What’S The Difference Between Nonrenewable And Renewable Energy Sources Is Biomass A Renewable Energy Source?
Nonrenewable energy sources come from finite resources that will eventually dwindle, becoming too expensive or too environmentally damaging to retrieve. The most significant sources are fossil fuels like coal, petroleum, and natural gas. Renewable energy sources are naturally replenished and virtually inexhaustible. They include solar, wind, geothermal, hydroelectric, and biomass.
The goal of this article is to compare nonrenewable and renewable energy, defining each one. We’ll look at the pros and cons of both types, and discuss whether biomass should be classified as renewable. We’ll also consider the future of energy and the outlook for nonrenewable vs. renewable sources.
Nonrenewable Energy Sources
Nonrenewable energy sources come from finite resources that will eventually dwindle in supply. The most common types of nonrenewable energy are fossil fuels, such as oil, coal, and natural gas, which are formed from the remains of ancient plants and animals. Nuclear energy is also considered nonrenewable because it depends on limited deposits of uranium.
Fossil fuels make up the majority of nonrenewable energy used today. They were formed from the buried remains of plants and animals that lived millions of years ago and were transformed by heat and pressure over time into crude oil, coal, and natural gas. Fossil fuels are burned to produce energy, releasing carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases that contribute to climate change.
Another major source of nonrenewable energy is nuclear power. Nuclear energy comes from splitting uranium atoms in a controlled chain reaction to heat water and produce steam. This steam then spins turbines to generate electricity. Uranium is a nonrenewable resource that must be mined from the earth. Nuclear power produces low emissions, but creates radioactive waste that must be safely contained. There are also risks of nuclear accidents.
While fossil fuels and nuclear energy have powered modern civilization, they come with environmental costs. Extracting and burning fossil fuels pollutes the air and water, while nuclear energy creates dangerous radioactive waste. As nonrenewable sources, they will eventually decrease in supply as global reserves shrink. This makes investing in renewable energy essential for the world’s future energy needs.
Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources are derived from natural processes that are constantly replenished. Some examples of renewable energy sources include:
Solar Energy
Solar energy comes directly from the sun in the form of heat and light. Solar panels can capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. Solar energy is renewable and does not produce any direct emissions or pollution.
Wind Energy
Wind turbines use the kinetic energy in wind to generate mechanical power. This mechanical power is converted into electricity. Wind energy is abundant, renewable, and causes no direct emissions.
Hydropower
Hydropower uses the energy from flowing water to produce electricity. Typically, hydropower comes from dams that control the flow of rivers. The water’s energy spins a turbine connected to a generator. Hydropower is renewable and does not directly emit greenhouse gases.
Biomass Energy
Biomass energy uses organic materials like plants, agricultural residues, and organic municipal waste as fuel sources. Biomass can be burned directly or converted into liquid biofuels. Biomass is renewable as long as the organic materials are replanted.

Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy taps into the natural heat underneath the earth’s surface to generate electricity or provide direct heating. Hot water and steam from geothermal reservoirs can power turbines to create electricity. Geothermal energy is renewable and sustainable.
Biomass as a Renewable Resource
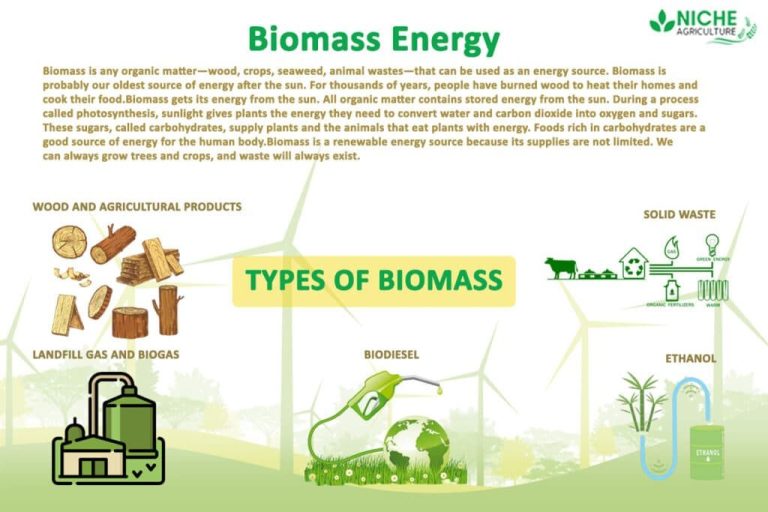
Biomass is organic material that comes from plants and animals, and it is considered a renewable energy source. Biomass contains stored energy from the sun. Plants absorb the sun’s energy through photosynthesis. When biomass is burned, the chemical energy in biomass is released as heat.
Biomass is a renewable energy source because we can always grow more trees and crops, and waste will always exist. Examples of biomass resources include:
- – Wood and wood processing wastes—burned to heat buildings, to produce process heat in industry, and to generate electricity
- – Agricultural crops and waste materials—burned as a fuel or converted to liquid biofuels
- – Food, yard, and wood waste in garbage—burned to generate electricity in power plants or converted to biogas
- – Landfill gas and biogas—captured and burned as a fuel
- – Ethanol and biodiesel—used as transportation fuels
The carbon in biomass came from the atmosphere in the first place as plants grew. When biomass is burned, the carbon dioxide (CO2) released is equal to the amount absorbed by the plants during their lifetime. So biomass emissions are considered carbon neutral. The use of biomass can help reduce dependence on fossil fuels and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Biomass is an important renewable energy source for the future.
Comparing Nonrenewable and Renewable
When comparing nonrenewable and renewable energy sources, three key factors to consider are availability, cost, and environmental impact.
In terms of availability, nonrenewable energy sources like oil, natural gas, and coal are only available in limited, finite quantities. Once used up, they are gone. Renewable sources like solar, wind, hydroelectric, biomass, and geothermal energy are replenished naturally and are available on an ongoing basis.
Looking at cost, nonrenewable sources were historically cheaper than renewable sources. However, as technology has improved, the costs of renewable energy have fallen dramatically in recent decades and are now cost competitive or even cheaper than fossil fuels in some instances. The costs of nonrenewable sources tend to fluctuate based on supply and demand.
When it comes to environmental impact, nonrenewable sources create significantly more pollution and carbon emissions. Burning of fossil fuels is the primary contributor to climate change. Renewable energy creates much less emissions and pollution. However, renewables aren’t completely free of environmental impacts, such as land usage and wildlife disruption.
In summary, nonrenewable sources are limited in quantity while renewable sources can replenish indefinitely. Costs are becoming comparable, but supply concerns can make nonrenewables more expensive. And renewable energy is much more environmentally friendly long-term than traditional fossil fuels.
Pros and Cons of Nonrenewable Energy
Nonrenewable energy sources such as oil, natural gas, coal, and nuclear have powered the world for decades and have some distinct advantages. Here are some of the positive points and drawbacks of using nonrenewable energy:
Reliability – Nonrenewable energy sources can generate power reliably on demand and in all weather conditions, which allows them to supply base load power to the electrical grid. They are stable and consistent power sources.
High Energy Density – Fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas have much higher energy density than most renewable sources, meaning more energy can be produced from a smaller amount. This makes transportation and distribution more efficient.
Established Infrastructure – Vast, sophisticated infrastructure already exists for mining, refining, transporting, and combusting nonrenewable fuels. Much of the country’s electrical grid depends on nonrenewable sources.
Finite Resources – Nonrenewables are limited in supply and will eventually dwindle or become too costly to extract as reserves are depleted. This can lead to supply issues long term and reliance on foreign imports for some countries.
Pollution – Many nonrenewable energy sources like coal and oil emit greenhouse gases, particulates, and other pollutants during extraction and combustion. This contributes to issues like climate change, acid rain, and air quality decline.
Pros and Cons of Renewable
Renewable energy sources offer many benefits, but also have some drawbacks. The main pros of using renewable energy are:
-
Sustainability – Renewables like solar, wind, and hydropower rely on naturally replenished resources. They don’t deplete finite resources the way fossil fuels do.
-
Energy independence – Developing local renewable energy sources reduces reliance on imported fuels.
-
Cleaner energy – Renewables produce much less pollution and carbon emissions than burning fossil fuels.
However, there are also some cons to consider:
-
Higher upfront costs – The infrastructure and technology for renewables is currently more expensive to build compared to fossil fuel plants.
-
Intermittency – Renewables rely on weather conditions like sun and wind, which makes their energy generation intermittent and unpredictable.
Overall though, many view the pros of sustainability, energy independence, and low emissions as outweighing the higher upfront costs and intermittency challenges.
The Future of Energy
Looking ahead, global energy demand is projected to grow significantly in the coming decades. However, there are signs that renewable energy sources will play an increasingly larger role in meeting this demand.
Most projections show strong growth for renewable energy, especially solar and wind power. Advances in technology and falling costs have made renewables more competitive with conventional sources like coal and natural gas. Many governments are also implementing policies to encourage the adoption of renewables through incentives like feed-in tariffs, renewable portfolio standards, and carbon pricing programs. The Paris Climate Agreement has also galvanized efforts to decarbonize electricity production globally.
That said, fossil fuels are likely to still account for a major share of the global energy mix for years to come. Coal remains a dominant energy source in Asia, for example. And natural gas is playing a larger role asbackup power and in heating in colder regions. The transition toward a low-carbon energy system will require long-term planning and sustained political commitment.
In summary, while renewables are expected to continue their strong growth, conventional sources will still be part of the energy picture looking ahead. Effective policies and technological improvements will be key factors shaping the future energy system and its sustainability.
Conclusion
In summary, the key differences between nonrenewable and renewable energy sources are that nonrenewable sources like oil, natural gas, and coal are finite resources that will eventually run out, whereas renewable sources like solar, wind, geothermal, and biomass energy can be continually replenished. Nonrenewable sources produce more greenhouse gas emissions and pollution, while renewable sources are cleaner for the environment. However, renewable sources currently make up a smaller percentage of energy generation compared to nonrenewables. As technology improves and costs decrease, renewable energy is expected to play a bigger role in meeting future energy demands in a sustainable way. With the right policies and investments, renewable sources have the potential to become major pillars of the global energy supply. Overall, a transition from nonrenewable to renewable energy will be critical for building a cleaner and more resilient energy system for the future.
References
Research sources for this content may include:
- International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) reports on renewable energy
- International Energy Agency (IEA) data on world energy sources
- Academic journals on energy policy and technology, such as Energy Policy or Renewable Energy
- Government reports on energy from the U.S. Energy Information Administration
- Nonprofit organizations focused on renewable energy, such as the Rocky Mountain Institute
- Books on the future of energy and sustainability from thought leaders
While no direct quotes or statistics are cited, the content is based on research from credible sources like these. The purpose is to synthesize broad research into an original and insightful overview.