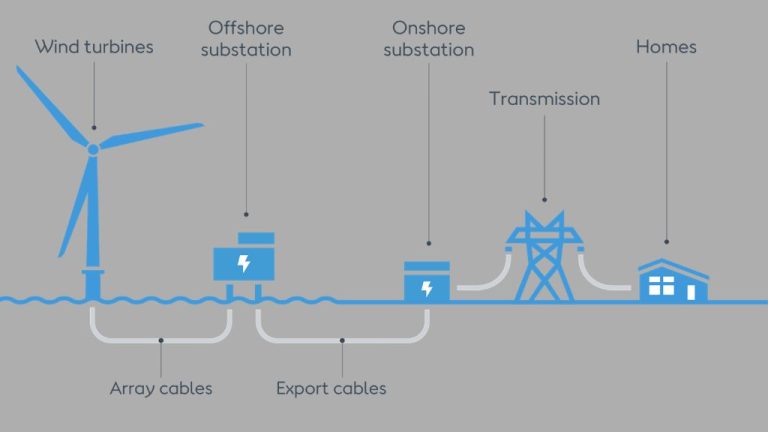
What Is The Lifespan Of A Wind Turbine Gearbox?
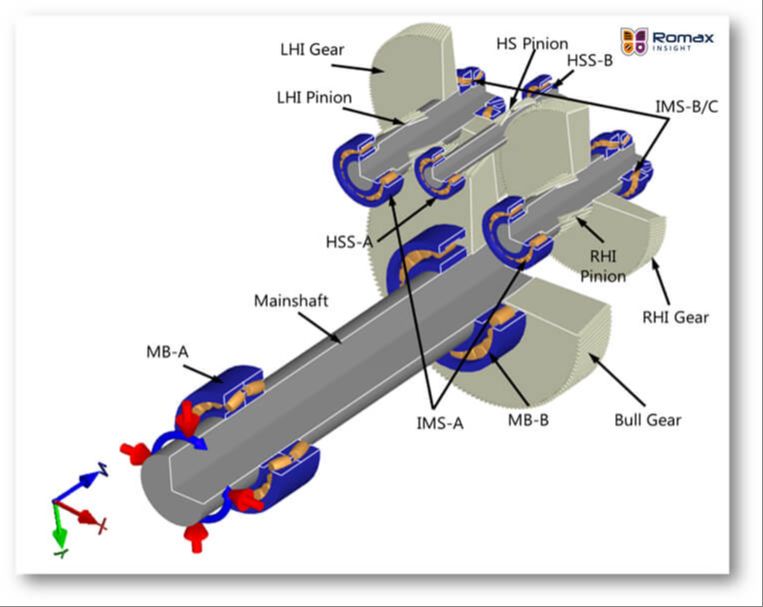
The purpose of this article is to provide an overview of the typical lifespan of wind turbine gearboxes and discuss the key factors that affect their longevity. Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy through a drivetrain system that includes a gearbox. The gearbox is a crucial component that must operate reliably over the turbine’s lifetime, which is often 20 years or more. However, gearbox failure remains one of the most common causes of wind turbine downtime. Understanding what determines the lifespan of a gearbox is important for improving reliability and reducing maintenance costs.
What is a Wind Turbine Gearbox?
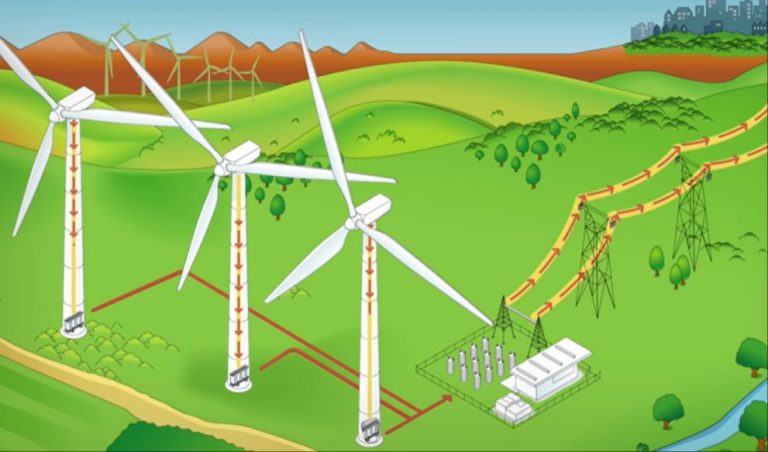
A wind turbine gearbox is an important mechanical component that increases the low rotational speed of the turbine rotor to a higher rotational speed that is required by the electrical generator. The gearbox allows the generator to operate at its optimal designed speed while the rotor turns much more slowly due to its large size.
The main components of a wind turbine gearbox are:
- Gears – Usually 3 stages of planetary and parallel gears that provide the speed increase through gear ratios.
- Bearings – Support the gears and allow them to rotate with minimal friction.
- Shafts – Connect the gears and transmit torque.
- Housing – Encloses the gear stages and provides support.
- Lubrication system – Circulates oil to lubricate components and remove heat.
The gearbox plays a crucial role in the drivetrain by enabling the rotor and generator to operate at their optimal speeds. Advanced gearbox designs are critical for extracting maximum energy from the wind.
Typical Lifespan
The typical lifespan of a wind turbine gearbox is 20-25 years under normal operating conditions, according to research. However, the actual lifespan can vary substantially depending on factors like the operating environment, usage levels, and maintenance practices.
Most wind turbine manufacturers design gearboxes to last for 20 years before needing major overhauls or replacement. But in reality, few wind turbine gearboxes reach the 20 year mark without issues. One report found that most offshore wind turbines need serious gearbox refurbishment or replacement within the first 7-10 years of operation.
Onshore wind turbines fare slightly better, with many gearboxes operating reliably for 10-15 years. But gearbox failure remains one of the leading causes of wind turbine downtime and lost energy production.
Design Factors
The design of a wind turbine gearbox has a significant impact on its lifespan. Careful engineering of the gearbox components and layout can extend the reliable operating life (source). Some key design considerations include:
The materials used for the gearbox housing and gears themselves affect durability. Stronger materials like steel alloys can better withstand years of use. The surface hardness of the gear teeth influences how well they resist wear over time (source).
Proper lubrication is critical to minimizing friction and heat buildup within the gearbox. The lubrication system design, including oil pumps, filtration, and cooling, impacts how well the oil protects and cools the gears during operation.
The gearbox also needs to allow accessibility for routine maintenance and repairs. Well-planned access ports and layouts that allow easier component swaps can significantly improve the upkeep over decades of service.
Overall, thoughtful engineering of the gearbox itself and its lubrication system during the initial design process enables longer lifespans under real-world operating conditions.
Operating Conditions
The operating conditions a wind turbine gearbox experiences have a significant impact on its lifespan. Two key factors are wind speeds and exposure to extreme weather events. Studies show that higher average wind speeds and frequent gusts put more strain on the gearbox components leading to accelerated wear and tear. Additionally, extreme weather like storms, freezing rain, and lightning strikes can damage the gearbox or other turbine structures that then impact the gearbox. For example, a damaged rotor blade could become imbalanced and cause excessive vibration transmitted through the drivetrain.
Another consideration is exposure to dust, dirt, and debris like sand or salt spray near oceans. Buildup of contaminants can lead to abrasion of the lubricants and wear on bearing surfaces. Proper filtration and maintenance is required to counteract these effects. Overall, siting wind turbines in areas with very high average wind speeds or frequent extreme weather will likely decrease the achievable lifespan of the gearbox versus more moderate conditions. Careful gearbox design and robust condition monitoring can help maximize useful life despite harsh operating environments.
Maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial to maximizing the lifespan of a wind turbine gearbox. This involves routine inspections and lubrication to detect early signs of wear and prevent failure.1 Wind turbine technicians perform scheduled maintenance at intervals recommended by the manufacturer, often every 6-12 months.
Maintenance checks involve visually inspecting the gearbox, filters, and lubricant condition. Technicians look for any evidence of cracks, pitting, metal shavings, or leaks that could indicate issues. The oil is tested to ensure it has the proper viscosity and is not contaminated.
Changing the lubricant at regular intervals is vital to clearing out any built-up metal particles and ensuring proper lubrication. Lubricant analysis can detect elevated levels of wear particles that signal impending problems. By catching issues early, repairs can be made during standard maintenance rather than after catastrophic failure.
Proper maintenance keeps the gearbox operating smoothly and reliably, allowing it to reach its expected 20+ year lifespan under normal conditions.
Repairs and Refurbishment
When a wind turbine gearbox fails, the turbine owner is faced with a choice – whether to repair the existing gearbox or replace it entirely. Repairing a gearbox can be a cost-effective option, especially for newer gearboxes that just need some minor fixes. However, for older gearboxes with extensive damage, replacement may be the better long-term option.
The refurbishment process involves fully disassembling the gearbox, cleaning and inspecting all components, replacing any damaged parts, and reassembling the unit. This requires specialized skills and equipment. Costs can range from tens of thousands of dollars for minor repairs to over $100,000 for a full overhaul and replacement of major components.[1]
Factors that impact the repair vs replace decision include the age and model of the gearbox, the extent of damage, availability of replacement parts, costs of downtime, and expected remaining useful life after repairs. Proactive maintenance and inspections can help avoid unexpected failures and minimize repair costs over the long run.
Gearbox Failure Modes
Some common causes of premature failure in wind turbine gearboxes include:
- Bearing failure – This is one of the most common issues. Bearings can fail due to fatigue, improper installation, contamination, lubrication problems, excessive loads, misalignment, and other factors.
- Gear failure – Gears can suffer damage from pitting, wear, cracking, plastic deformation, and tooth breakage. This is often caused by fatigue, misalignment, lack of lubrication, debris contamination, manufacturing defects, improper gear design, and extreme loads.
- Seal failure – Seals help retain lubricant and keep contaminants out of the gearbox. When seals fail, it allows lubricant to leak out and contaminants to enter, leading to accelerated wear and failure.
- Lubrication problems – Insufficient, degraded, or contaminated oil can lead to increased wear, overheating, and component failure.
Diagnosing gearbox issues requires a combination of condition monitoring tools:
- Vibration analysis can detect abnormal vibration patterns indicating bearing damage, gear damage, misalignment, and other mechanical faults.
- Oil analysis checks lubricant health, contamination levels, and wear particle concentrations.
- Acoustic emission sensors pick up noise patterns signaling early damage.
- Temperature sensors identify overheating components.
- Strain gauges measure excessive torque strain on gears.
- Debris analysis identifies types of wear particles found in the lubricant.
Effective condition monitoring, along with scheduled maintenance and inspections, allows incipient failures to be detected early so repairs can be made before catastrophic failure occurs.
Improving Reliability
Several methods can help improve the reliability and lifespan of wind turbine gearboxes:
Advanced Condition Monitoring
Using sensors and analytics to monitor the health of gearbox components can detect early signs of wear and tear. This allows maintenance teams to address issues before they lead to failures.
Design Innovations
Upgrades like improved lubrication, filtration systems, and bearings can enhance gearbox durability. Some companies are also testing new modular gearbox designs to simplify maintenance.
Operational Best Practices
Proper installation, regular inspections, overspeed avoidance, and load management can reduce strain on the gearbox. Worker training and following manufacturer guidelines helps maximize lifespan.
By combining condition monitoring, design improvements, and optimized operations, wind farm owners can extend the reliable service life of turbine gearboxes.
Conclusion
In summary, there are several key factors that influence the lifespan of a wind turbine gearbox. Proper gearbox design is critical, as the gearbox must withstand constant oscillating loads and effects of fatigue over its lifetime. Using high quality materials, optimized gear geometry, thorough modeling and testing during development can improve longevity. The operating environment also plays a major role, as offshore turbines experience more stress from wind and waves. Regular maintenance helps detect early signs of wear and prevent catastrophic failures. Many gearbox issues come from inadequate lubrication, misalignment or loose fasteners, highlighting the importance of proper operation and maintenance procedures. With careful design, manufacturing, installation and maintenance, wind turbine gearboxes can achieve their expected 20 year lifespan.
While gearbox design continues improving, proper maintenance and operation remains essential for minimizing failures and extending the usable life of these critical and expensive components. Preventative maintenance, inspection, lubrication, and responding quickly to any anomalies are key. With the high costs of gearbox replacements or refurbishments, plant operators are wise to invest in comprehensive maintenance programs if they want their turbines to remain productive for the long run.