependence on fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas, which are non-renewable and major contributors to climate change. Fossil fuels are being depleted much faster than they are being replenished naturally.
Second, increasing renewable energy production mitigates climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Fossil fuels release high levels of carbon dioxide when burned to produce electricity. Renewables like solar, wind and hydropower produce negligible emissions.
Third, renewable energy provides public health benefits by reducing air pollution, which causes respiratory diseases and premature deaths linked to fossil fuels. Expanding renewables can help improve air quality and public health, especially in developing countries.
The transition to renewable energy is crucial for building a sustainable future with clean and unlimited energy sources. Renewables can fulfill energy needs while mitigating environmental damage and climate change risks from fossil fuel dependence. This makes renewable energy an essential investment for the 21st century and beyond.
Reduction of Fossil Fuel Dependence
The world currently relies heavily on fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas to meet energy needs. However, overreliance on these sources poses risks.
Fossil fuels are finite resources that will eventually be depleted. Supply disruptions and price volatility are constant threats. The Energy Information Administration notes that “extended supply disruptions may cause sharp price increases in the short run” (source). This affects energy security and makes economies vulnerable to shocks.
Moving away from fossil fuels diversifies energy supply. Renewables can supplement and replace finite resources over time. This reduces the risks of supply disruption, price spikes, and dependence on any one source.
Mitigating Climate Change
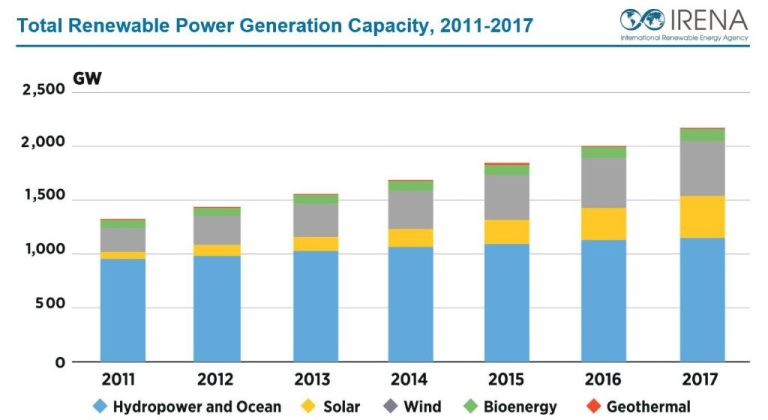
Transitioning to renewable energy sources like solar, wind, geothermal, and hydroelectric power is crucial for reducing greenhouse gas emissions that contribute to climate change. Unlike fossil fuels, renewables produce little to no carbon dioxide and other emissions that trap heat in the atmosphere. According to a report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, the world must reach net zero carbon emissions by 2050 to limit global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels and avoid catastrophic climate impacts. Widespread adoption of renewables is essential for reaching this goal. Renewable energy already accounts for 26% of global electricity generation and its share is growing every year. With the costs of renewables steadily decreasing, they are becoming more affordable and accessible around the world. Continued investment in renewable power along with phasing out fossil fuel use, particularly coal, can put us on track to achieve the deep emissions reductions required to mitigate climate change.
Source:
https://pr.euractiv.com/pr/eurobat-appoints-gert-meylemans-senior-communications-manager-174446
Public Health Benefits
Transitioning to renewable energy sources like wind and solar would dramatically reduce air pollution from burning fossil fuels. According to Harvard’s Center for Climate, Health, and the Global Environment (C-CHANGE), producing and burning fossil fuels creates air pollution that contains fine particulate matter, ozone, nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, carbon monoxide, volatile organic compounds, and heavy metals – all of which are damaging to human health. This air pollution leads to increased rates of asthma, lung cancer, heart disease, stroke, and premature death.
The impacts are especially severe in developing countries. A 2018 study in Environmental Research found that pollution from fossil fuel combustion leads to 16,000 premature deaths per day worldwide. The study notes that pollution impacts like fetal growth restriction and impaired cognitive development may be “seeded” in early life. Transitioning these developing nations to clean, renewable energy sources would significantly reduce fossil fuel air pollution and improve public health.
Sources:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5800116/
Environmental Sustainability
Transitioning to renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower can reduce pollution and habitat destruction caused by extracting and burning fossil fuels. Fossil fuel extraction through mining and drilling often contaminates air and water supplies in surrounding communities. Burning fossil fuels also releases large amounts of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases that contribute to climate change. According to research, the environmental impact of fossil fuel extraction is profound and far-reaching.
In contrast, renewable energy sources replenish themselves naturally and do not require dangerous extraction processes. Solar panels and wind turbines can be installed with relatively little habitat disturbance or environmental damage. While renewable energy technologies do have some negative environmental impacts from raw material mining and manufacturing, these are small compared to the massive habitat destruction and pollution caused by fossil fuels. Increased use of renewable energy would allow more lands to be conserved in their natural state rather than being degraded by fossil fuel extraction.
Sources:
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/environmental-impact-fossil-fuel-extraction-nkechi-miaeng-mnse-
Economic Development
Investing in renewable energy leads to significant job creation and economic growth opportunities. According to research from Yale University, renewable energy development on public lands in the U.S. could support over 300,000 construction jobs and 150,000 operational jobs by 2025 (Key Economic Benefits of Renewable Energy on Public Lands). The renewable energy industry employs over 800,000 people in the U.S. alone. Growth of the industry leads to increased high-skilled employment in manufacturing, construction, engineering, and other fields.
In the developing world, access to renewable energy enables economic advancement. The International Renewable Energy Agency estimates that achieving universal energy access with renewables could create over 2 million jobs annually in sub-Saharan Africa alone. Renewable mini-grid systems provide affordable and reliable electricity to power small businesses and connect rural communities to the global economy.
Technological Innovation
Technological advances and innovations are driving down the costs of renewable energy while improving efficiency and performance. According to the NREL, the levelized cost of energy for utility-scale solar PV dropped 88% between 2009 and 20191. Wind turbine costs have also fallen 69% during the same period2. These cost reductions make renewables more economically competitive with fossil fuels.
Continued investments into R&D and manufacturing scale will accelerate improvements in renewable technologies. There are also opportunities to develop domestic manufacturing capacity, creating jobs and economic growth. With the proper policies and investments, the renewable energy sector can become a major driver of technological innovation and opportunity.
Energy Security
The decentralized nature of renewable energy increases grid resilience and energy security (Smart grid technology: benefits and security challenges, 2021). By generating electricity from multiple smaller distributed sources rather than a few large centralized plants, the grid is less susceptible to major disruptions if any one source fails. Renewable microgrids with local generation and storage can operate independently as “islands” and keep providing power to communities during larger outages (10 Benefits of using a Microgrid, 2023). This prevents cascading blackouts from disruptions. Renewable energy sources are also domestically produced, reducing reliance on imported fuels prone to global supply shocks. This insulation from global fuel markets increases national energy security (Renewable Energy to Support Energy Security, Cox, 2019). The decentralized and domestic nature of renewable sources provides greater energy reliability and resilience.
Lower Long-Term Costs
Renewable energy becomes more cost-competitive with traditional fossil fuels every year. With technological improvements and accelerating deployment, the costs of renewables continue to decline. Solar and wind power are a testament to this rapid cost reduction.
In contrast, traditional fossil fuels face unpredictable price fluctuations as finite resources deplete over the long-term. The sun shining and the wind blowing are eternally free fuels that protect renewables against fuel cost volatility. Stable and often decreasing renewable energy costs provide greater economic certainty and insulation from future fossil fuel price shocks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, renewable energy has numerous critical benefits for the environment, economy, and security that make it an integral part of a sustainable future. Renewable sources like solar, wind, and hydropower produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels, helping mitigate climate change. Widespread adoption of renewables improves public health by reducing air pollution and creates new economic opportunities and jobs in the clean energy sector. Transitioning to renewables bolsters energy security by relying on inexhaustible domestic resources rather than imported fossil fuels subject to geopolitical tensions. While renewables require upfront investments, their long-term costs are decreasing and projected to be lower than conventional sources. With their environmental sustainability, job creation, energy independence, and affordable power, renewables are key to building a clean energy economy and must play an expanded role in energy systems worldwide. The transition to renewables won’t be easy, but it is necessary to combat climate change, reduce pollution, and maintain prosperity. With smart policies and continued technological advances, a future powered by renewable energy is within reach.