What Turns Wind Into Power?
Over the last few decades, wind power has emerged as one of the fastest growing and most promising renewable energy sources worldwide. As concerns over climate change and dependence on fossil fuels mount, many view wind as a critical part of building a sustainable energy future. But what exactly turns the kinetic energy of wind into usable electricity? In this article, we’ll unpack the mechanics behind wind power generation and highlight some key facts around this increasingly pivotal technology.
What is Wind?
Wind is simply air in motion. It is caused by the uneven heating of the earth’s surface by the sun. As the earth’s surface absorbs the sun’s radiation, the atmosphere warms unevenly. Warmer air expands and rises, while cooler air contracts and sinks. This movement causes wind patterns across the earth.
The rotation of the earth also impacts global wind patterns. The Coriolis effect causes wind to curve as air moves from high to low pressure zones in the Northern and Southern hemispheres. Wind flows clockwise around high pressure zones in the Northern hemisphere while it flows counterclockwise around those in the Southern hemisphere. The jet stream is also influenced by the Coriolis effect and helps determine weather patterns across the world.
Wind speed and direction are determined by differences in air pressure and forces like the Coriolis effect. Over the course of a day, the strength and direction of wind can change significantly. However, over the course of seasons and years, predominant wind patterns emerge for a given location based on climate and geography.
Wind Turbine Design
Modern wind turbines consist of a few main components that allow them to convert the kinetic energy in wind into electrical energy. The key components are:
- Rotor – The blades and hub that rotate when wind blows past them.
- Nacelle – The body that sits atop the tower and contains the gearbox, generator, controller, etc.
- Tower – Supports the nacelle and rotor high up where wind speeds are greater.
- Generator – Converts the rotational mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- Gearbox – Increases the rotational speed from the rotor to spin the generator faster.
- Yaw System – Orients the nacelle and rotor into the wind.
- Anemometer – Measures wind speed and sends data to the controller.
- Controller – Starts up the turbine at set wind speeds and shuts it down if winds are too high.
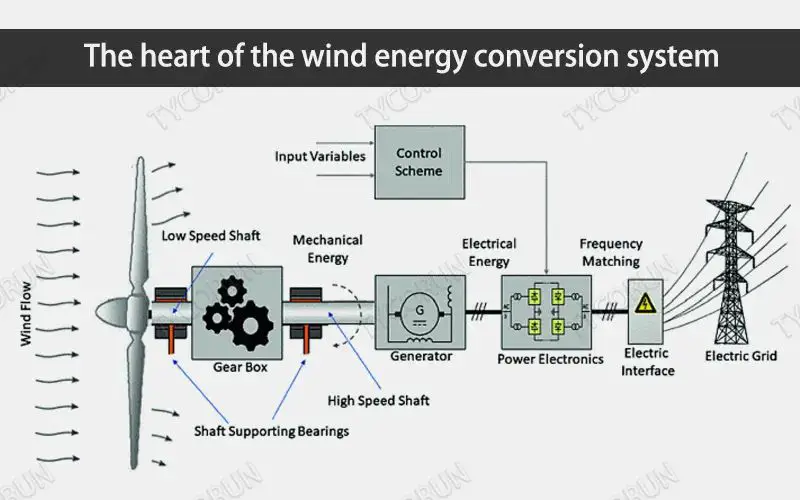
The blades are made to capture the wind energy and rotate at a variable speed based on wind conditions. The rotational energy is transferred via a main shaft through the gearbox which increases the rotations per minute. The high speed shaft then turns the generator to produce electricity. The power output is continuously regulated by controlling the generator and blade pitch angle.
Generating Electricity
The wind turbine converts wind energy into rotational kinetic energy and then into electrical energy through a series of components inside the turbine. Here is how it works:
The rotor blades capture the wind and rotate the main shaft connected to them. The rotor is connected to a gearbox which increases the rotational speed coming into the generator. The generator contains magnets which rotate around copper wire coils, creating an electromagnetic field that pushes electrons through the coils and generates an electric current. This electric current is fed into a transformer which converts it from low voltage to high voltage so it can be transmitted efficiently. Finally, the electricity is sent through cables down the turbine tower and fed into the utility grid for everyday use.
So in summary, the wind first spins the blades, which spin a shaft connected to a gearbox and generator, creating an electromagnetic field that generates electricity. With this elegant conversion process, the natural kinetic energy of the wind gets turned into usable electrical power for our homes and businesses.
Wind Farm Setup
Setting up a wind farm requires extensive planning and coordination. Choosing the right location is crucial – areas with consistent strong winds, available transmission lines, appropriate zoning, and access to roads and construction equipment are ideal. The wind turbines, which can be over 300 feet tall, must be spaced properly to avoid interfering with each other’s wind flow.
Once a site is selected, the land must be cleared and access roads constructed. Foundations are poured, sometimes secured with steel rebar cages. Crane pads are prepared so the massive cranes used to erect the turbines have a stable, level base. The wind turbine components like the tower sections, nacelle, hub, and blades are trucked in and staged near their assembly locations.
The tower sections are bolted together and secured to the foundation. The nacelle, containing the gearbox, generator, controller and other components, is lifted to the top of the tower. The blades are attached to the hub which connects to the nacelle. Wires run from the nacelle down the tower to connect to an underground collector system which aggregates the power output. This connects to a substation which steps up the voltage so it can be transmitted long distance over power lines to connect with the electric grid.
Once fully assembled and connected, the wind turbines operate automatically to maximize power production while specialized software and computer controls monitor performance and grid conditions. Technicians perform regular maintenance at each turbine to keep them functioning properly. With hundreds of turbines in some large wind farms, operating and maintaining them is a highly complex endeavor.
Pros of Wind Power
Wind power has several advantages that make it an attractive renewable energy source. Some of the main pros of wind power include:
Cost – Once a wind farm is set up, the cost of generating electricity is very low. Wind power is cheaper than fossil fuels and competitive with other renewable energy sources like solar power. The fuel itself (wind) is free.
Renewable – Wind is a renewable energy source that will never run out. This makes wind a sustainable long-term solution compared to finite sources like coal, oil, and natural gas. Wind farms can continue producing clean energy for decades.
Clean Energy – Wind power creates no air or water pollution because no fuels are burned. Expanding wind energy can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.
Domestic Source – Wind farms can be built on land to supply renewable electricity to local communities. This limits dependence on imported fuels. Good wind resources are available in many regions globally.
Jobs – Constructing and operating wind farms creates employment opportunities. Wind turbine technicians are currently one of the fastest growing occupations in the U.S.
Cons of Wind Power
While wind power offers many benefits, it also has some drawbacks that need to be considered. One of the main cons of wind power is its intermittent nature. The wind doesn’t blow all the time, so wind turbines only generate electricity when the wind speed is sufficient. This can make wind power unreliable as a continuous source of energy.
Land use is another potential con of wind power. Wind farms require large areas of land, since turbines need to be spaced far apart to maximize wind capture and minimize turbulence. The land between turbines can still be used for farming or grazing, but the turbines themselves and associated infrastructure like access roads take up space. There are also concerns about the visual impact and noise of wind turbines for people living nearby.
Wind power can also have environmental impacts on birds and bats that may collide with turbines. Proper site selection and turbine design can help minimize risks, but it remains a consideration. The manufacturing, construction, and eventual decommissioning of turbines also comes with greenhouse gas emissions that should be weighed against the clean energy generated.
Lastly, wind power can be more expensive than conventional sources depending on the location of the wind farm and government subsidies. Transmission infrastructure is needed to bring wind energy from favorable wind sites to population centers. While costs have come down dramatically, wind is still one of the more expensive renewable energy sources.
Interesting Facts About Wind Power
Here are some fascinating facts about wind power:
- Wind power is one of the fastest growing energy sources in the world. Global wind power capacity has increased over 25% annually in recent years.
- As of 2019, the country with the most installed wind power capacity is China, followed by the United States, Germany, India and Spain.
- The largest wind farm in the world is Gansu Wind Farm in China. It has a capacity of over 6,000 MW generated by more than 7,000 wind turbines.
- Wind turbines can now be built taller than the Eiffel Tower. Modern wind turbines are usually around 200 meters high.
Future of Wind Power
The future looks bright for wind power. As technology continues to advance, wind turbines are becoming more efficient and cost-effective. Several innovations are driving growth in the wind industry:
Larger turbines: New wind turbines have larger blades spanning over 120 meters across. These massive turbines can generate more power at lower wind speeds. Wind farm developers are increasingly using these larger models.
Offshore wind farms: Installing wind farms offshore provides access to stronger and more consistent winds. Floating offshore platforms are also being developed that can access deeper water areas. The Biden administration has set a goal for the U.S. to deploy 30 gigawatts of offshore wind by 2030.
Smart turbines: New computer software helps optimize the performance of wind turbines. This allows the blades to be adjusted precisely based on changing wind conditions to maximize power generation.
Increased height: Taller wind turbine towers allow access to stronger winds and boost energy production. Tower heights have grown from 50-60 meters to over 140 meters for some next-generation designs.
With these technology improvements, wind power is poised to continue expanding its share of renewable energy generation worldwide. Costs are expected to fall, making wind an increasingly competitive source of clean electricity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, wind power harnesses the renewable energy of wind to generate clean electricity. Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of wind into mechanical power, which then turns electrical generators to produce electricity. Wind farms comprised of multiple turbines provide grid-scale renewable energy. Wind power emits no greenhouse gases during operation and helps lower our dependence on fossil fuels. While wind power has limitations like intermittent generation, advances in technology like taller turbines, software, and energy storage help maximize productivity. Overall, wind energy holds great potential as a sustainable part of our clean energy future.