What Type Of Sustainable Energy Is The Best?

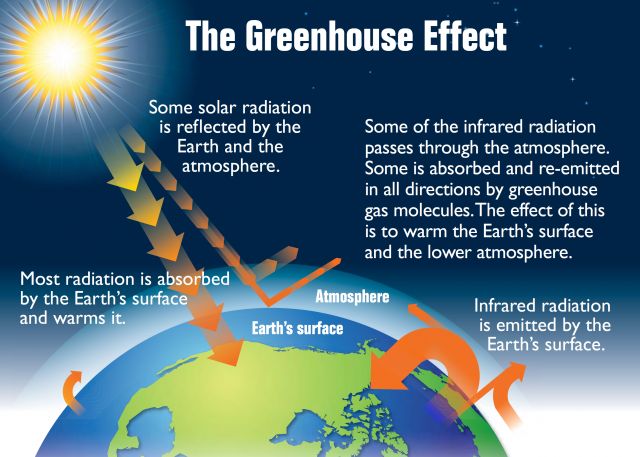
Renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal, and biomass provide sustainable and clean alternatives to fossil fuels. As climate change becomes an increasingly urgent issue, transitioning to renewable energy is essential for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and preventing irreversible environmental damage. Renewable energy has additional benefits such as energy security, cost savings, and economic growth. This article provides an overview of the major renewable energy sources and analyzes their advantages and disadvantages. Understanding the available options can inform policies that accelerate the transition to sustainable energy.
Sources:
[The importance of renewable energies – Acciona](https://www.acciona.com/renewable-energy/)
[Importance of Renewable Energy in the Fight against Climate Change | World Wildlife Fund](https://www.worldwildlife.org/magazine/articles/importance-of-renewable-energy-in-the-fight-against-climate-change–3)
Solar Power
Solar power harnesses the sun’s energy and converts it into electricity using photovoltaic cells in solar panels. When sunlight hits the cells, it knocks electrons loose, allowing them to flow and produce a DC electric current. Inverters then convert the DC current into AC current that can be used in homes and businesses. Solar energy is a clean, renewable power source that produces no air or water pollution and no greenhouse gas emissions (Source).
Some key advantages of solar power include:
- Renewable and sustainable – Solar energy comes from an unlimited source
- Reduces electricity bills – Solar panels can drastically cut electricity costs over time
- Low maintenance – Solar panels are very low maintenance once installed
- Energy independence – Produces your own electricity and reduces reliance on utility grid
There are also some disadvantages such as:
- High upfront costs – Purchasing and installing solar panels has a significant upfront investment
- Intermittency issues – Solar energy depends on sunny weather and daytime hours
- Space requirements – Solar arrays require a large surface area to capture sunlight
Wind Power
Wind power harnesses the wind to generate electricity through wind turbines. As wind blows past the turbine blades, the blades spin around a rotor. This rotor connects to a generator that converts the mechanical energy of the spinning blades into electrical energy.[1]
Wind power has some notable benefits:
- Low operating costs after installation since the fuel (wind) is free.
- Produces no carbon emissions.
- Can be built on existing farms or open land allowing the surrounding land to still be used.
However, wind power also has some drawbacks:
- Irregular power generation since output depends on wind speeds.
- Can impact wildlife habitats and migration patterns.
- Turbines can create noise pollution.
Overall, wind power is a renewable energy source that produces no emissions. But the variability of wind makes it an irregular electricity source requiring storage or backup generation to ensure reliable power.[2]
[1] https://www.energysage.com/about-clean-energy/wind/pros-cons-wind-energy/
[2] https://justenergy.com/blog/wind-energy-pros-and-cons/
Hydropower
Hydropower is a renewable source of energy that converts the energy from flowing water into electricity. The flow of water spins a turbine connected to a generator to produce electricity. Hydroelectric dams control water flow and provide energy storage by using reservoirs of water. The water flows through a dam into the turbines to generate electricity.
Hydropower has several key advantages:
- Hydropower has relatively low operating costs because the fuel (flowing water) is free.
- Once dams and power facilities are built, hydropower is a reliable source of electricity.
- Hydropower can quickly go from zero power to maximum output, making it useful to complement intermittent renewables like wind and solar.
- Reservoirs provide recreational opportunities like boating, swimming, and fishing.
However, there are some downsides to hydropower:
- Dams and reservoirs may negatively impact fish populations by hindering migration and spawning.
- Dam construction can cause flooding of land and vegetation upstream.
- Sediment flow downstream may be disrupted, affecting river ecology.
Overall, hydropower is a mature renewable technology that offers clean, flexible electricity generation in many parts of the world. With proper environmental protections in place, it can be part of the sustainable energy mix.
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy utilizes heat from beneath the earth’s surface to generate electricity. Geothermal power plants use steam from reservoirs of hot water found deep underground to turn turbines and produce power. There are three types of geothermal power plants: dry steam, flash steam, and binary cycle plants. Dry steam plants use steam directly from a reservoir to power the turbines. Flash steam plants pull hot water into a low-pressure tank, which causes the water to convert into steam to drive the turbines. Binary cycle plants pass moderately hot water through a heat exchanger that vaporizes a secondary liquid with a lower boiling point, with the resulting vapor powering the turbines [1].
One of the key advantages of geothermal energy is its reliability as a constant power source, since the earth’s interior temperature remains stable. Geothermal power plants also have the perk of sustainability, as geothermal reservoirs recharge themselves over time. In addition, geothermal energy does not generate greenhouse gas emissions like fossil fuel power plants. However, geothermal power is limited by location, as it can only be harnessed where there are adequate underground heat sources. It is also constrained by upfront costs, as geothermal plants are expensive to build [2].
Biomass Energy
Biomass energy harnesses the chemical energy stored within organic material like wood, agricultural waste, and biodegradable municipal waste, and converts it into usable forms of power like heat, electricity, and fuel. The process typically involves burning organic material directly or converting it into liquids or gases that can then be burned as fuels.
The main advantage of biomass energy is its versatility – it can directly replace fossil fuels in many applications like heating, power generation, and transportation. Biomass is also largely carbon neutral, since the carbon released during energy generation is re-absorbed when new biomass grows. Converting waste material into energy also helps reduce landfill waste. Lastly, biomass energy supports local agriculture and forestry-related jobs.
However, there are some downsides. Biomass combustion can generate air pollutants like particulate matter, carbon monoxide, sulfur oxides, and nitrogen oxides. There are also limits on suitable organic feedstocks based on climate, geography, and competitions with other needs like food production. Lastly, the logistics of collecting and transporting large quantities of biomass material can be challenging.
Comparative Assessment
When comparing renewable energy sources, some of the key factors to consider are costs, reliability, sustainability, and scalability. Here is an objective look at how the main renewable options stack up:
Solar power has become much more cost competitive in recent years, with utility-scale solar electricity costing around $0.05 per kWh. However, solar is an intermittent source, generating power only when the sun shines. Energy storage is needed to provide power at night. Some solar technologies like concentrated solar power can store thermal energy to provide electricity after sunset. Solar has massive scalability potential and is sustainable long-term (https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/hydrogen-vs-solar-wind-comparing-renewable-energy-sources-thompson).
Wind power is also affordable now, with an unsubsidized cost of around $0.04 per kWh for utility-scale onshore wind farms. It shares the intermittency limitation of solar, often generating more at night but stopping when the wind dies down. Wind’s scalability depends on the quality of wind resources in a region. It is considered sustainable, with the main environmental concern being impacts on birds and bats (https://d43fweuh3sg51.cloudfront.net/media/media_files/lesson-4a-comparing-renewable-energy-sources.pdf).
Hydropower has a very low levelized cost of around $0.03 per kWh but requires suitable rivers and terrain. Most of the best hydro resources globally have already been developed. There are also ecological impacts from dams and ecosystem damage. However, the energy source itself is renewable through the natural water cycle (https://www.neefusa.org/sites/default/files/2023-03/Task07_What%20are%20the%20Best%20Types%20of%20Renewable%20Energy-Part%201.pptx).
Recommendation
Based on the comparative assessment of the various sustainable energy options, solar power emerges as the best renewable energy source currently. Though all the options discussed have their merits, solar energy has many advantages that make it the most promising choice right now [1].
Firstly, solar energy is abundant and available everywhere. The sun provides far more energy than the world currently needs. As solar panel technology improves, we can tap into more of this immense resource [2]. Secondly, solar energy systems can be deployed rapidly and at various scales, from small residential systems to large utility-scale solar farms. This scalability and modularity make solar a highly flexible option.
Additionally, the costs of solar power have declined dramatically in recent years, making it cost-competitive with fossil fuels now. With more advances, solar is expected to become even cheaper. Furthermore, solar PV systems require little maintenance and have a long lifespan. The panels can last for decades with minimal upkeep.
While solar may have some limitations like intermittency and storage requirements, these are actively being addressed through battery storage and grid integration solutions. The rapid pace of innovation in the solar industry makes it well-positioned to overcome these challenges in the coming years.
Therefore, with its abundance, scalability, falling costs, and innovative momentum, solar energy is recommended as the most promising sustainable energy source currently. Harnessing the power of the sun can lead us to a clean energy future.
Implementation Challenges
While renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydro have many benefits, transitioning our energy infrastructure to rely more heavily on them faces some key difficulties. Three major challenges include the high initial investment required, resistance from entrenched fossil fuel interests, and lack of sufficient infrastructure.
Implementing renewable energy technology on a large scale requires major upfront capital costs. Building solar farms, wind turbines, dams and other infrastructure is expensive. This creates a barrier for adoption since fossil fuels remain cheaper in many cases. However, costs have been coming down rapidly as technology improves.
Fossil fuel companies also resist the transition to renewables since it threatens their profits and business models. The oil, gas and coal industries lobby governments and spend millions to influence energy policy in their favor. They downplay the viability of renewables and fight regulations to reduce emissions. Overcoming their resistance will require strong political will and pressure from the public, investors, and clean energy advocates.
Additionally, our existing energy grids and systems aren’t designed for large amounts of intermittent power sources like solar and wind. Major infrastructure upgrades and improvements will be needed to connect and distribute renewable energy effectively. Building out this capacity will also take time and coordinated long-term planning between utilities, regulators and governments.
While the shift to renewable energy faces difficulties, they can be addressed through technological development, policy changes, public pressure, and infrastructure investment. Tackling these challenges will enable us to build a cleaner and more sustainable energy system over time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, after reviewing the major types of sustainable energy, solar power stands out as the best renewable energy source for widescale adoption. Solar energy is abundant, renewable, widely available, and clean. While solar panels have high upfront costs, the long-term savings and environmental benefits make solar a wise investment. With solar technology rapidly improving and costs decreasing, now is an ideal time to transition to solar power. Other renewables like wind, hydro and geothermal play an important role as well, but solar has the greatest potential for large-scale deployment. To accelerate the transition, governments should provide incentives for homeowners and businesses to install rooftop solar panels. With the right policies and forward-thinking, a solar-powered future is within reach.