What Is The Renewable Energy Initiative In Qatar?
Qatar is one of the world’s leading producers and exporters of oil and natural gas. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, Qatar has the third largest natural gas reserves in the world after Russia and Iran, with over 25 trillion cubic meters. As of 2021, over 60% of Qatar’s GDP came from oil and gas exports.
Qatar’s economy and government budget is heavily reliant on income from oil and gas exports. The country has profited immensely over the past two decades from the increase in global energy prices. However, Qatar has also recognized the need to diversify its economy and reduce its carbon emissions in line with climate change goals. This has led to initiatives aimed at increasing renewable energy and sustainability.
Overview of Qatar’s Renewable Energy Initiative
Qatar’s renewable energy initiative started in 2008 when the country established the Qatar National Food Security Programme. This led to the creation of the Qatar National Development Strategy 2011-2016, which set a target for Qatar to generate 2% of its energy from solar power by 2030.
In 2012, Qatar established the Qatar General Electricity & Water Corporation’s (KAHRAMAA) Renewable Energy Department to oversee renewable energy development in the country. KAHRAMAA launched an official renewable energy strategy in 2018 with the goal for 20% of Qatar’s electricity to come from solar energy by 2030.
The renewable energy initiative is led by the government and key organizations like KAHRAMAA and the Qatar Environment & Energy Research Institute (QEERI) to support renewable energy growth in Qatar.
Goals & Targets
Qatar has set ambitious renewable energy goals and targets in its nationwide initiative. In 2008, Qatar established the Qatar National Vision 2030, which set a target for Qatar to obtain 20% of its energy from renewable sources by 2030. Specifically, it aims to install up to 5 gigawatts of solar energy and 1 gigawatt of waste-to-energy capacity by 2030.
In 2011, Qatar established the Qatar National Development Strategy 2011–2016, which set interim renewable energy targets of 2% by 2016 and 6% by 2020. In 2016, Qatar updated its strategy in the Qatar National Development Strategy II 2018-2022. This strategy aimed for 10% of Qatar’s energy to come from renewable sources by 2022.
More recently in 2021, Qatar Energy set a target of producing 25% of its electricity from solar energy by 2030 as part of its sustainability strategy. It is making steady progress towards these national renewable energy goals through large-scale investments and projects.
Progress So Far
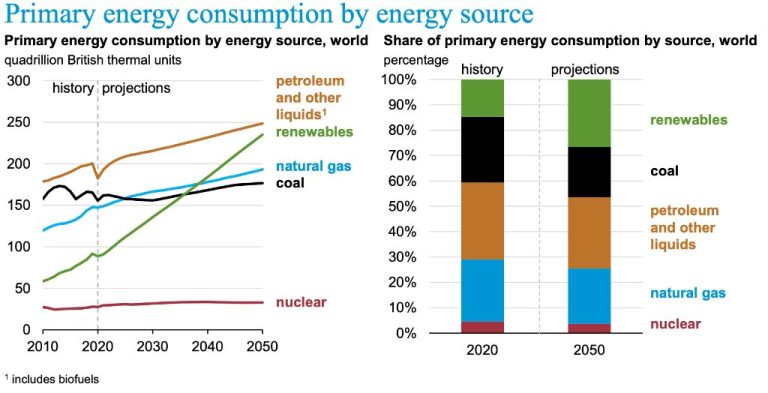
Qatar has made significant progress in developing renewable energy sources over the last decade, although starting from a very low base. As of 2018, renewable energy accounted for less than 0.2% of Qatar’s total energy mix. However, Qatar has set a target for 20% of its electricity to come from renewable sources by 2030. To meet this goal, Qatar is rapidly scaling up investments in solar, wind and waste-to-energy projects.
In terms of capacity, Qatar had just 13 megawatts (MW) of installed solar power in 2018. By 2022, this had increased exponentially to over 1,000 MW, thanks to large-scale solar plants like Al Kharsaah (800 MW) coming online. Qatar is also making progress on wind energy, with the Al Daayen wind farm slated to provide 105 MW when completed in 2024. Overall, Qatar aims to install 3,200 MW of additional renewable power capacity by 2030.
As a result of these new renewable projects, the share of Qatar’s electricity generated from clean energy is projected to reach around 10% by 2024. While still below the 2030 target, this demonstrates an impressive trajectory given Qatar’s heavy reliance on natural gas. Continued investments and capacity building in solar, wind and waste energy will be key to fulfilling Qatar’s renewable energy goals going forward.
Key Renewable Energy Projects
Qatar has several major solar and wind projects completed or underway as part of its renewable energy initiative:
The Al Kharsaah Solar Power Plant is one of the largest solar projects in the world. With a capacity of 800 MW, the $467 million project spans over 10 square kilometers west of Doha and will meet about 10% of Qatar’s peak electricity demand when completed in 2022 (source). Construction began in 2019 by Total and Marubeni as part of Qatar’s plans to utilize solar power for 20% of its energy by 2030.
The Al Shaheen offshore oil field project will supply 80 MW of solar power by 2023, becoming one of the world’s largest solar projects in an onshore oilfield. The project is being developed by QatarEnergy and TotalEnergies (source).
The 800 MW Al Kharsaah Solar PV Independent Power Project achieved financial close in March 2022. The $467 million project is being developed by a consortium of TotalEnergies and Marubeni as part of Qatar’s plans to produce 20% of its energy from solar by 2030 (source).
In 2021, QatarEnergy awarded a contract to Consolidated Contractors Company for the Al Kharsaah Solar PV Plant, which will have a capacity of 800 MW (source).
Investments
The Qatar government and private companies have made major investments in renewable energy projects in recent years. According to Dentons, in May 2023 Qatar announced a US$630 million investment in two further solar plants in Mesaieed and Ras Laffan industrial cities. The Qatar Investment Authority has also made sustainability a key investment focus, allocating over $5 billion to green technologies and sustainable companies.
Additionally, the Al Kharsaah solar power plant received over $500 million in international investment, with a consortium of Total Solar and Marubeni developing the project. According to Euromoney, this 800 MW plant will be one of the largest solar farms in the world upon completion.
These major investments highlight both the government and private sector’s commitment to scaling up renewable energy to meet Qatar’s national sustainability goals.
Challenges & Critiques
While Qatar has set ambitious goals for renewable energy development, there have been some challenges and critiques of the progress made so far. The renewable energy target of 20% by 2030 has been described by some as not aggressive enough, considering Qatar’s high solar irradiance and wind speeds (Source). There are concerns that natural gas will continue to dominate Qatar’s energy mix for decades to come.
Some of the key challenges for scaling up renewable energy in Qatar include the high upfront costs, the need for storage solutions to address intermittency of solar and wind, and developing the grid infrastructure to handle variable renewable energy sources (Source). The renewable energy investments and projects so far represent only a fraction of Qatar’s fossil fuel infrastructure and energy system.
Critics argue that Qatar could be transitioning to renewable energy at a faster pace, given its immense financial resources. However, the lack of domestic manufacturing capabilities, limited solar or wind expertise, and the absence of competitive procurement practices have constrained the growth of renewables.
Future Outlook
Qatar has ambitious plans for renewable energy growth over the next 5-10 years. According to the Qatar National Vision 2030, the country aims to generate 20% of its electricity from renewable sources by 2030. To achieve this target, Qatar is planning major investments in solar and wind energy projects.
One key development is the Al-Kharsaah Solar Power Plant, which will be the largest solar project in Qatar’s history. When completed in 2022, Al-Kharsaah will have an 800 MW capacity and provide 10% of Qatar’s electricity needs. Qatar is also developing additional large-scale solar plants, with a total capacity of over 2 GW in the pipeline.
For wind energy, Qatar plans to develop wind farms with a total capacity of 500 MW by 2024. Major wind projects currently under development include the Dukhan and Umm Al-Houl wind farms. Going forward, Qatar aims to scale up investments in wind energy and harness its wind power potential.
Overall, renewable energy investments are expected to reach over $3-5 billion by 2025 to meet Qatar’s targets. The country’s focus and policy support for renewables will continue driving rapid growth over the next decade.
Benefits
The renewable energy initiative in Qatar provides many benefits, including economic, environmental, and social benefits.
Environmentally, renewable energy helps reduce Qatar’s carbon emissions and environmental impact. Compared to fossil fuels, renewable energy sources like solar and wind energy produce little to no greenhouse gases or other pollutants (https://www.dentons.com/en/insights/alerts/2023/may/10/qatars-plans-for-renewable-energy). This supports Qatar’s climate goals and protects local ecosystems.
Economically, investing in renewable energy diversifies Qatar’s energy mix and provides energy security. As Qatar transitions from reliance on oil and gas, renewable energy creates new jobs and industries. Qatar is hoping to become an exporter of renewable energy technology and expertise to the region (https://alannabielectronics.weebly.com/blog/benefits-of-switching-to-solar-energy-in-qatar).
Socially, renewable energy improves quality of life by reducing pollution and environmental degradation. It also enhances sustainability, which allows Qatar to preserve its natural resources for future generations. Renewable energy projects engage local communities and provide educational opportunities.
Conclusion
In summary, Qatar’s renewable energy initiative is an important endeavor to transition the country towards clean energy sources and reduce dependence on fossil fuels. The government has set ambitious targets for renewable energy adoption, including 20% of electricity generation from solar power by 2030. Major investments have been made in large-scale solar and wind energy projects to help meet these goals.
While progress has been steady, Qatar still faces challenges in scaling up renewable energy, such as the high costs compared to natural gas and logistical difficulties. However, the country is committed to overcoming these hurdles. Transitioning to renewables will bring many long-term benefits for Qatar, from creating new high-tech jobs and economic diversification to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. The renewable energy initiative serves as a model for other nations looking to embrace clean energy. By persisting with this undertaking, Qatar can solidify its position as a pioneer of sustainability in the Gulf region.