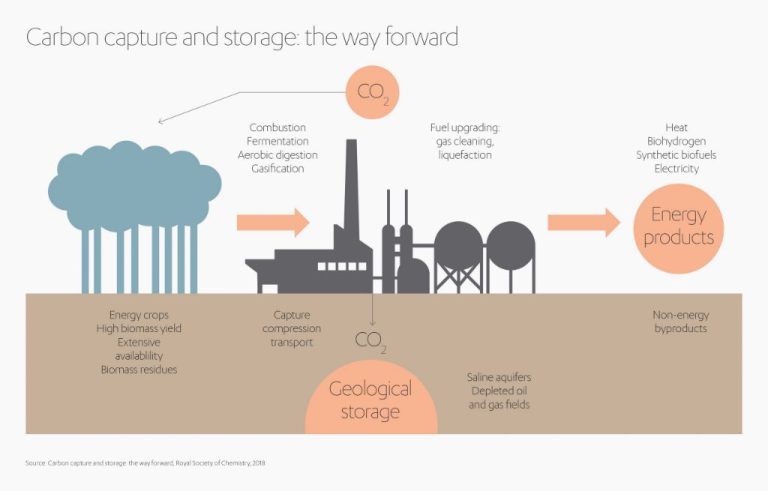
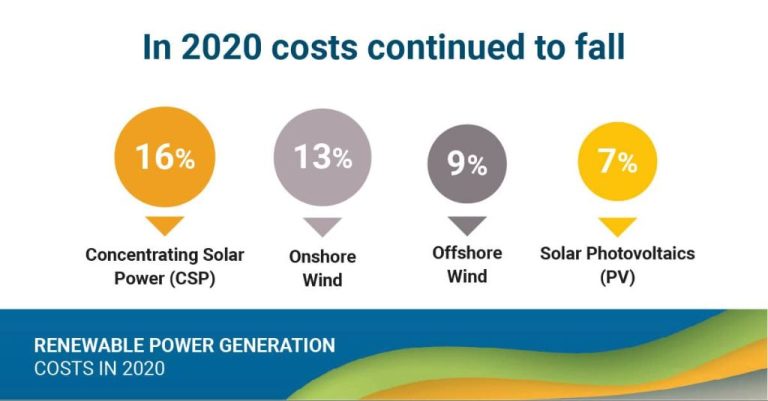
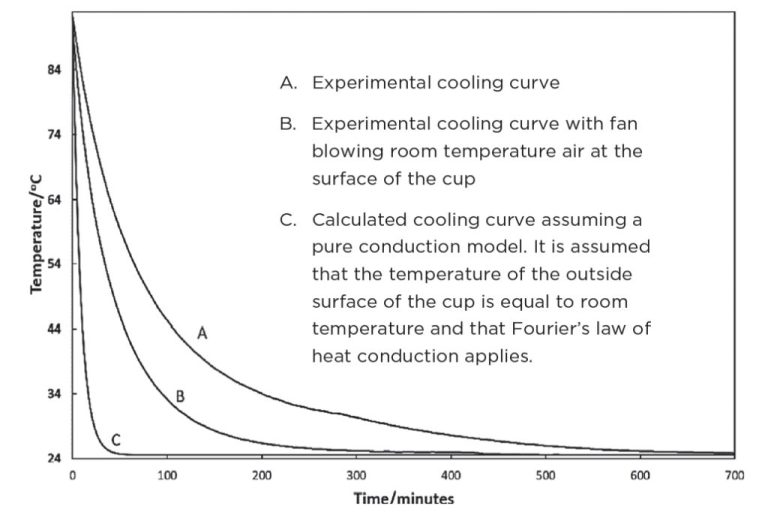
Why Is Renewable Energy Called Green Energy?
Renewable energy is energy generated from natural resources that are continuously replenished, such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves, and geothermal heat (https://www.nationalgeographic.org/article/renewable-energy-explained/). The five major types of renewable energy are wind, solar, hydroelectric, biomass, and geothermal. Renewable energy is also referred to as “clean energy” or “green energy” because it produces little to no greenhouse gas emissions or air pollutants (https://www.prysmiangroup.com/en/insight/sustainability/renewable-energy-definition-and-types-of-clean-energy). Unlike fossil fuels which emit harmful pollutants, renewable energy sources are considered environmentally sustainable and critical to mitigating climate change and reducing air pollution.
Reduces Pollution
Renewable energy sources like solar, wind, geothermal, and hydroelectric produce very little air and water pollution compared to fossil fuels. Burning coal, oil, and natural gas releases pollutants like nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, particulate matter, and mercury into the air which contributes to acid rain, smog, respiratory illnesses, and climate change (Source). Fossil fuel power plants also release wastewater containing metals and salts that can pollute water sources. In contrast, most renewable energy installations like solar panels and wind turbines generate electricity without emitting air pollutants or wastewater. Some geothermal plants release small amounts of hydrogen sulfide, but this can be captured and converted into usable byproducts. Overall, transitioning to renewable sources provides huge reductions in air and water pollution.
Reduces Greenhouse Gases
One of the main reasons renewable energy is called “green” is because it significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas. Greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide (CO2), methane, and nitrous oxide absorb heat in the atmosphere, causing global temperatures to rise. Fossil fuels release large amounts of these gases when burned to produce energy.
In contrast, most renewable energy sources produce little to no greenhouse gases. According to the UN, transitioning to renewable energy could reduce carbon emissions in the power sector by up to 90% by 2050 [1]. Wind, solar, hydropower and geothermal energy emit essentially zero greenhouse gases during operation. And bioenergy from plant materials only releases the carbon that plants absorbed during growth.
Because renewable energy displaces fossil fuel generation, it reduces overall greenhouse gas emissions. Multiple studies confirm renewables’ role in lowering CO2. For example, one analysis by the World Resources Institute found that aggressive expansion of renewables and energy efficiency could provide over 90% of the emissions reductions needed in the energy sector [2].
Conserves Natural Resources
The term “renewable energy” refers to energy sources that can be replenished in a short period of time through natural processes. Renewable sources like solar, wind, geothermal and hydropower don’t deplete finite resources like coal, oil and natural gas. Fossil fuels are non-renewable – once used up they are gone. By switching to renewables, we can conserve these limited natural resources for future generations.
The sun, wind, water and heat from the earth won’t run out anytime soon. These renewable resources are constantly replenished and will be available for the foreseeable future. So investing in solar, wind, hydro and geothermal power helps protect our finite fossil fuel reserves. The more we can rely on renewables, the less we’ll have to tap into coal, oil and natural gas.
Renewables allow us to generate electricity, heat homes and power vehicles without rapidly drawing down our limited stockpiles of non-renewable resources. This conservation of natural resources ensures we don’t use them up too quickly. Renewable energy sources are sustainable long-term energy solutions.
Creates Jobs
Building renewable energy infrastructure like wind turbines and solar panels creates domestic jobs in construction, manufacturing, operations, and maintenance roles. According to a documentary film, renewable energy has already created hundreds of thousands of jobs across the United States. There are also economic benefits in the communities where renewable projects are built. Construction of a new wind or solar farm requires hiring local workers and can bring much-needed employment opportunities to rural areas. Once built, these projects continue providing jobs for maintenance workers and technicians in the area. The renewable energy industry offers careers ranging from entry-level installer positions to highly skilled engineering and technician roles. With the right training programs in place, building the new green economy can provide stable and well-paying jobs.
Lowers Energy Prices
Increasing renewable energy generation puts downward pressure on electricity prices. As reported by the American Progress, investing in clean energy would reduce average household energy costs by $500 per year. Renewable sources like wind and solar have very low operating costs compared to fossil fuels. Fossil fuels require continual mining/drilling and price fluctuations based on global markets. Renewables like solar and wind have free and inexhaustible fuel sources. Even though renewable technology requires high upfront costs, the International Renewable Energy Agency found that renewables remain cost-competitive amid rising fossil fuel prices. As renewable technology continues advancing and scale increases, prices are projected to decline further.
Supports Energy Independence
Using domestic renewable sources like wind and solar power reduces reliance on imported fossil fuels like oil, coal, and natural gas. According to a report from the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy, renewable energy improves energy independence and security by tapping into domestic energy resources. The more renewable power the U.S. generates at home through sources like wind, solar, hydropower, and geothermal, the less dependent the country becomes on imported fossil fuels. This NRDC article notes that clean renewable energy from domestic sources is key for real energy independence.
Improves Public Health
Renewable energy helps improve public health by reducing air pollution from fossil fuel emissions. Burning fossil fuels like coal and natural gas creates pollutants like particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, mercury, and other toxins that reduce air quality. According to the EPA, air pollution contributes to heart disease, lung cancer, asthma, and other respiratory diseases.
Transitioning to renewable energy sources like wind, solar, geothermal, and hydropower can significantly cut these harmful emissions. For example, a 2021 study found that increasing renewable electricity generation in the US by 25% could prevent over 10,000 premature deaths annually. The cleaner air leads to reduced rates of respiratory and cardiovascular hospitalizations. Renewable energy’s public health benefits provide significant economic value by lowering healthcare costs and increasing productivity.
Many renewable energy sources also produce no emissions at the point of generation. This helps improve indoor air quality and health. For example, installing solar panels on homes avoids pollution and dangerous fumes from backup diesel generators. Cleaner indoor and outdoor air thanks to renewable energy translates into better public health outcomes.
Source: https://simpleblog.ai/blog-ideas/Renewable-energy-usage
Helps Rural Communities
Renewable energy projects can provide significant economic benefits for rural communities. According to Mother Earth News, renewable energy investments in rural areas create new job opportunities, boost local economies through lease payments to landowners, and demonstrate long-term commitment to rural development.
Rural communities often struggle economically compared to urban areas. Renewable energy projects provide new revenue sources that can revitalize local economies. Construction of wind farms, solar arrays, and biofuel facilities creates short-term employment opportunities. Operating these facilities provides steady long-term jobs for rural residents.
Rural landowners also receive lease payments from wind and solar developers to build projects on their properties. These lease payments provide landowners with a stable income stream that supports the local economy. Overall, renewable energy investments demonstrate private sector commitment to the future of rural communities.
Conclusion
Renewable energy provides extensive environmental, economic and social benefits that make it a key part of building a sustainable future. Renewables reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution when displacing fossil fuel sources, helping to mitigate climate change and improve public health. They conserve natural resources by relying on constantly replenished sources like sunlight, wind and water instead of finite resources like coal and natural gas. The renewable energy industry also creates green jobs and can provide affordable local power options to businesses and communities. Most importantly, renewables increase energy independence and security by relying on domestic resources rather than imported fuels. For all these reasons, renewable energy is called “green energy” – it provides solutions to our most pressing environmental problems while powering society and the economy.