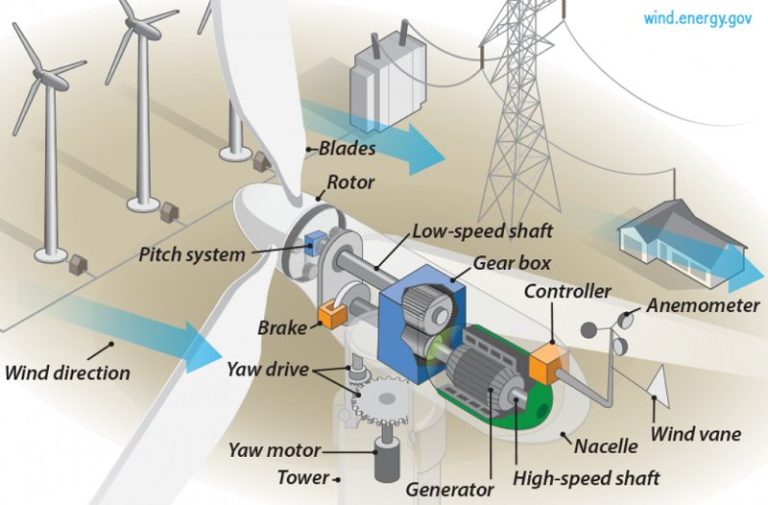
Where Is The New England Wind Farm?
The New England offshore wind project, also known as Park City Wind, is a proposed 804 megawatt offshore wind farm located off the coast of Massachusetts that is being developed by Avangrid Renewables and Copenhagen Infrastructure Partners. The project is slated to be the largest offshore wind farm in New England once completed. It represents a crucial component in helping New England states meet their renewable energy and emission reduction goals. Park City Wind has the potential to generate enough electricity to power 400,000 homes and offset over 1.3 million metric tons of carbon emissions annually. The USD $4.5 billion project is currently under review by federal and state agencies and faces some opposition from local groups, but overall it signifies the momentum behind offshore wind development along the U.S. East Coast.
Location
The New England offshore wind farm will be located off the coast of Massachusetts, approximately 20 miles south of Martha’s Vineyard and Nantucket in the Atlantic Ocean. The lease areas for the project span over 128,000 acres and are located in federal waters on the Outer Continental Shelf.
Specifically, the project will be built in two main lease areas – Lease OCS-A 0501 and Lease OCS-A 0520. Lease OCS-A 0501 is located 20 miles southeast of Martha’s Vineyard while Lease OCS-A 0520 is located 22 miles south of Nantucket and Martha’s Vineyard. The majority of the wind turbines will be installed in these two lease areas.
Overall, the geographical coordinates for the New England offshore wind project range from 40°50’N to 41°20’N latitude and 69°30’W to 70°20’W longitude. This places the wind farm in the waters between Rhode Island, Massachusetts, and islands like Martha’s Vineyard and Nantucket.
The developers have stated that the offshore location was chosen due to strong and consistent wind resources as well as proximity to coastal electricity demand centers. The lease areas also avoided any designated shipping lanes or Department of Defense exercise areas.
Project Details
The Revolution Wind Farm is a proposed offshore wind project to be located off the coast of Massachusetts in southern New England [1]. It will have the capacity to generate over 1,200 megawatts (MW) of electricity, enough to power more than 400,000 homes. The project is being developed by Ørsted and Eversource through a 50-50 partnership.
The wind farm will consist of 100 wind turbine generators spaced one nautical mile apart in an area covering 130,000 acres. Each turbine will have a capacity of 12-15 MW. The total project cost is estimated to be around $3 billion. Construction is set to begin in 2023, with the wind farm expected to be fully commissioned and operational by 2025 [2].
Developers and Partners
The New England offshore wind project is being developed through a partnership between Avangrid Renewables and Copenhagen Infrastructure Partners (CIP). Avangrid, headquartered in Orange, Connecticut, is a leading sustainable energy company and subsidiary of Iberdrola Group. CIP is a fund management company based in Denmark focused on renewable energy investments. Additional project partners include Vineyard Wind, Equinor, and Park City Wind.
Key government agencies and organizations involved include the Massachusetts Clean Energy Center, the Rhode Island Coastal Resources Management Council, the Connecticut Department of Energy and Environmental Protection, the Bureau of Ocean Energy Management, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
According to a recent article by CT Mirror (https://ctmirror.org/2023/10/03/cts-biggest-offshore-wind-project-nearly-dead-in-the-water/), the 804 megawatt Park City Wind project being developed by Avangrid and CIP recently obtained federal approval to supply renewable energy to Connecticut.
Environmental Impact
The New England wind farm went through an extensive environmental review process led by the Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM) to assess the impact on marine life. This included a draft Environmental Impact Statement (EIS) that analyzed the effects on animals like whales, sea turtles, and birds.
Overall, the EIS concluded the wind farm would have minor to moderate impacts on the environment. It found there could be some risks to certain wildlife from noise disturbance and collisions with turbines, but these were not expected to be significant. Mitigation measures like spatial planning of turbines were identified to further reduce risks. Monitoring will also occur during construction and operation to study effects on species like the endangered North Atlantic right whale.
While the wind farm will alter local habitats, BOEM determined it is not likely to jeopardize protected species or result in population-level impacts. The developer and regulators will continue working to minimize ecological harm. But the project will also have long-term benefits by displacing fossil fuel plants and helping curb climate change, which poses threats to oceans and marine life.
Sources:
https://ctmirror.org/2023/10/03/cts-biggest-offshore-wind-project-nearly-dead-in-the-water/
Community Feedback
The New England Wind offshore wind farm has received mixed feedback from local communities regarding its potential onshore impacts. According to a 2018 study by Yale University, over 90% of nearly 100 surveyed New England residents expressed support for offshore wind power [1]. However, some concerns have been raised about how the energy will be used. Research indicates that residents are less likely to support the project if the energy is transmitted to other states instead of benefiting local communities [2]. There are also concerns about impacts to coastal views and fishing areas from offshore infrastructure and onshore substations.
Economic Benefits
The New England wind farm is projected to create hundreds of local jobs during construction and operation. According to a report from the Rhode Island Office of Energy Resources, offshore wind investments could generate over 1,000 long-term jobs in fields like operations, maintenance, and port logistics [1]. Many short-term construction and development jobs will also be created. In 2016, the Department of Energy estimated the New England wind farm would support 160 full-time equivalent jobs per year over its lifetime [2].
The project will bring significant investment into the local economy. Developers have committed to investing in Rhode Island’s ports and workforce training programs. Local manufacturing and service companies will benefit from supplying turbine components, vessels, and other services. Annual operations and maintenance expenditures are projected around $10-15 million, further supporting local jobs [1]. Overall, the New England wind farm represents a major economic opportunity for the region.
Energy Production
The New England offshore wind project is estimated to generate up to 2,400 megawatts of electricity annually, enough to power over 1 million homes. This would be a major boost to meeting clean energy goals in the region. According to the developer Equinor, the project aims to contribute significantly to state mandates that utilities procure electricity from renewable sources. For example, Connecticut has a goal of procuring 2,000 megawatts from offshore wind by 2030, and this project alone could provide over half that target if fully completed.
The scale of the New England wind farm means it could make a sizable dent in the region’s carbon emissions from electricity generation. Replacing fossil fuel plants with emissions-free wind power will help states across New England reduce their greenhouse gas output. Studies have shown offshore wind in the area could reduce carbon dioxide emissions by over 5 million metric tons per year. The developers highlight the climate benefits as a key motivation behind the ambitious scope of the project.
Overall, the New England offshore wind project represents a major investment in renewable energy for the region. Meeting the estimated annual production target would be a big step towards a clean energy future and help set an example nationally for offshore wind development. The project’s scale and generation capacity reflect a commitment to harnessing this resource to combat climate change.
Future Expansion
There are plans and potential for further offshore wind development in the New England region beyond the initial wind farm projects currently underway. Massachusetts, along with neighboring states like Rhode Island, aim to continue growing the offshore wind industry off the New England coast.
In October 2023, Massachusetts joined with other New England states to announce coordinated efforts to advance additional offshore wind projects in the region. Governor Healey stated Massachusetts is “proud to join with our neighboring states to continue to grow New England’s offshore wind industry” (Vineyard Gazette).
Rhode Island in particular has been a leader in offshore wind development and has a goal of deploying 600 MW of offshore wind capacity by 2050. The state is working with developers on projects like South Fork Wind to contribute to this target (New England for Offshore Wind).
With strong wind resources off the New England coast and cross-state cooperation, there is significant potential for offshore wind to continue expanding in the region in the coming years.
Conclusion
The New England offshore wind project marks a major milestone for renewable energy in the region. With a capacity of over 800 megawatts, it will be one of the largest offshore wind farms in the United States once completed. The project demonstrates the Northeast’s commitment to transitioning to clean energy and reducing greenhouse gas emissions from the power sector. Offshore wind has huge potential to help states meet their renewable energy and emission reduction goals. This project alone will provide enough electricity to power over 400,000 homes. Its success will pave the way for more large-scale offshore wind development off the New England coast, helping accelerate the region’s clean energy transition.