What Is The Role Of Photosynthesis In The Carbon Cycle Quizlet?
Photosynthesis and the carbon cycle are key biological processes that shape life on Earth. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into oxygen and energy-rich glucose molecules. The carbon cycle describes how carbon atoms are recycled through the biosphere, lithosphere, atmosphere, and oceans.
Photosynthesis plays a central role in the carbon cycle by absorbing atmospheric carbon dioxide and converting it into organic carbon compounds like carbohydrates. As plants respire and decay, this fixed carbon is released back into the atmosphere or deposited in soil. The carbon cycle maintains a balance of carbon in the environment across various reservoirs like the atmosphere, biosphere, oceans, and geologic deposits.
Overview of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process plants use to convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into energy in the form of glucose or sugar. This process takes place in plant leaves and requires chlorophyll. The overall chemical reaction looks like this:
6CO2 + 6H2O + Light Energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Where:
- CO2 = Carbon Dioxide
- H2O = Water
- Light Energy = Energy from Sunlight
- C6H12O6 = Glucose (sugar)
- O2 = Oxygen
So in summary, the inputs for photosynthesis are carbon dioxide, water and sunlight. The outputs are glucose (sugar) and oxygen. The glucose is used by plants for energy and to build other molecules like cellulose and starch. The oxygen is released into the atmosphere as a byproduct.
The Carbon Cycle
The carbon cycle is the process by which carbon moves through the Earth’s atmosphere, land, water and living things. Carbon is a building block for all life on Earth because it is found in all organisms.
Carbon moves between the atmosphere, land, plants, animals and oceans in a continuous cycle. Plants and aquatic organisms absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and oceans through photosynthesis. Animals consume plants and other carbon-containing organisms and release carbon through respiration. Dead plants, animals, and waste products contain carbon and are decomposed by bacteria, returning carbon to the atmosphere or oceans. Carbon is also moved through the environment when forests burn or fossil fuels are burned for energy.
While carbon is constantly cycling through ecosystems, the amount of carbon in the environment remains balanced over time through this natural recycling. Human activities such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation have upset the natural carbon cycle by adding excess carbon to the atmosphere and oceans.
Role of Photosynthesis in Carbon Cycle
Photosynthesis plays a crucial role in the carbon cycle by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and converting it into organic compounds like glucose. During photosynthesis, plants, algae and cyanobacteria take in CO2 from the air and, using energy from sunlight, convert it into carbohydrates. The overall chemical reaction looks like this:
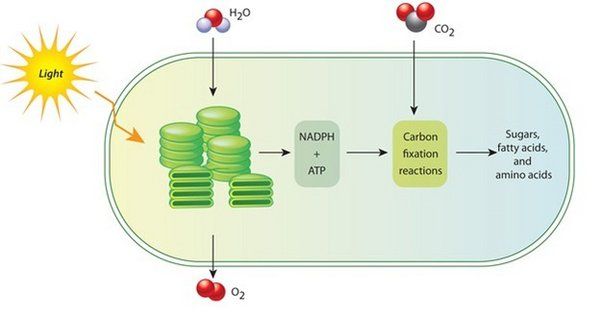
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
This reaction takes place in chloroplasts within plant cells. The CO2 enters the leaves through stomata, tiny pores on the underside of the leaf. Using the radiant energy from the sun, the chloroplasts split the CO2 molecules and combine the carbon with hydrogen and oxygen to form glucose or other carbohydrates. In this way, carbon atoms from CO2 in the atmosphere become incorporated into plant matter. Photosynthesis thus acts as a sink for atmospheric CO2, absorbing it and converting it into biological compounds.
Through photosynthesis, plants play a critical role in the carbon cycle by removing CO2 from the air and incorporating the carbon into their tissues. All organisms depend on photosynthesis to provide the carbohydrates and oxygen needed for life.
Photosynthesis Stores Carbon
Photosynthesis is the process plants use to convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into glucose for energy and oxygen. This process allows plants to absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and incorporate the carbon into their tissues. During photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide (CO2) through small pores on their leaves called stomata. The CO2 molecules combine with water molecules, using energy from sunlight, to produce glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (O2). The glucose provides plants with the energy and carbon they need for growth and maintenance. The oxygen is released back into the atmosphere.
Because plants absorb CO2 and incorporate the carbon into their tissues, photosynthesis effectively removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and stores it within plants. Through this process, the carbon that makes up plants originates from carbon dioxide in the air. Photosynthesis is the primary means by which carbon dioxide is extracted from the atmosphere and stored in organic matter. This storage or “sink” of carbon can remain locked up in plant tissues for quite a long time.
Respiration Releases Carbon
Plants not only take in carbon through photosynthesis, but they also release carbon back into the atmosphere through a process called cellular respiration. When plants use the glucose they produce during photosynthesis, they break down the glucose molecules and release carbon dioxide as a byproduct. Respiration occurs continuously day and night, while photosynthesis only occurs in the presence of sunlight. Therefore, while photosynthesis stores carbon in plants during the day, respiration returns some of that stored carbon to the atmosphere at night.
This cycle of plants taking in and releasing carbon helps maintain balance in the global carbon cycle. Photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide from the air, while respiration contributes it back. However, plants store more carbon through photosynthesis than they release through respiration. These carbon stocks in plants contribute to reducing the total carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere, helping to combat climate change.
Decay or Combustion Releases Carbon
When plants die, their tissues and cells begin to break down through a natural process called decay. Fungi, bacteria, and other decomposer organisms consume and break down the complex organic molecules in dead plant matter into simpler inorganic compounds. In particular, the carbon that was stored in the plant’s biomass through photosynthesis is released back into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide gas during decay.
In addition to natural decay, the burning or combustion of dead plant material also converts the carbon stored in plants back into atmospheric carbon dioxide. Wildfires, the burning of crop residues after harvest, and the burning of wood for fuel all release large quantities of carbon dioxide quickly into the air from the combustion of plant biomass.
Therefore, decay and combustion both serve as major pathways for converting organic plant carbon back into inorganic carbon dioxide gas. The carbon that was fixed into plant biomass through photosynthesis is thus released back into the air when those plants die, continuing the cyclic movement of carbon through the biosphere.
Carbon Enters Atmosphere
Carbon returns to the atmosphere through the processes of respiration and decay. Respiration occurs when living organisms like animals, plants, bacteria and fungi breathe. This releases carbon dioxide as a byproduct. When organisms die and their remains decay or are burned in fire, this also releases carbon back into the atmosphere.
Both respiration and decay convert organic carbon compounds like carbohydrates, fats and proteins back into carbon dioxide gas. This carbon dioxide then enters the atmosphere where it is available for reuse by photosynthesizing organisms. The cycling of carbon between the atmosphere, living things and dead organic matter is part of the larger carbon cycle.
Carbon Recycled Through Photosynthesis
The carbon that is released into the atmosphere by respiration and decomposition is recycled and reabsorbed through the process of photosynthesis. As plants perform photosynthesis, they take in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and convert it into glucose, storing the carbon in their tissues. This carbon makes up the plants’ stems, leaves, roots, fruits and more. So photosynthesis acts as the recycling mechanism in the carbon cycle, taking carbon expelled through other processes and incorporating it back into organic matter. Without photosynthesis continuously pulling carbon back out of the atmosphere, respiration and decomposition would fill the atmosphere with too much carbon dioxide for life to be sustained. The recycling of carbon through photosynthesis is crucial for maintaining balance in the carbon cycle.
Conclusion
In summary, photosynthesis plays a vital role in the carbon cycle by removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and converting it into carbohydrates in plants. The carbon stored in plants can then be passed along the food chain as animals consume plants. Respiration and decomposition return carbon to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide, allowing the cycle to continue. Photosynthesis is the only major process by which carbon is removed from the atmosphere and stored in organic matter. Without photosynthesis, carbon would continue building up in the atmosphere. Therefore, photosynthesis provides an essential service to the carbon cycle by absorbing this greenhouse gas from the air and incorporating the carbon into new plant matter.