What Is The Best Light Bulb To Save Energy?
Choosing the right light bulb can make a big difference in your home’s energy use and electricity bill. With many different types of bulbs on the market today, from incandescent and CFL to LED, it’s important to understand the pros and cons of each to find the most energy efficient option. Using energy efficient light bulbs is an easy way to reduce your environmental impact and save money on electricity costs over the lifetime of the bulb. This article provides an overview of the different bulb types, costs comparisons, brightness levels, and recommendations to help you choose the best energy saving light bulb for your needs.
Types of Light Bulbs
There are several main types of light bulbs to choose from:
Incandescent Bulbs
Incandescent bulbs are the traditional light bulb that has been used for over a century. They work by heating a filament inside the bulb until it glows and produces light. While inexpensive, incandescent bulbs are inefficient – over 90% of the energy consumed is emitted as heat rather than light (https://www.homedepot.com/c/ab/types-of-light-bulbs/9ba683603be9fa5395fab90e1115f39).
CFL Bulbs
CFL (compact fluorescent lamp) bulbs are more energy efficient than incandescent bulbs. They work by sending an electrical discharge through a tube containing argon and mercury vapor. This produces ultraviolet light that then hits a phosphor coating, causing it to glow and emit visible light. CFLs use about 75% less energy than incandescents (https://www.wayfair.com/sca/ideas-and-advice/renovation/types-of-lightbulbs-how-to-choose-the-right-one-T5256).
LED Bulbs
LED (light-emitting diode) bulbs are currently the most energy efficient light bulbs available. LEDs produce light by passing electricity through a semiconductor material. This provides more light output per watt compared to incandescent or CFL bulbs. LED bulbs can reduce energy usage by 80-90% versus traditional incandescents (https://www.homedepot.com/c/ab/types-of-light-bulbs/9ba683603be9fa5395fab90e1115f39).
Halogen Bulbs
Halogen bulbs are a type of incandescent bulb with halogen gas added inside the bulb. This allows the filament to burn hotter, producing brighter light while using less energy. Halogens are about 25% more efficient than regular incandescents (https://www.wayfair.com/sca/ideas-and-advice/renovation/types-of-lightbulbs-how-to-choose-the-right-one-T5256).
How Light Bulbs Work
Light bulbs produce light by passing electricity through a filament, gas, or semiconductor to produce light. Traditional incandescent light bulbs work by heating a tungsten filament wire to a high temperature until it glows white hot, producing visible light. According to the How Stuff Works article, “Atoms release light photons when their electrons become excited. If you’ve read How Atoms Work, then you know that electrons are the negatively charged particles that orbit the positively charged nuclei of atoms. When an electron absorbs enough energy, it jumps up to a higher energy level. When it falls back down, the electron releases that energy in the form of a photon of light.” https://home.howstuffworks.com/light-bulb.htm
More modern fluorescent bulbs pass electricity through a gas like argon and mercury vapor, which excites the gases and causes them to release ultraviolet light. The ultraviolet light is then absorbed by a fluorescent coating inside the bulb, causing it to glow or fluoresce. According to the How Stuff Works article, “A fluorescent lamp converts electrical power into useful light much more efficiently than an incandescent lamp. For example, a 100-watt fluorescent lamp produces about the same amount of visible light as a 150-watt incandescent lamp. And fluorescent lamps usually last 10 to 20 times longer than incandescents before burning out.” https://home.howstuffworks.com/light-bulb.htm
LED bulbs pass electricity through a semiconductor material, causing electrons to release light particles called photons. According to the Lampsplus article, “In an LED bulb, electricity flows into a semiconductor. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light depends on the energy required for electrons to cross the semiconductor band gap.” https://www.lampsplus.com/ideas-and-advice/how-an-incandescent-light-bulb-works/
Energy Efficiency of Various Bulbs
Energy efficiency is a key consideration when choosing light bulbs. Some bulbs are much more efficient, producing more light (lumens) per watt of electricity consumed. A typical incandescent bulb produces around 15 lumens per watt, while CFLs produce around 60 lumens per watt, and LEDs can produce between 70 – 100 lumens per watt (LumenNow, 2022). Therefore LED and CFL bulbs produce substantially more light for the same amount of electricity.
Lifetime is another factor. Incandescent bulbs last 1000-2000 hours on average, CFLs can last 10,000 hours, and LEDs last around 25,000 hours or more (Energy.gov, 2022). Thus LED and CFL bulbs don’t need to be replaced nearly as often. This makes them more convenient as well as cost effective over the long run. While LED and CFL bulbs have a higher upfront cost, they end up saving money due to their dramatically longer lifetimes and lower electricity consumption (GE Lighting, 2022).
Cost Comparison
When comparing costs of different light bulb types, it’s important to look at both the upfront purchase price as well as the long-term electricity costs. LED bulbs have a higher initial cost, but make up for it with significant energy savings over time.
An incandescent 60W bulb costs around $1, while a comparable LED bulb ranges from $2-$5. However, incandescents burn out faster and use more electricity. Over a 10 year lifespan, an incandescent bulb will cost over $50 in energy bills, compared to around $8-15 for an LED (Source).
So while LEDs are more expensive upfront, they pay for themselves within a year through electricity savings. Over 10 years, LEDs save $35-45 per bulb compared to incandescents. For a home with around 40 light bulb sockets, switching entirely to LEDs could save $1,400-$1,800 over a decade (Source).
Brightness
The brightness of a light bulb is measured in lumens. Lumens indicate the amount of visible light a bulb produces. Generally, the more lumens a bulb has, the brighter it is (Westinghouse).
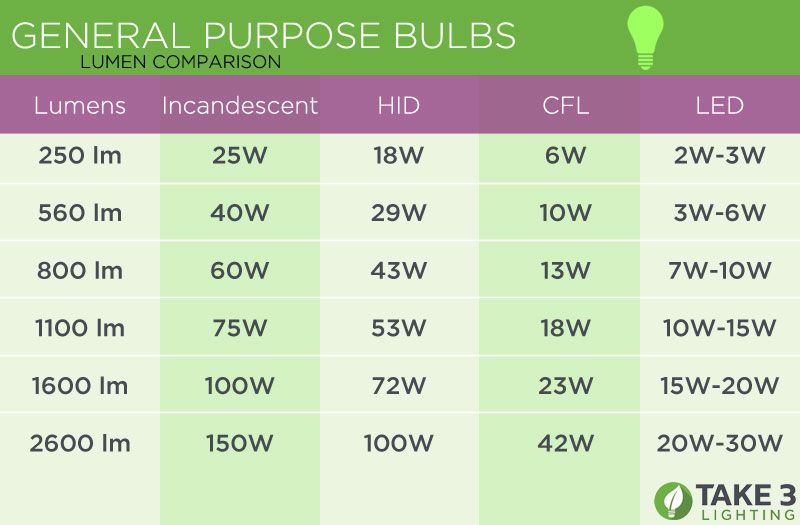
Most standard household bulbs range from 450 to 2600 lumens. A 100-watt incandescent bulb, for example, produces about 1600 lumens. To replace a 100-watt bulb, choose an energy-efficient LED or CFL bulb with a similar lumen output.
Bulbs with a higher number of lumens appear brighter. Bulbs under 750 lumens are best for decorative lamps, while bulbs above 1500 lumens are well-suited for kitchens, offices and workshops that need abundant light. The average reading lamp requires 600-1000 lumens (Energy Saver).
Color temperature also impacts a bulb’s appearance. Bulbs with lower color temperatures (2700K-3000K) give off a warm, yellowish light. Bulbs with higher color temperatures (3500K-5000K) emit a cooler, bluish-white light that seems brighter.
Dimmability
One of the key differences between LED light bulbs is whether they are dimmable or not. This refers to whether the brightness of the bulb can be adjusted through a dimmer switch.
Traditional incandescent bulbs are inherently dimmable, but LEDs require special dimming circuitry built into the bulb to work with a dimmer switch. Non-dimmable LED bulbs will simply not turn on or flicker if used with a dimmer. Dimmable LEDs are more expensive but allow you to control the light brightness.
You can identify dimmable LED bulbs by looking for the term “dimmable” printed on the packaging or light bulb base. They will also have a “DY” marking. Non-dimmable bulbs are usually labeled “non-dimmable.” When buying an LED bulb for use with a dimmer, always ensure it’s marked for dimming compatibility.
According to LED Supply, dimmable LEDs work best with electronic low-voltage dimmers for smooth performance. Older rheostat dimmers can cause flickering and other issues.
Disposal and Recycling
Proper disposal of light bulbs is important, especially for bulbs containing mercury like CFLs. CFLs contain a small amount of mercury which can be harmful if released into the environment. The EPA recommends recycling CFLs to prevent mercury contamination.
There are several options for CFL recycling. Many retailers like Home Depot accept CFLs for recycling. You can also find mail-back recycling programs or drop-off locations in your community. When recycling, the mercury and other components are safely contained.
LED bulbs do not contain mercury so they are generally considered non-toxic. However, LEDs do contain some electronic components and it is still best practice to recycle them. LEDs can often be recycled with other household electronics or through retailer programs.
When disposing of any light bulb, make sure to keep it intact and undamaged. Broken CFLs or LEDs can release components that should be properly contained. The best option is always to recycle responsibly whenever possible.
Recommended Bulbs
When looking for the most energy efficient LED light bulbs, there are a few key factors to consider – efficiency, cost savings, and brightness. Based on expert testing and reviews, here are some top picks:
For the best balance of efficiency, cost-savings, and brightness, the Philips Ultra Efficient LED is a top choice. These bulbs use up to 40% less energy than standard LEDs, lasting over 15 years. Though more expensive upfront, they offer significant long-term savings. Wirecutter found they have excellent light quality and a brightness comparable to a 60W incandescent.
If your priority is maximizing energy savings, the Feit Electric LED is one of the most energy efficient options. Using less than 9 watts, it meets strict Energy Star requirements while providing sufficient illumination for most household needs.
For the brightest light, the Philips LED Daylight bulbs shine the most light per watt compared to other LEDs. With a bright white light perfect for task lighting, they are significantly more luminous than old-fashioned incandescents.
Consulting consumer reports and expert recommendations can help identify the most suitable energy saving LED bulbs for your specific lighting needs and budget.
Conclusion
When choosing the best light bulb for energy savings, LED bulbs are the clear winner. They use up to 80% less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs and last up to 25 times longer. Though more expensive upfront, LEDs pay for themselves over time through energy savings. For the brightest, most efficient and long-lasting lighting, choose ENERGY STAR-certified LED bulbs. Consider dimmable LEDs for adjustable light levels. Recycle CFLs and LEDs properly at the end of their lifetime. Make the switch to LEDs in your home to save energy and money while reducing environmental impact.
The key takeaways are:
- LED bulbs use 80% less energy than incandescent.
- LEDs last over 25 times longer than traditional bulbs.
- Though more expensive initially, LEDs save money over time.
- Look for ENERGY STAR-rated LED bulbs.
- Recycle CFLs and LEDs at end of life.
Take action by replacing all light bulbs in your home with energy-saving LED bulbs. Start with the bulbs that are on most often to see the biggest savings. Make the switch to LEDs today!