Who Pays For Green Energy?
Green energy, also known as clean or renewable energy, refers to energy that is generated from natural sources or processes that are constantly replenished. Some of the most common examples of green energy sources include solar, wind, geothermal, hydropower, and biomass. According to National Grid, green energy comes from sources that are naturally replenished and cause minimal pollution or environmental damage. Unlike fossil fuels which emit greenhouse gases, most forms of green energy generation produce little to no global warming emissions.
The term “green energy” is often used interchangeably with “renewable energy,” which the Inspire Clean Energy defines as energy from sources that are naturally replenished within a human timescale. The key aspect that makes an energy source green or renewable is that it cannot be depleted or does not produce waste products that cannot be handled naturally on a sustainable basis.
Government Support
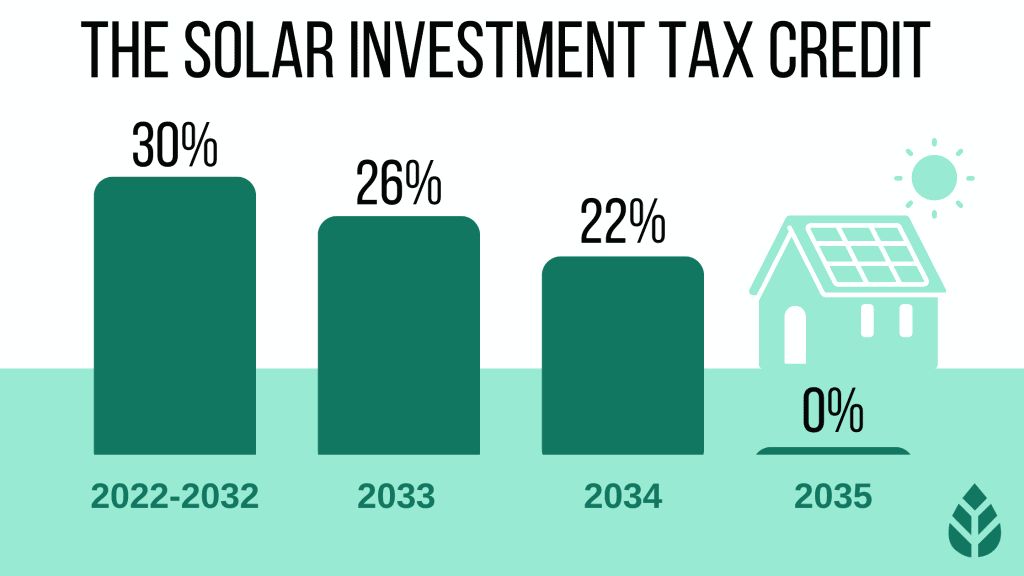
Government incentives play a major role in funding renewable energy projects and making green power more affordable. One of the most significant incentives is the federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC), which provides a tax credit for up to 30% of the cost of installing solar panels or other renewable energy systems (https://wrxnews.com/government-incentives-for-renewable-energy/). Many states also offer additional tax credits and rebates to further reduce the upfront costs of renewable energy. For example, California offers both state tax credits and rebates through the Self-Generation Incentive Program (https://wrxnews.com/government-incentives-for-renewable-energy/). These financial incentives make the high initial investment of renewable power more feasible for residential, commercial, and utility customers.
Utility Company Investments
Utility companies are major investors in renewable energy such as wind and solar power. As the article “How & Why Utilities Companies Are Investing in Renewable Energy” from Insight Global states, “By investing in renewable energy, they can ensure a stable energy supply in the future and remain competitive in an evolving industry.” (Source). Some key investments include:
Many leading utility companies like NextEra, Duke Energy, Southern Company, and others have made substantial investments in building new solar and wind farms across the United States. For example, NextEra Energy alone has invested over $50 billion in renewable energy projects. Duke Energy plans to double its renewable energy capacity by 2025. Southern Company has invested $20 billion in renewable energy in the past decade.
According to Clean Power, “$408 billion in domestic utility-scale clean energy investments have been announced since August 2022.” Much of this investment is going into wind and solar projects to expand renewable energy nationwide (Source). Utility companies see renewable energy investments as vital for meeting customer demand for clean energy while ensuring long-term business growth and stability.
Businesses
One major source of investment in renewable energy comes from businesses. Many corporations are buying renewable energy credits and installing solar panels to meet sustainability goals and reduce energy costs [1]. According to Eurowind Energy, businesses invested $288.9 billion in renewable energy projects globally in 2018 [1]. Corporations like Google, Apple, and Amazon have made major commitments to power their operations with 100% renewable energy [2]. Investing in on-site solar panels allows companies to lock in long-term electricity rates and hedge against fossil fuel price volatility. Tax incentives like the Investment Tax Credit also make solar power attractive for business owners [3]. As more companies set ambitious carbon reduction targets, corporate investments in renewable energy are set to rise.
Residential Customers
Homeowners are increasingly adopting renewable energy sources like rooftop solar panels or purchasing clean energy from their utility (Twumasi, 2022). The high upfront costs of purchasing and installing solar panels or wind turbines can deter some homeowners. However, federal and state tax credits and rebates can offset 30-50% or more of the cost of residential solar panel systems (DigitalCCbeta, n.d.). Many homeowners take out loans to finance rooftop solar installations and make back their investment over time through electricity bill savings. Some utility companies and local governments also offer incentives for households to go solar.
For homeowners who do not want to install their own renewable energy systems, many utilities now offer options to purchase clean power. Often called green power plans, these programs allow residential customers to pay a premium on their electricity bill to support development of renewable energy sources. The extra charge is usually only a few extra dollars per month. Green power plans make it easy for households to reduce their environmental impact and support clean electricity generation.
Non-Profits
Many non-profit organizations are dedicated to promoting renewable energy and sustainability. For example, the Center for Sustainable Energy is a nonprofit focused on decarbonization through clean transportation and energy programs. They provide services like program design, management, evaluation, and more to drive adoption of renewable energy solutions.
There are also nonprofits focused on leveraging technology to fight climate change. Tech To The Rescue highlights groups using technology for climate education, renewable energy, carbon removal, and emissions reduction. This includes things like creating apps to track carbon footprints and online platforms to connect climate activists.
At a national level, the American Council on Renewable Energy (ACORE) unites finance, policy and technology leaders to accelerate the transition to renewable energy. They provide research, education, networking events, and policy advocacy to drive the adoption of renewable energy solutions nationwide.
Crowdfunding
Crowdfunding has emerged as an innovative way for communities to collectively fund renewable energy projects. Through online platforms, individuals can make small contributions that add up to the capital needed to develop solar, wind, hydro, and other green power initiatives. According to CrowdFundRES, crowdfunding unleashes the potential for financing renewables by enabling public participation and investment.
Crowdfunding renewable projects allows investors to support the transition to clean energy alongside banks and other institutions. As noted by Invesdor, crowdfunding gives people the chance to determine the energy future they want. The European Commission has recognized the promise of crowdfunding, supporting research like the CrowdFundRES project to maximize its potential.
With crowdfunding, local communities can rally around renewable projects that benefit them directly. Instead of relying solely on utilities or government, people can fund solutions tailored to their region’s needs and resources. By democratizing clean energy investment, crowdfunding provides a grassroots way to enable the transition away from fossil fuels.
Pros of Green Energy
Green energy provides numerous environmental benefits over conventional fossil fuels. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, renewable energy results in lower carbon emissions, which helps combat climate change (https://www.energy.gov/eere/renewable-energy). Additionally, green energy does not produce air pollutants like nitrogen oxides and sulfur dioxide, improving air quality and public health. The Environmental Protection Agency found replacing fossil fuel electricity with renewables could prevent thousands of premature deaths in the U.S. each year.
Transitioning to renewable energy also provides energy independence and security. Relying on domestic green energy instead of imported fossil fuels reduces vulnerability to volatile global oil and gas prices. The Department of Energy reports renewable energy consumed in the U.S. displaced the equivalent of over 450 million barrels of petroleum in 2019. With abundant renewable resources available, increased green energy would allow the U.S. to rely primarily on its own energy supplies.
Cons of Green Energy
While renewable energy has many benefits, there are also some challenges and drawbacks to be aware of. One of the biggest cons is the higher upfront cost compared to fossil fuels. The infrastructure, technology, and installation of renewable energy systems can be quite expensive.
For example, installing a residential solar system can cost $20,000 or more, depending on the size. Similarly, commercial-scale wind and solar farms require major capital investments before they start generating energy and revenue. The costs of batteries and energy storage systems also add to the expense. This makes the initial switch to renewables more challenging despite the long-term savings.
Another disadvantage is the reliability and intermittency of renewable sources like wind and solar. Since the sun doesn’t always shine and the wind doesn’t always blow, these technologies generate varying amounts of energy throughout the day and year. This unpredictability makes it difficult to exactly match supply and demand. Until large-scale, cost-effective energy storage is available, intermittency remains a key obstacle.
Sources:
https://www.greenmatch.co.uk/blog/2021/09/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-renewable-energy
Conclusion
In summary, green and renewable energy is paid for through investments and contributions from a variety of sources. Governments provide tax incentives and subsidies to support green energy projects. Utility companies are making major investments into renewable power as old infrastructure needs upgrading and energy portfolios shift. Businesses are buying renewable energy to meet sustainability goals and reduce emissions. Residential customers can choose to pay more on utility bills to access renewable power, or invest in systems like rooftop solar for their homes. Non-profits help fund community renewable energy projects through grant funding and donations. Crowdfunding platforms allow individuals to collectively fund green energy ventures. The costs and benefits are spread across many stakeholders, from governments and corporations down to individual households.
While renewable energy requires significant upfront investment, it provides environmental benefits over the long term and energy cost savings once infrastructure is in place. There are still challenges around making green power affordable and accessible to all communities, but the growth of renewable energy demonstrates willingness from many sectors to pay extra costs to reduce emissions and build a more sustainable future.





