Why Is Light So Important?
Light is essential for life on Earth. We often take light for granted, but it plays a profoundly important role across nature, science, technology, and human life. Light allows plants to grow through photosynthesis, provides vision and visual perception, enables the production of vitamin D, regulates circadian rhythms and sleep, impacts mood and mental health, powers solar energy, and makes environments safe and navigable. This article will explore the scientific principles behind light and overview the many ways that light underpins fundamental aspects of life and society.
Photosynthesis Requires Light
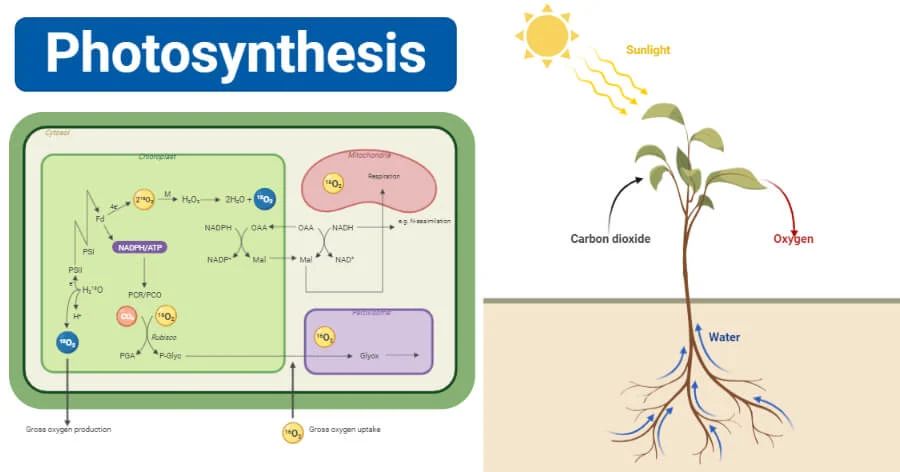
Photosynthesis is the process that converts light energy into chemical energy and sustains almost all life on Earth. During photosynthesis, plants use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce carbohydrates and oxygen. The carbohydrates fuel the plant’s activities, while the oxygen is released into the atmosphere. Without photosynthesis, complex life forms would not have the energy sources they need to survive. By converting sunlight into usable energy, photosynthesis provides the foundation for the vast diversity of life we see today.
The critical role of light in photosynthesis begins when light is absorbed by chlorophyll and other photosynthetic pigments. These pigments are located in plant cells within structures called chloroplasts. The pigments absorb certain wavelengths of light, which provides energy for the subsequent chemical reactions. During these light-dependent reactions, the energy from sunlight is used to split water molecules, releasing oxygen as a byproduct. The oxygen generated through photosynthesis is what enabled Earth’s atmosphere to become oxygenated over billions of years. In fact, the oxygen in every other breath you take originally came from photosynthesis. Clearly, without light as an energy source, photosynthesis could not occur, and life as we know it would not exist.
Vision
Light is essential for vision. The human eye contains light receptors called rods and cones that detect light and trigger nerve impulses to the brain, enabling us to see. Cones are responsible for color vision and distinguishing fine details, while rods operate in low light conditions. The amount and quality of light entering the eye directly impacts what we are able to see. With insufficient light, vision becomes challenging or impossible. Certain wavelengths of light, like UV and blue light, can also damage the retina over time if there is overexposure. Quality lighting design takes the properties of light and the human eye into account to optimize environments for visibility and visual comfort.
Vitamin D
One of the most vital roles that sunlight plays in human health is enabling vitamin D production in the skin. When ultraviolet B (UVB) rays from the sun hit the skin, they trigger a chemical reaction that converts cholesterol into vitamin D. This “sunshine vitamin” is essential for regulating calcium absorption and promoting bone growth and strength. Vitamin D also supports muscle, brain, and nervous system function.
In the absence of adequate sun exposure, vitamin D deficiency can occur, leading to soft, thin, or brittle bones. Children need vitamin D to enable proper bone development and prevent rickets, while adults need it to prevent osteomalacia and osteoporosis later in life. Given the importance of vitamin D for overall health, medical experts recommend getting 10-30 minutes of unprotected sun exposure two to three times per week. This provides the body enough UVB rays to maintain sufficient vitamin D levels.
While vitamin D is available through some foods and supplements, nothing compares to what the sun provides. Natural vitamin D production from sunlight is the most efficient and beneficial way for the body to obtain this critical nutrient. Ensuring adequate sun exposure through outdoor time is therefore essential for good health.
Circadian Rhythms
Light plays a pivotal role in regulating circadian rhythms and sleep patterns. Circadian rhythms are the roughly 24-hour cycles governed by our internal biological clock that influence critical bodily functions such as metabolism, hormone release, and sleep-wake cycles. Light, especially natural daylight, is the primary cue that calibrates our circadian rhythms to Earth’s day-night cycle.
When our eyes detect light, especially bright morning light, it suppresses the secretion of melatonin (a hormone that promotes sleep) and shifts our circadian rhythm, making us feel more alert. This daily light exposure helps synchronize our internal clock to the external environment. By contrast, darkness triggers the release of melatonin, inducing sleepiness. Hence exposure to light versus darkness signals to our body when to be awake versus asleep.
Disruptions to our natural circadian rhythms from inadequate light exposure during the day or excessive artificial light exposure at night can desynchronize our internal clock. This misalignment between our circadian rhythms and the earth’s 24-hour light-dark cycle can severely impact the quantity and quality of sleep, leading to a host of adverse health effects.
Light Improves Mood and Fights Depression
Light exposure has a profound effect on mood and mental health. Scientific research shows that bright light therapy can dramatically improve depression symptoms in people with seasonal affective disorder (SAD). SAD is a type of depression that occurs during the darker winter months when there is less natural sunlight. Light therapy works by resetting the body’s internal clock to match the increased daylight hours of spring and summer. Just spending time outdoors on a sunny day or sitting by a window can boost mood.
Studies also indicate that proper exposure to sunlight decreases depression and anxiety levels in people without SAD. Light sends signals to the parts of the brain that regulate mood, alertness and sleep. It seems that getting enough bright light during the day helps keep the brain chemistry in balance. Darkness triggers the brain to excrete melatonin, making you sleepy. But too much time spent indoors away from natural light can upset the circadian rhythm. Make sure to spend time outdoors or sit near windows to get daily sunlight. This simple habit can naturally improve mood and relieve symptoms of depression.
Agriculture
Light is absolutely essential for agriculture and food production. Plants use sunlight to power photosynthesis, the process by which they convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. Photosynthesis provides plants with the energy they need to grow and produce fruits, vegetables, grains and more. Without adequate sunlight, crop yields would dramatically decrease.
Different plants require different amounts of sunlight. Some plants, like tomatoes, peppers and eggplants, need at least 6 hours of direct sunlight per day. Others, like lettuce, spinach and kale, actually prefer partial shade. Farmers must carefully consider sunlight requirements when deciding where and when to plant their crops.
In addition to enabling photosynthesis, sunlight impacts plants in other ways that are important for agriculture. Light signals to plants when to flower and fruit based on changing day length. It also influences their growth patterns and development. Farmers can manipulate interior lighting conditions to optimize plant development year round.
Sunlight even affects the quality and taste of produce. Vegetables and fruits that receive more sun exposure often have higher sugar content and more robust flavors. For example, grapes grown in sunny vineyards make tastier wines than grapes grown in heavily shaded areas.
Without the light provided by the sun, agriculture as we know it simply would not exist. Our entire food system depends on plants efficiently capturing and converting sunlight into energy and biomass through photosynthesis. Light is arguably the single most important abiotic factor enabling humans to grow bountiful crops and nourish civilizations.
Energy
Light is a vital source of energy that powers much of life on Earth. The most obvious example is solar energy. For millennia, humans have harnessed the power of the sun to provide heat, light, and electricity. Today, solar energy is one of the fastest growing renewable energy sources. Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity that powers homes, businesses, and even entire cities.
Solar energy has many benefits. It is clean, renewable, widely available, and eliminates reliance on fossil fuels that pollute the environment. Solar also provides energy independence and security. While the sun shines each day, the supply of solar energy is virtually limitless. Solar technology is also rapidly improving, becoming more efficient and affordable each year. With sufficient investment and research, solar energy could someday power the world.
Light is literally power. Without the light from the sun, solar energy would not be possible. Solar energy demonstrates how light is a vital source of renewable power that holds great promise for the future of humankind.
Safety
Light plays a crucial role in safety by allowing navigation, improving visibility, and illuminating potential hazards. Street lamps, vehicle headlights, and even the glow of the moon help us find our way at night. Reflective strips and markings harness light to delineate roads, pathways, obstacles and more. From lighthouses guiding ships to flashlights aiding searches, light enables safer movement.
By lighting up dark spaces, light helps identify risks and dangers that could otherwise cause harm. It reveals cracked steps, spilled liquids, prowling animals, and other hazards that are difficult to detect in the dark. Proper lighting in workplaces and public venues reduces accidents and injuries. Lighting deters crime and enhances security through increased visibility.
The ability to see clearly is key for performing most daily tasks safely. Good lighting improves visibility and visual acuity, reducing eye strain. It enables quicker reaction times for braking, dodging obstacles, maintaining balance, and more. Light makes it easier to read signs, instructions, and warnings that convey vital safety information. Overall, light plays an indispensable role in safety across many aspects of life.
Conclusion
Light is indeed an essential part of life on Earth. As we have explored, light enables plants and phytoplankton to produce energy and oxygen through photosynthesis. It allows humans and animals to see and make sense of the world around them through vision. Light exposure helps our bodies synthesize vitamin D and regulates circadian rhythms that are crucial for sleep, alertness, hormone production, and more. Light even impacts our moods and emotions. Across history, the harnessing of light has transformed agriculture, infrastructure, transportation, communication, and energy production. Light keeps us safe by illuminating potential hazards at night. In summary, light profoundly shapes life on Earth. It sustains ecosystems, organisms, societies, and technologies. Appreciating the far-reaching importance of light gives us perspective on this electromagnetic radiation that we depend on each day.