What Is The Difference Between Alternative And Renewable Energy Sources?
As concerns about climate change and fossil fuel dependence grow, there is increasing interest in alternative energy sources that are renewable and more sustainable. Both alternative energy and renewable energy refer to power generation from sources other than fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas. However, there are some key differences between the two terms.
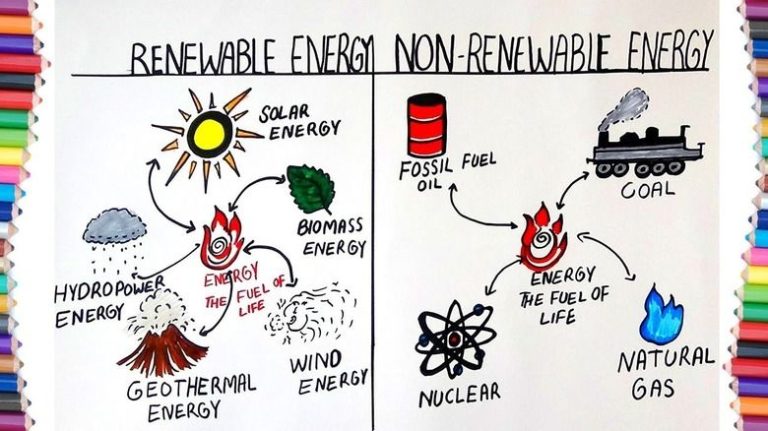
Alternative energy encompasses anything other than the traditional energy sources dominant today – mainly fossil fuels. This includes renewable sources like solar, wind, and hydropower, but also nuclear power. Renewable energy refers specifically to sources that regenerate and cannot be depleted – solar, wind, water, geothermal, and biomass. Understanding the distinction between these two terms is important when evaluating energy options for the future.
Definitions
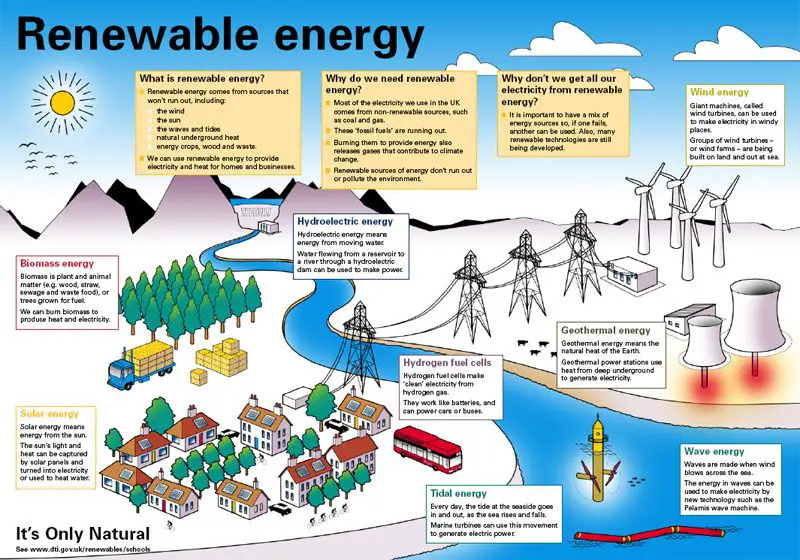
Alternative energy refers to energy sources that are considered alternatives to traditional fossil fuels like coal, oil and natural gas. Alternative energy sources are often renewable and include things like solar, wind, geothermal, hydroelectric, and biomass energy. The key aspect of alternative energy is that it comes from sources other than fossil fuels, though some alternative energy sources like nuclear and hydrogen are not renewable.
Renewable energy refers more specifically to energy derived from sources that regenerate and cannot be depleted – things like sunlight, wind, water, and geothermal heat. The five main renewable energy sources are:
- Solar energy from the sun
- Wind energy
- Hydropower from flowing water
- Geothermal energy from heat inside the earth
- Biomass from plants and organic waste
The key aspect of renewable energy is that it comes from naturally replenished resources.
Types of Alternative Energy
There are several major forms of alternative energy that are used as alternatives to fossil fuels like coal, oil and natural gas. Some of the most common types of alternative energy sources include:
Solar Energy
Solar energy harnesses the power of the sun to generate electricity and provide lighting and heating. Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity that can power homes, businesses and the electric grid. Solar thermal collectors can capture heat from the sun to warm buildings and water.
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy tapping into the internal heat of the earth to generate clean power. Geothermal power plants use hot water or steam from geothermal reservoirs in the earth’s crust to turn turbines and generate electricity. Geothermal heating and cooling systems use stable ground temperatures near the earth’s surface for residential and commercial heating and cooling.
Biomass Energy
Biomass energy uses organic materials like plants, agricultural waste and garbage as fuel to produce electricity and heat. Biomass can be burned directly or converted to biogas or biofuels like ethanol and biodiesel. Examples of biomass fuels include wood, crops, landfill gas and alcohol fuels.
Hydrogen Energy
Hydrogen can be used as a fuel source to power vehicles, generate electricity and heat buildings. Hydrogen is an energy carrier, not a primary energy source – it must be produced from another resource. Hydrogen fuel cells combine hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity without combustion or pollution.
Types of Renewable Energy
There are several major types of renewable energy sources that are in use today or under development.
Solar Energy
Solar energy harnesses the sun’s rays to generate electricity and provide lighting and heating. Technologies like photovoltaic solar panels and concentrated solar power plants allow sunlight to be converted directly into electricity.
Wind Energy
Wind turbines use the kinetic energy of wind motion to spin large blades connected to generators that create electricity. Wind farms comprised of many turbines are being built onshore and offshore to harness wind energy.
Hydroelectric Power
Hydropower uses the energy of flowing or falling water to turn turbines and generate electricity. Hydroelectric dams provide a consistent and reliable source of renewable power in many parts of the world.
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal power taps into underground reservoirs of steam or hot water to drive geothermal plants. This heat energy from the earth’s core can be accessed directly or converted into electricity.
Biomass Energy
Biomass refers to organic plant and animal materials like wood, crops, and waste that can be burned to create heat and electricity. Biomass is considered renewable if replanted after use.
Key Differences
There are some important distinctions between alternative and renewable energy sources. The key differences include:
Renewability – Renewable energy sources like solar, wind, geothermal and hydro are considered renewable because they are replenished naturally over time. The fuel sources for renewable energy are essentially limitless. Alternative energy encompasses renewable sources, but also includes non-renewable sources like natural gas, oil, coal, and nuclear energy.
Environmental Impact – Renewable energy sources are widely considered to be more environmentally friendly and sustainable than many alternative energy sources. Renewables like solar and wind create very little pollution and carbon emissions. Some alternatives like natural gas create less emissions than coal or oil, but still produce byproducts.
Availability – Renewable energy sources are dependent on location and weather conditions, while alternatives like natural gas and coal are available through widespread infrastructure. Renewables may have variability and intermittency issues that alternatives do not.
Cost – In recent years, renewables have become more cost competitive with conventional alternative energy sources. But alternatives like natural gas tend to be cheaper overall in many markets. The long-term costs of renewables continue to decline.
Pros and Cons
Both alternative and renewable energy sources have their advantages and disadvantages compared to traditional fossil fuels like coal, oil and natural gas.
Pros of Alternative Energy
Some benefits of alternative energy sources like nuclear, hydrogen and biofuels include:
- Abundant fuel supply – Uranium for nuclear power is readily available. Biofuels can be produced from many types of organic matter. Hydrogen is the most abundant element.
- Low carbon emissions – Most alternative energy sources produce little to no greenhouse gases. This helps combat climate change.
- Energy independence – Alternative fuels can be produced domestically, reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels.
- Job creation – Building new alternative energy facilities creates economic growth and jobs.
Cons of Alternative Energy
Some drawbacks of alternative energy sources include:
- High upfront costs – Nuclear, hydrogen and biofuel plants are expensive to build.
- Safety concerns – Nuclear power accidents can cause radiation leaks. Hydrogen is flammable and explosive.
- Waste issues – Nuclear waste must be stored safely for thousands of years. Some biofuels produce air pollution.
- Limitations – Biofuels may use food crops, raising food prices. Hydrogen requires special storage and transportation.
Pros of Renewable Energy
Benefits of renewable energy like solar, wind, hydro and geothermal include:
- Clean power – Renewables produce little to no global warming emissions or air pollution.
- Declining costs – Technology advances are making renewables more affordable.
- Energy security – Renewable energy is generated domestically from endless fuel sources.
- Job growth – Renewable energy is a rapidly growing industry creating many new jobs.
Cons of Renewable Energy
Drawbacks of renewable energy sources include:
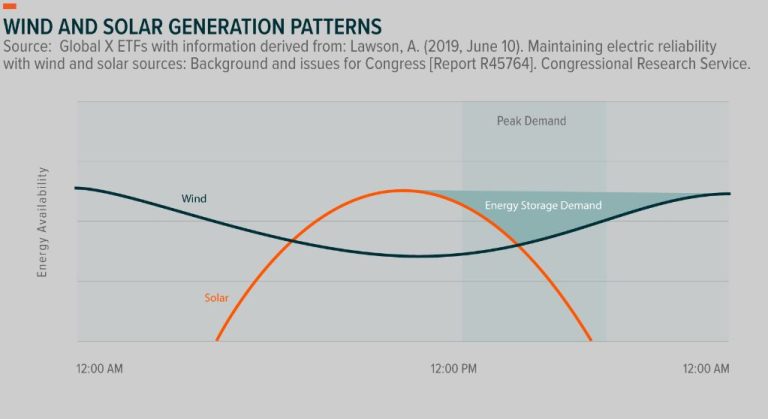
- Intermittency – Solar and wind power depend on weather and so are not available 24/7.
- High upfront costs – Building large solar or wind farms requires significant initial investment.
- Land use conflicts – Renewable projects sometimes face opposition over land or habitat usage.
- Expensive storage – Effective storage solutions are needed to provide renewable power when the sun isn’t shining or wind isn’t blowing.
Cost Comparison
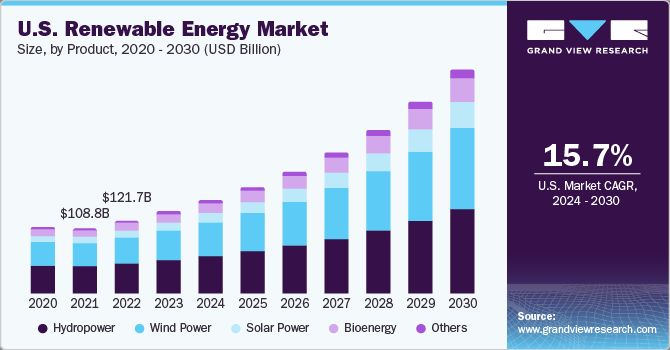
When comparing the costs of alternative energy versus renewable energy, there are a few key factors to consider. Renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower have seen dramatic decreases in cost over the past decade as technology has improved. The levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) for utility-scale solar PV dropped 88% from 2009 to 2019. Onshore wind dropped 70% and offshore wind dropped 71% in LCOE in the same time frame. These sources can now often compete with fossil fuels on cost.
However, alternative energy sources like nuclear, natural gas, and coal plants require massive upfront capital costs. A nuclear plant can cost $6-9 billion to build, while a new coal plant is around $3 billion. These plants take years to build and must operate for decades to recoup the initial investment. And as renewable prices fall, operating existing fossil fuel plants becomes less profitable over time.
When accounting for externalities like environmental and health costs which are not included in market prices, renewables are significantly more cost effective than alternatives. A 2015 study found external costs for natural gas were over $1.5 billion annually, and over $62 billion for coal. Overall, renewable energy sources like wind and solar provide cleaner and increasingly cost-competitive options over alternative fossil fuels.
Environmental Impact
Both alternative and renewable energy sources have potential environmental advantages over conventional fossil fuels like coal, oil and natural gas. However, they also have some unique environmental considerations.
Many alternative energy sources like nuclear, hydrogen and biofuels emit much lower levels of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide when generating electricity. This can help reduce the impact of climate change. However, nuclear power creates radioactive waste that must be carefully stored for thousands of years. Biofuels may require large amounts of land and water resources to grow the fuel crops.
Renewable energy sources like solar, wind and hydropower emit no greenhouse gases during operation. This makes their environmental footprint much smaller than fossil fuels. However, they may have indirect impacts, like wind turbines potentially harming birds. Large solar and wind farms can also impact local habitats. Hydropower dams may change downstream river environments.
Overall, both alternative and renewable energy sources tend to be more environmentally sustainable than traditional fossil fuels in the long run. But each technology has unique advantages and disadvantages that must be weighed carefully. With thoughtful implementation, they can provide much cleaner energy options for the future.
Future Outlook
The future viability and growth potential of alternative and renewable energy continues to expand as technology improves and costs decline. Renewable energy sources such as solar and wind are projected to be the fastest growing energy sources over the next few decades. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), renewables are expected to account for over 90% of global power capacity growth in the next 5 years. The costs of renewables and energy storage are decreasing rapidly, making them more economically competitive with fossil fuels.
Many governments around the world are implementing policies and initiatives to increase the adoption of renewables and phase out fossil fuel dependence. The Paris Agreement objectives require countries to transition towards low-carbon energy systems, which is spurring large-scale investments and infrastructure changes. Emerging markets in developing countries also present major growth opportunities for distributed renewable energy solutions. While fossil fuels will continue to play a role in the global energy mix, the transition towards clean energy is clearly underway and projected to accelerate.
Certain alternative energy sources like nuclear have more barriers to rapid growth due to high costs and public opposition. But new nuclear technologies are being developed that are smaller, safer and more flexible to operate. Overall, the viability of alternative and renewable energy continues to improve substantially, making them essential options for building sustainable, low-emissions energy systems. Their future growth and expansion will be vital for addressing climate change and energy access globally.
Conclusion
In summary, the key differences between alternative and renewable energy sources are that alternative energy refers to energy sources that serve as alternatives to fossil fuels, while renewable energy refers specifically to energy from sources that replenish naturally. Though there is overlap, not all alternative energy sources are renewable, and vice versa.
Understanding these differences is important when evaluating energy options based on factors like sustainability, cost, reliability, and environmental impact. Renewable sources provide sustainable long-term energy but often at a higher cost, while alternative sources like nuclear can provide affordable and reliable energy but with waste concerns. Going forward, pursuing a mix of both alternative and renewable solutions can allow society to transition away from fossil fuels while meeting energy needs.
As technology advances and prices evolve, the distinctions between alternative and renewable may blur. But for now, appreciating their unique advantages and drawbacks will lead to more informed energy choices.