What Is The Most Environmentally Friendly Energy?
Environmentally friendly energy refers to energy sources that do not deplete natural resources or cause significant damage to the environment. The goal is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and reliance on fossil fuels by transitioning to renewable energy sources. When determining which energy sources are most eco-friendly, factors like carbon emissions, pollution, waste, and land/water use must be considered. Based on a holistic evaluation, this article argues that wind and solar energy are currently the most sustainable and environmentally friendly options.
Solar
Solar power has emerged as one of the most environmentally friendly sources of renewable energy. Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity without emitting greenhouse gases or other pollutants (UCSUSA). According to the U.S. Department of Energy, solar energy plays an important role in reducing emissions and mitigating climate change (DOE).

The main environmental benefits of solar power include:
- Zero emissions during operation
- Low carbon footprint compared to fossil fuels
- Reduce air and water pollution
- Require very little water usage once installed
Potential environmental concerns include:
- Land usage for large solar farms
- Impact on wildlife habitats
- Use of hazardous materials during manufacturing
- Difficulty disposing of old solar panels
However, solar panel efficiency is improving while costs are declining. With proper siting and wildlife protection measures, solar energy can provide clean renewable power with minimal long-term impact on the environment.
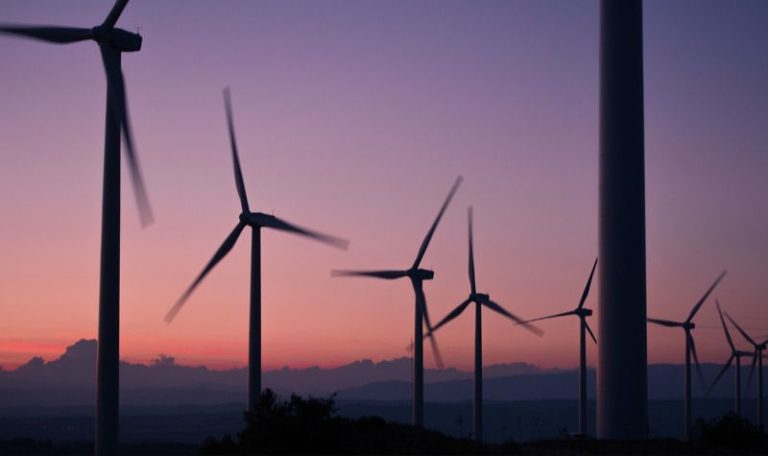
Wind
Wind power is considered a clean and renewable energy source. Wind turbines do not produce air pollution or greenhouse gases while operating. Wind is also abundant, renewable, and affordable (1). However, wind power does have some negative environmental effects. Wind turbines can impact local wildlife, like birds and bats that can collide with the blades. The turbines also produce noise pollution that can disturb residents living close by. There are also visual impacts, as wind farms with many large turbines change the aesthetics of the landscape (2).
(1) https://www.eia.gov/energyexplained/wind/wind-energy-and-the-environment.php
(2) https://www.ucsusa.org/resources/environmental-impacts-wind-power
Hydroelectric
Hydroelectric power is generated from the energy of flowing water, which is captured and turned into electricity by hydropower plants. Hydropower comes from dammed rivers where water builds up in reservoirs. When the water is released, it flows through turbines, activating a generator to produce electricity.
Hydroelectric power does not directly emit air pollutants and is therefore considered a clean renewable energy source. However, damming rivers and building reservoirs can have significant environmental impacts (Environmental Impacts of Hydroelectric Power, n.d.)
.
Some pros of hydroelectric power for the environment include:
- Low emissions compared to fossil fuel-based electricity generation.
- Hydropower reservoirs can serve other purposes like recreation and flood control.
Some cons of hydroelectric power for the environment include:
- Building dams and flooding large areas alters natural habitats for fish and wildlife. It can disrupt river ecosystems.
- Hydropower facilities can obstruct fish migration and affect their populations.
- Reservoirs produce methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
Overall, hydroelectric power is considered an important renewable energy source. But steps must be taken to mitigate its environmental impacts through careful facility design and operations (Hydropower and the environment – U.S. Energy Information Administration, n.d.).
Geothermal
Geothermal energy comes from the natural heat of the earth. It is considered a renewable energy source because the heat emanating from deep within the earth is essentially limitless. Geothermal energy is used for electricity generation and direct applications like heating and cooling. There are three main types of geothermal energy systems: hydrothermal, enhanced geothermal systems (EGS), and geothermal heat pumps (GHPs) [1].
Geothermal energy has several environmental benefits. It produces no air pollution or carbon emissions. Hydrothermal and EGS facilities release some gases, but at much lower levels than fossil fuel plants. GHPs release no emissions. Geothermal plants require very little land compared to other renewable sources and do not negatively impact wildlife habitats. However, geothermal development can impact water consumption and quality. Hot wastewater sometimes contains hazardous materials that must be properly disposed of. Overall, geothermal is considered an environmentally preferable energy source [2].
Biomass
Biomass energy comes from organic matter such as plants and animal waste. It is considered a renewable energy source because biomass can be regrown over relatively short periods of time compared to the hundreds of millions of years needed for fossil fuels to form (Source). When biomass is burned, carbon dioxide is released which is then absorbed by new plant growth, making it close to carbon neutral (Source).
However, biomass facilities can produce air pollutants like nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, volatile organic compounds, and particulate matter. These can have negative health and environmental effects locally (Source). There are also concerns over unsustainable harvesting practices negatively impacting ecosystems. Overall, biomass can be a renewable and carbon neutral energy source, but proper management is needed to minimize any adverse environmental and health impacts.
Nuclear
Nuclear power produces electricity through nuclear reactions. Uranium is used as the fuel in nuclear reactors to produce energy through fission. Nuclear power plants do not produce air pollution or carbon dioxide while operating, which is a major advantage compared to fossil fuel sources like coal and natural gas. However, there are environmental concerns related to nuclear power, including the potential for accidents and the creation of radioactive waste products that must be contained and isolated from the environment for thousands of years.
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, nuclear power plants do not emit air pollutants or carbon dioxide, however they do produce radioactive waste that requires careful management
(https://www.eia.gov/energyexplained/nuclear/nuclear-power-and-the-environment.php). The most radioactive waste products from nuclear reactors need to be isolated for tens of thousands of years. Managing and disposing of nuclear waste responsibly is a major challenge. There have also been serious nuclear accidents like Chernobyl and Fukushima that caused major environmental contamination.
Overall, nuclear power has tradeoffs with respect to environmental impacts. It has the benefit of not emitting greenhouse gases or air pollution, but challenges remain around properly managing radioactive nuclear waste for many generations. More research and investment may be needed to develop safer and more sustainable nuclear technologies.
Natural Gas
Natural gas is a hydrocarbon gas mixture consisting primarily of methane (CH4). It is a relatively clean burning fossil fuel, emitting lower greenhouse gas and pollutant emissions compared to coal and oil when burned (U.S. Energy Information Administration, 2022). Natural gas has some advantages for the environment compared to other fossil fuels, but still has negative impacts.
Burning natural gas emits 50-60% less carbon dioxide (CO2) compared to emitting coal, and 30-40% less than oil per unit of energy produced (U.S. Energy Information Administration, 2022). It also emits lower amounts of air pollutants like nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide and particulate matter versus coal or oil. This makes natural gas a cleaner option for producing electricity or heating/cooling buildings.
However, natural gas systems do leak methane, a potent greenhouse gas, during extraction and transport. Extracting natural gas also produces wastewater that can contaminate local water sources if not properly disposed of. While natural gas may have some advantages over coal and oil, it still contributes significantly to global warming emissions and environmental pollution compared to truly clean energy sources.
Coal
Coal power is generated from burning coal. Coal is a carbon-rich fossil fuel that is unearthed through mining. While coal power is inexpensive and plentiful (according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, coal reserves are expected to last about 200 years at current rates of consumption), it has major environmental downsides. Burning coal produces air pollution like nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, particulate matter and heavy metals, which have been linked with respiratory illnesses, heart disease and premature death [1]. Coal mining and burning also produces methane, a potent greenhouse gas that traps heat and contributes to climate change. Waste from coal power, like ash, sludge and coal refuse, contains toxic substances like mercury that can pollute waterways. Overall, coal power has very high emissions of carbon dioxide, making it the most carbon-intensive energy source per unit of electricity generated.
Conclusion
When it comes to environmentally friendly energy sources, renewable options like solar, wind, hydroelectric, geothermal and biomass tend to have the smallest carbon footprint and least negative impacts compared to fossil fuels. Though no energy source is completely without environmental costs, solar and wind are generally considered the greenest options since they don’t directly emit any air or water pollution. They also don’t require mining or drilling which can disrupt landscapes and wildlife.
While natural gas burns cleaner than coal, both still contribute substantially to climate change through their greenhouse gas emissions. Meanwhile, nuclear avoids carbon emissions but presents risks of radioactive waste and accidents. Ultimately, transitioning our energy infrastructure towards an optimal mix of renewables and steadily phasing out dependence on fossil fuels appears the most sustainable path forward.