What Is Sustainable Vs Renewable Energy Examples?

Sustainable energy and renewable energy are related but distinct concepts. Sustainable energy refers to energy sources that meet current energy needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs. It involves using energy efficiently and sourcing it responsibly. Renewable energy is a subset of sustainable energy. It refers specifically to energy derived from naturally replenishing sources like sunlight, wind, water, plants, and geothermal heat.
Understanding the difference between sustainable energy and renewable energy is important as the world transitions to cleaner energy systems that support economic and social development while protecting the environment. This article will provide an overview of sustainable energy, renewable energy, key differences between the two concepts, and examples of each.
The goal is to clarify the meaning of these important terms that are shaping energy policy and infrastructure globally. With clear definitions and real-world examples, readers will gain better insight into sustainable energy solutions.
Sustainable Energy
Sustainable energy can be defined as energy produced and used in a way that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their energy needs [1]. It involves using energy sources that can be replenished naturally within a human lifespan, so those resources are not depleted or used up. The key aspects of sustainable energy include:
– Using renewable energy sources like solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal, and biomass that can be replenished naturally.
– Employing technologies that utilize these renewable resources efficiently with minimal waste or environmental impact.
– Meeting current energy demands through renewable resources rather than finite fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas.
– Conserving energy and improving efficiency of usage to reduce overall energy demands.
– Ensuring equitable access to clean, renewable energy globally.
– Avoiding depletion of natural resources so they are preserved for future generations. This might involve reducing overall consumption or employing alternatives.
The goal of sustainable energy is to satisfy user needs for power in a way that sustains natural resources and the environment so that future generations can also meet their energy needs. It requires transitioning from finite, polluting energy sources to lasting renewables that do not produce greenhouse gases or toxins that harm people and ecosystems.
Renewable Energy
Renewable energy, as the name suggests, is energy that comes from naturally regenerative sources such as the sun, wind, rain, tides, and geothermal heat and can be naturally replenished (Decathlon, 2023). The key aspect of renewable energy is that the sources are practically inexhaustible or can be replenished in a relatively short timeframe. Renewable energy stands in contrast to fossil fuels, which take millions of years to form naturally. Renewable energy sources include:
- Solar power from the sun
- Wind energy
- Hydropower from flowing water
- Geothermal energy from heat inside the earth
- Biomass from plants
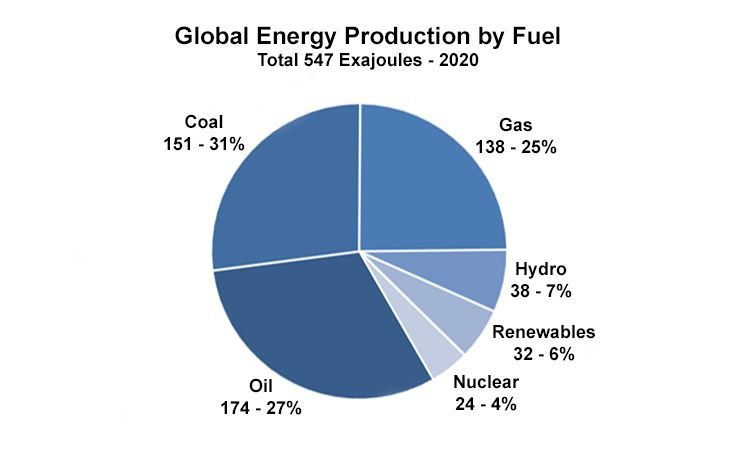
The key advantage of renewable sources is that they are sustainable over long periods of time, unlike fossil fuels which are finite. Renewable energy sources are naturally replenished and so will not run out. Using renewable energy over fossil fuels has significant environmental benefits in reducing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. There is growing adoption of renewable energy worldwide as costs have fallen dramatically in recent years.
Key Differences
There are some notable differences between sustainable and renewable energy. Here are some of the key points:
Sustainable energy includes sources that are not necessarily renewable, but have minimal environmental impact. For example, nuclear power is considered sustainable by some but not renewable. On the other hand, renewable energy comes from naturally occurring sources that are essentially inexhaustible. So renewable energy is a subset of sustainable energy sources.
In terms of environmental impact, sustainable energy aims to meet current energy needs without compromising the environment and ability of future generations to meet their needs. Renewable energy has environmental advantages over fossil fuels, but some types like biofuels may still have sustainability concerns. Overall, sustainable energy takes a broader systems view of minimizing environmental harm.
When comparing sustainable energy vs renewable energy, renewable energy is always sustainable but not all sustainable energy is renewable. The key focus of sustainability is environmental stewardship, while renewability centers on replenishment of the energy source. Both concepts are vital to developing clean energy systems for the future.
Examples of Sustainable Energy
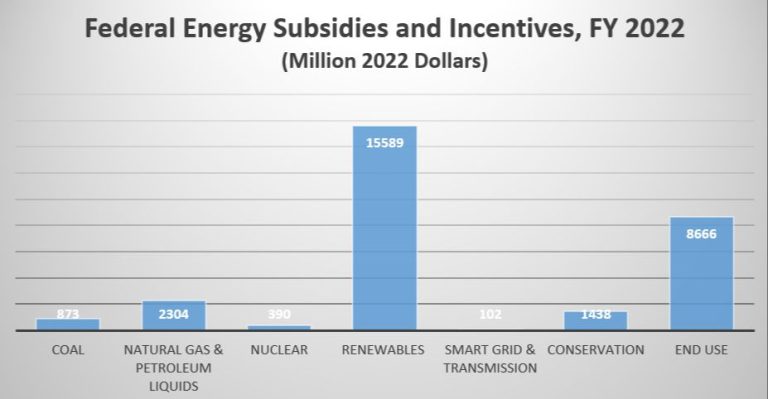
Some common examples of sustainable energy sources include nuclear energy, natural gas, clean coal, energy efficiency improvements, and smart grid technology.
Nuclear energy is considered sustainable because uranium, the fuel source, is extremely energy dense. This means a small amount of uranium can produce a large amount of electricity. Uranium is also abundant and found across the world. Nuclear power plants produce minimal air pollution and carbon emissions. However, there are challenges with radioactive waste disposal and safety concerns.
Natural gas is another sustainable energy source. It burns cleaner than coal and petroleum and is very abundant. Natural gas power plants emit 50-60% less carbon dioxide compared to coal. Using natural gas instead of coal has helped reduce U.S. carbon emissions. However, leakage during natural gas production and transportation can release methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Proper monitoring and maintenance is required.
Clean coal technology can make coal a more sustainable energy source. Methods like carbon capture and storage trap CO2 emissions before they enter the atmosphere. Coal gasification converts coal into syngas, which burns more cleanly. Implementing clean coal reduces air pollutants and greenhouse gas emissions from traditional coal-burning.
Increasing energy efficiency in homes, buildings, electronics and vehicles reduces overall energy demand. Efficient appliances, proper insulation and weatherization, and LED light bulbs are examples. Smart grid technology also promotes sustainability through real-time monitoring of energy supply and demand.
Examples of Renewable Energy
Renewable energy comes from natural sources that are continuously replenished. Here are some of the main types of renewable energy:
Solar Energy
Solar energy comes directly from the sun. It can be harnessed through solar panels to generate electricity, or through solar heating systems for water and space heating. Solar is one of the fastest growing renewable energy sources (National Grid).
Wind Power
Wind power captures the kinetic energy of wind, usually via large wind turbines, and converts it into electricity. Wind power capacity and generation continues to expand rapidly across the globe (National Grid).
Hydroelectric Power
Hydropower harnesses the energy of flowing water to generate electricity. Typically, hydropower comes from dams that control the flow of rivers. Hydropower supplies 16% of the world’s electricity (UC Berkeley).
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy taps into the natural heat beneath the earth’s surface for heating, electricity generation, and other applications. Geothermal energy can be accessed from natural hot springs or by drilling wells (UC Berkeley).
Biomass
Biomass energy uses organic matter like plants, agricultural residues, and waste as fuel. Biomass can be directly burned to produce heat or converted into transportation fuels and electricity (National Grid).
Solar Energy
Solar energy refers to the energy produced by harnessing sunlight and converting it into thermal or electrical energy. There are two main types of solar technologies: solar photovoltaics (PV) and solar thermal systems.
Solar PV systems use solar panels containing photovoltaic cells to directly convert sunlight into electricity. These cells are made of semiconducting materials that absorb photons from sunlight and generate an electric current. Solar PV has seen tremendous growth in recent years due to decreasing costs and policy support. In 2020, global solar PV installations reached over 140 gigawatts.
Solar thermal systems use the sun’s heat to provide hot water, space heating, or to generate electricity. Common examples include solar water heating systems, concentrating solar power plants, and passive solar building designs. While the growth of solar thermal has been more modest than solar PV, it still provides a valuable carbon-free energy solution.
The benefits of solar energy include its renewable, inexhaustible nature, low environmental impact and emissions, modularity and declining costs. Limitations include intermittency, storage requirements, large land usage, and geographic constraints. Overall, solar energy will play a major role in the global transition to sustainable energy systems.
(Source: https://www.greenmatch.co.uk/blog/2014/08/5-advantages-and-5-disadvantages-of-solar-energy)
Wind Energy
Wind energy harnesses the power of the wind to generate electricity using wind turbines. There are two main types of wind turbines: horizontal axis and vertical axis. Horizontal axis turbines are the most common and have blades that spin perpendicular to the wind. Vertical axis turbines have blades that spin parallel to the wind. Wind turbines can stand alone or be grouped together in wind farms to generate larger amounts of electricity.
Wind energy has experienced tremendous growth over the past decade. Global wind power capacity has increased over 10 fold since 2000. Many countries like Denmark and Germany get a substantial amount of their electricity from wind. The United States is now the second largest producer of wind power after China.
Wind energy provides a number of important benefits. Wind turbines produce electricity without emitting any greenhouse gases or other air pollutants. Wind is also one of the lowest priced renewable energy technologies. Land around wind turbines can still be used for agriculture or livestock grazing. However, wind power does have some limitations. The intermittent nature of wind necessitates having backup power sources like natural gas. Suitable wind sites are often located far from major cities necessitating long transmission lines. Wind turbines can also impact local wildlife like birds and bats. Overall though, wind energy will continue to play a major role in the transition to renewable energy. (source)
Hydroelectric Power
Hydroelectric power is generated from flowing water, often from dams or tidal power. Dams are built across rivers to store water in reservoirs, which is then released through turbines to generate electricity. Tidal power harnesses the flow of tidal waters to turn turbines. Globally, hydroelectric power generates around 16% of electricity and is considered a renewable energy source as it relies on the water cycle (BusinessWire, 2018). Growth in hydroelectric power has slowed in recent decades, but it still offers benefits and limitations.
Some key benefits of hydroelectric power include:
- It is a renewable and sustainable energy source.
- It produces minimal greenhouse gas emissions.
- Dams provide reservoirs for drinking water, irrigation and recreation.
- It is a relatively reliable and consistent power source.
- Facilities have long lifespans of 50-100 years.
- It helps meet peak energy demands when demand is high.
However, there are also some limitations:
- Dams and reservoirs can impact local ecosystems and displace communities.
- Silt buildup can reduce dam effectiveness over time.
- Droughts can impact electricity generation.
- Upfront costs of building facilities are very high.
- Some greenhouse gas emissions are still produced during construction.
Overall, hydroelectric power offers clean, renewable energy but also has environmental impacts that must be managed. Growth is slowing but it still plays an important role in the global renewable energy mix (IvyPanda, 2023).
Conclusion
In summary, the key differences between sustainable and renewable energy are that sustainable energy sources can be replaced at the same rate they are consumed, while renewable energy comes from unlimited natural sources. Both play an important role in reducing reliance on finite fossil fuels.
While renewable energy like solar and wind are essential for a sustainable future, we likely still need a mix of energy sources. Renewables are intermittent and energy storage technology needs further development. Sustainable biofuels and nuclear can provide more reliable baseload power to complement renewables.
Expanding renewable energy is crucial for climate change mitigation and energy security. Government policies, public-private partnerships, research and public awareness can accelerate the transition. With wise energy choices, we can meet our needs today while preserving resources for future generations.