Who Are The Top Escos In The Us?
ESCO stands for Energy Service Company. An ESCO is a company that provides energy efficiency-related and other value-added services. According to Wikipedia, ESCOs first emerged in the 1970s in response to the energy crisis at that time. The ESCO industry has grown significantly since then, driven by a continued focus on energy efficiency, sustainability, and cost savings.[1]
ESCOs play an important role in promoting energy efficiency, especially in large facilities like government buildings, universities, and hospitals. They provide integrated solutions including designing and implementing energy savings projects, arranging financing, and monitoring energy savings over the long-term. By providing energy savings performance contracts (ESPCs), ESCOs allow facility owners to implement energy upgrades with no upfront capital costs and share in the energy savings generated.
What is an ESCO?
ESCO stands for Energy Service Company. As defined by the U.S. Department of Energy, “Energy service companies (ESCOs) develop, design, build, and arrange financing for projects that save energy, reduce energy costs, and decrease operations and maintenance costs at their customers’ facilities”.[1] ESCOs focus on providing energy efficiency-related and other value-added services.
The key aspects of the ESCO business model are:
- They offer energy efficiency, renewable energy, and distributed generation facilities upgrades to existing facilities.
- They provide the capital required to implement these projects in exchange for a share of the energy savings over the life of the contract.
So in essence, ESCOs enable building upgrades to be funded through energy savings, requiring little to no upfront capital expenditure by the client. They offer clients the opportunity to modernize aging infrastructure while recovering costs through lowering energy usage and costs.[2]
[1] https://www.energy.gov/femp/energy-service-companies
[2] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Energy_service_company
Largest ESCOs
Based on industry research, below are the top 10 largest ESCOs in the United States ranked by annual revenue:
1. Ameresco
Ameresco is currently the largest ESCO in the US with over $1 billion in revenue in 2020. They are headquartered in Framingham, MA and provide energy efficiency, renewable energy, distributed generation, and sustainability services. Some of their key services include energy audits, energy retrofits, solar PV, CHP, and battery storage. Notable projects include a 6.9 MW solar installation at the Savannah River Site and numerous projects for federal agencies (source).
2. Engie Impact
Engie Impact (previously Ecova) is headquartered in Spokane, WA and offers sustainability consulting and implementation services. They help clients develop and execute environmental strategies and programs. Engie Impact reported over $600 million in revenue in 2019 (source).
3. Honeywell
Honeywell is a Fortune 100 company that provides energy savings performance contracts, demand response, solar PV, energy storage, and other energy services. They are based in Charlotte, NC and reported $517 million in ESCO revenue in 2019. Notable projects include an energy savings performance contract at the Empire State Building (source).
4. Siemens
Siemens is a multinational conglomerate with its ESCO headquarters in Buffalo Grove, IL. They offer performance contracting, onsite generation, renewable energy, microgrids, and other energy services. Siemens brought in $438 million in US ESCO revenue in 2019 (source).
5. Schneider Electric
Schneider Electric, headquartered in Andover, MA, provides energy management and efficiency services including building automation and industrial optimization. They reported $333 million in revenue from their ESCO business in 2019 (source).
6. Constellation
Constellation is an ESCO business unit of Exelon Corporation based in Baltimore, MD. They offer energy efficiency, demand response, onsite generation, and other energy solutions. Constellation brought in over $200 million in revenue in 2019 (source).
7. CLEAResult
CLEAResult is headquartered in Austin, TX and specializes in energy efficiency program design, implementation, and evaluation. They work with utilities and governments to administer efficiency programs and reported over $200 million in revenue in 2019 (source).
8. Trane Technologies
Trane Technologies, formerly Ingersoll Rand, is based in Davidson, NC. They offer HVAC systems and building management services aimed at improving energy efficiency. Trane brought in around $150 million in U.S. ESCO revenue in 2019 (source).
9. Veolia
Veolia, headquartered in Boston, MA, provides water, waste, and energy management services. Their ESCO offerings include energy performance contracts, onsite generation, and other energy efficiency solutions. Veolia reported $141 million in U.S. ESCO revenue in 2019 (source).
10. ENGIE North America
ENGIE North America, based in Houston, TX, offers a range of energy services including efficiency upgrades, renewable energy, distributed generation, and microgrids. They brought in $133 million in U.S. ESCO revenue in 2019 (source).
Key Services
ESCOs provide a range of energy efficiency and facility improvement services to help clients reduce energy costs and meet sustainability goals. Some of the key services offered by ESCOs include:
Energy audits – ESCOs conduct detailed energy audits and analysis to identify opportunities for efficiency improvements and savings. This involves examining building systems, operations, and energy usage patterns.
Lighting upgrades – One of the most common ESCO services is upgrading lighting systems to more efficient technologies like LEDs. This can significantly reduce electricity usage for lighting.
HVAC system upgrades – ESCOs install and optimize heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems for optimal efficiency and performance. This includes new equipment as well as controls and automation.
Onsite generation – ESCOs help clients install onsite power generation systems like solar PV, wind turbines, cogeneration, and fuel cells to reduce purchased electricity.
Building automation – ESCOs implement building automation systems to optimize HVAC, lighting and other systems through sensors, controls and data analytics.
Energy procurement – Some ESCOs offer energy procurement services, acting as consultants to help clients manage energy spending and procurement strategies.
By providing expertise across these areas, ESCOs take a whole-building approach to reducing clients’ energy costs and environmental footprint.
Financing
Typical financing options for ESCOs include Power Purchase Agreements and Energy Savings Performance Contracts. With a Power Purchase Agreement (source), the ESCO owns, operates, and maintains the energy efficiency equipment and sells power to the building owner at a set rate that is competitive with utility rates. An Energy Savings Performance Contract (source) is where the ESCO provides the upfront financing for the equipment and installation costs and is paid back over time from the energy savings generated by the project.
Under an Energy Savings Performance Contract, the ESCO guarantees the energy savings and bears the risk if they do not materialize. This type of performance-based contract is popular with ESCOs as they can leverage future energy savings to provide financing for projects. The payments to the ESCO are contingent upon realizing the projected savings. Energy Savings Performance Contracts typically have a term of 10-20 years (source).
Notable Projects
Among the largest ESCO projects completed in recent years are Boston’s City Hall and Faneuil Hall Lighting Retrofit Project and the Empire State Building Lighting and Window Retrofit Project in New York City.
The City Hall and Faneuil Hall project, completed in 2012 by Ameresco, upgraded lighting and controls in the two historic buildings in downtown Boston. The $5 million project replaced over 3,000 inefficient light fixtures with LEDs, updated lighting controls, and installed occupancy sensors. It resulted in $200,000 in annual energy savings and an impressive 2.6 million kWh reduction in electricity use per year.
In the Empire State Building project finished in 2013, Johnson Controls completed a top to bottom retrofit of the iconic skyscraper. The $20 million project upgraded 6,500 windows, installed LED and fluorescent fixtures, added occupancy sensors and daylight dimming controls, and overhauled the heating and cooling systems. After completion, the building reduced its energy use by 38%, saving $4.4 million in annual utility costs.
These large-scale retrofit projects exemplify the energy and cost savings that can be achieved through ESCO services. With their energy expertise and innovative financing, ESCOs are able to deliver substantial upgrades that significantly reduce energy consumption in older commercial buildings.
Industry Trends
The ESCO industry has experienced significant growth over the past decade. According to a 2017 study by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, the U.S. ESCO industry generated $7.6 billion in revenue in 2016, representing a compound annual growth rate of 10% from 2011-2016. The ESCO market is expected to continue growing as energy efficiency and sustainability become higher priorities.
ESCOs have also started offering new services and business models beyond their traditional focus of energy performance contracts. These include public-private partnerships, on-bill financing programs, and software-as-a-service models for energy management and analytics. Some ESCOs have expanded into solar power purchase agreements, microgrids, and other distributed energy resources. Additionally, ESCOs are placing greater emphasis on water efficiency, zero waste, and other sustainability services for their clients.
Challenges
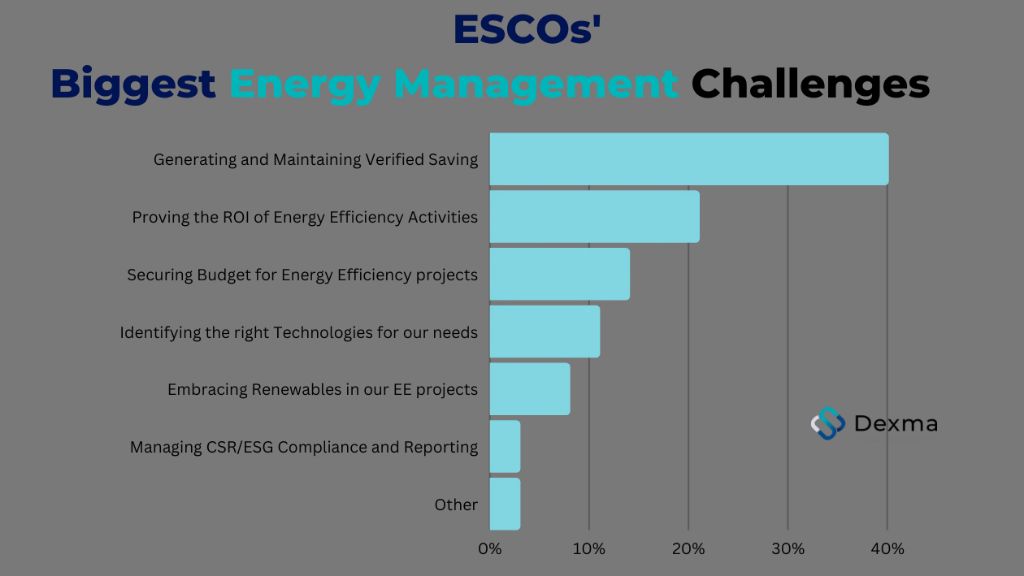
The ESCO industry faces several key challenges that can impact business operations and growth. Some of the main difficulties include:
Declining energy prices – With the shale gas boom in the U.S., energy prices have declined sharply over the past decade. This makes the payback period longer for energy efficiency projects, which reduces their attractiveness to customers. Lower energy prices make it harder for ESCOs to demonstrate the cost savings from their projects.
Access to financing – ESCO projects often require significant upfront capital expenditures which are recouped over time through energy savings. Accessing financing at reasonable rates is essential for ESCOs to grow their project pipeline. However, getting loans and credit can be challenging, especially for smaller ESCOs with limited capital and track records.[1]
Long sales cycles – The sales process for ESCO projects is lengthy, often lasting 6-12 months. Prospects must be educated on the benefits and convinced to make large capital investments. The long sales cycle ties up significant sales resources for ESCOs. Customers also tend to be risk averse and conservative when making major facility upgrades.[2]
Future Outlook
The ESCO industry is projected to continue growing steadily in the coming years. According to a LBNL report, the US ESCO industry has grown at a compound annual growth rate of 8% from 1990-2008. Although growth slowed after the 2008 recession, the industry is still expanding. LBNL projects the ESCO market size will reach $7-$12 billion by 2020.
Key areas of expansion for ESCOs include public sector projects, new technologies like LED lighting, and growth in energy service agreements (ESA) for commercial buildings. As ESCOs continue to prove the value of energy efficiency to clients, they are likely to be involved in larger, more complex projects. International expansion also represents an opportunity for major US ESCOs.
Conclusion
In summary, ESCOs are playing an increasingly vital role in improving energy efficiency and sustainability for organizations across the United States. As energy costs continue to rise, ESCOs allow companies and institutions to update outdated infrastructure and adopt renewable solutions without upfront capital expenditures. Through innovative financing methods like energy savings performance contracts, ESCOs make it financially viable for organizations to modernize.
The largest ESCOs stand out for their technical expertise, breadth of services, access to capital, and proven track records on major projects. While the ESCO industry faces challenges like unclear regulations and lack of awareness in some sectors, demand for energy efficiency is expected to drive continued growth. With their specialized knowledge and holistic approach, ESCOs will remain instrumental in building a more sustainable future.
By partnering with a leading ESCO, organizations can modernize their energy systems while minimizing risk. This enables them to save substantially on utility bills, meet emissions and sustainability targets, and focus their budgets on core operations. As energy efficiency becomes increasingly critical, ESCOs provide the experience and capabilities to turn ambitious goals into measurable results.