What Is Solar Energy In A Simple Way?
What is Solar Energy?
Solar energy is the conversion of the sun’s rays into usable light, heat, or electricity. The sun produces energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation from the fusion reaction in its core. This radiation travels the 93 million miles from the sun to the earth in the form of photons and waves. When the photons strike the earth, they may be converted into different forms of energy:
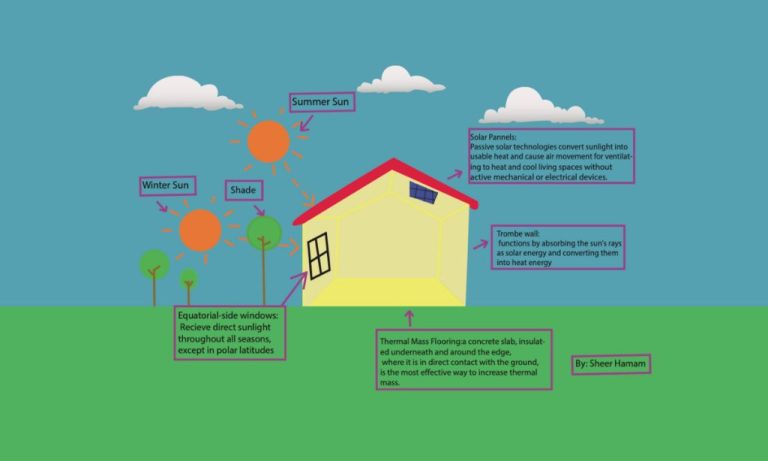
The most common conversion is into heat or thermal energy. This allows solar thermal collectors to heat water or spaces. The photons can also be converted directly into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. Photovoltaic (PV) panels, or solar panels, are made up of solar cells that absorb the photons and release electrons, generating an electric current. Solar energy can be stored, concentrated, and converted in a variety of other ways as well.
Solar energy is considered a renewable energy source. The supply is virtually unlimited and it does not produce greenhouse gases or toxic pollutants. However, solar energy is an intermittent resource since it only works when the sun is shining. Methods to store and concentrate solar energy are improving but remain limited.
Overall, solar power harnesses the sun’s energy in a clean and sustainable way, providing an alternative to fossil fuels. The potential to expand its use and reduce reliance on nonrenewables is considerable (NREL – Solar Energy and Technologies). Advances in efficiency and affordability will continue to shape the future of solar energy.
History of Solar Panels
The history of solar panels dates back to 1839 when French physicist Edmond Becquerel first discovered the photovoltaic effect while experimenting with an electrolytic cell made up of two metal electrodes. Although Becquerel had created the world’s first photovoltaic cell, his discovery went largely unnoticed at the time.
In 1883, American inventor Charles Fritts built the first true solar cells using selenium coated with a thin layer of gold. Fritts’s cells were only about 1% efficient at converting sunlight into electricity. But this milestone marked the first major step towards developing solar technology.
The first silicon solar cell was created in 1941 by Russell Ohl, an American inventor who worked for Bell Laboratories. His cells reached 4% efficiency. Ohl’s design became the basis for all silicon-based solar cells we have today.
The first practical solar cell for converting enough sunlight into power came about in 1954 from Bell Laboratories. The new silicon solar cell was 4.5% efficient and paved the way for wider applications of solar photovoltaics.
NASA helped drive many key innovations in solar cell technology in the 1950s-60s for use in space satellites. This helped bring down costs and improve efficiency up to 14% by 1964.
With the energy crisis in the 1970s, there was greater interest and investment in renewable energy like solar. Solar panels began being used in small niche markets as costs started to decline.
In the past few decades, solar panel efficiency has increased to over 20% while costs have plummeted, making solar PV competitive with conventional power. Many homes and businesses now utilize solar energy.
The future looks bright for solar power as technology improves and solar continues displacing fossil fuels.
How Do Solar Panels Work?
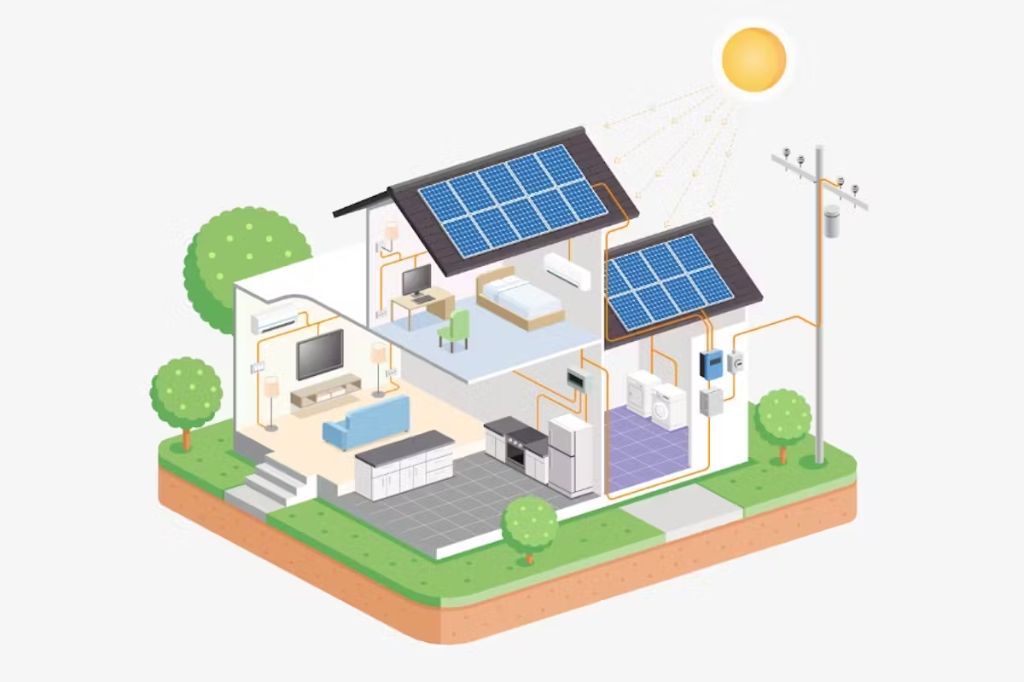
Solar panels work through the photovoltaic effect, which is the process of converting sunlight into electricity. At the heart of a solar panel are solar cells made up of semiconducting materials, most commonly silicon. When sunlight hits these solar cells, the energy from the photons in the light knocks electrons loose in the semiconducting material, allowing them to flow and produce an electric current (Source: https://pickmysolar.com/how-solar-panels-work/).
The basic building block of solar panels is the solar cell. Solar cells have one side with a positive electrical charge and one side with a negative electrical charge. When sunlight hits the solar cell, energy from the photons excite the electrons from the negative side to jump over to the positive side. This flow of electrons produces electricity. Multiple solar cells are connected together and sealed behind glass to form a solar panel (Source: https://science.howstuffworks.com/environmental/energy/solar-cell.htm).
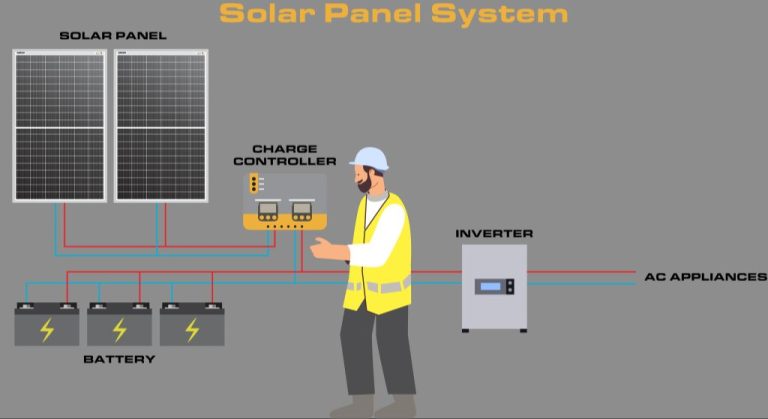
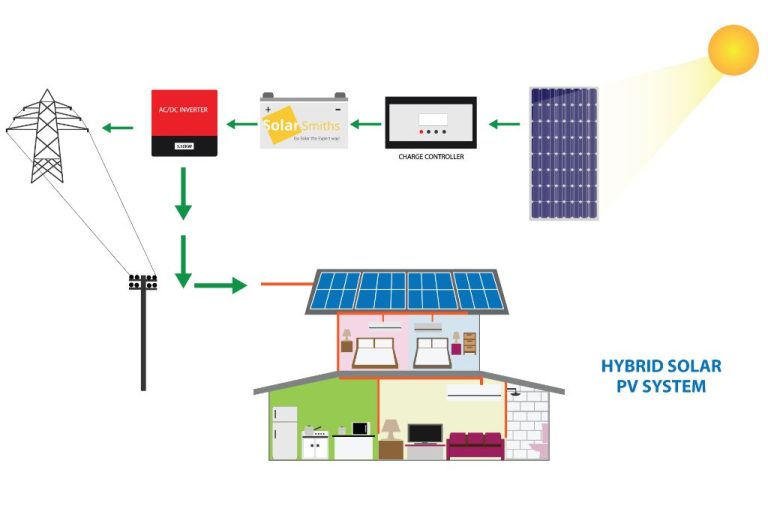
Solar panels are composed of many solar cells wired together in series and parallel circuits to produce higher voltages and currents. The direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels then goes through an inverter to convert it into alternating current (AC) electricity that is used in homes and businesses.
Types of Solar Panels
There are two major types of solar power generation technologies: photovoltaics (PV) and concentrated solar power (CSP).
Photovoltaic solar panels, or solar PV, convert sunlight directly into electricity using semiconducting materials. PV panels come in a few different types:
- Monocrystalline silicon – Made from a single crystal of silicon, these are the most efficient but also most expensive.
- Polycrystalline silicon – Made from multiple silicon crystal fragments, less efficient than monocrystalline but cheaper.
- Thin-film – Made by depositing extremely thin layers of photosensitive materials on glass, metal or plastic. Less efficient but cheaper than crystalline silicon.
PV panels can be mounted on rooftops or ground-mounted as part of a larger solar array. Most residential and commercial solar installations use PV panels.
Concentrated solar power (CSP) systems use mirrors to concentrate sunlight to drive traditional steam turbines or engines. CSP allows energy storage by heating molten salt to generate power when direct sunlight is not available.
CSP plants are very large scale compared to PV and generate utility-scale solar power. CSP accounts for a small fraction of global solar generation capacity compared to PV.
Overall, PV solar panels, especially crystalline silicon types, are the most common and widespread solar power technology today [1].
Solar Panel Efficiency
Solar panel efficiency refers to the percentage of sunlight that hits the panel and gets converted into electricity. The average solar panel efficiency rating today is around 15-20%. However, panel efficiency can vary significantly depending on the type of solar panel technology.
Some key factors that affect solar panel efficiency include:
- Solar cell material – Materials like monocrystalline silicon tend to be more efficient than polycrystalline silicon.
- Temperature – Solar panels become less efficient as temperatures rise. Cooler climates yield higher efficiency.
- Shading – Even small amounts of shading from trees or buildings can greatly reduce efficiency.
- Age – Solar panel efficiency slowly decreases over time as materials degrade.
Research shows average solar panel efficiency has increased about 0.5% annually over the past 10 years. Continued advances in materials and manufacturing allow companies to produce ever more efficient solar panels. For example, SunPower now offers residential panels rated up to 22.8% efficiency, significantly better than the 15% panels commonly available just a few years ago.
Higher efficiency panels generate more electricity per square foot, so they can offset more of your home’s energy needs. When shopping for solar panels, carefully consider the efficiency ratings to maximize your long-term energy production.
Solar Energy Pros
Some of the main benefits of solar energy include:
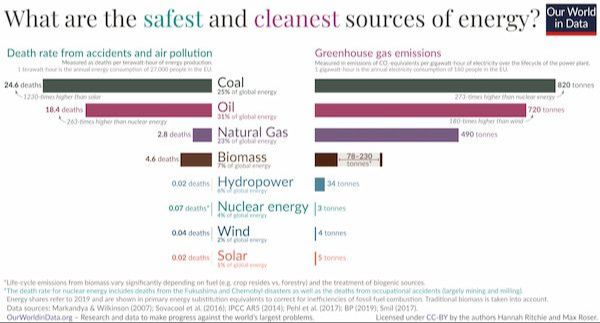
Solar is a renewable energy source. Unlike fossil fuels which are finite, the sun provides unlimited, clean energy. Sunlight can be harnessed indefinitely without ever running out.
Solar energy reduces carbon emissions. Generating electricity from solar panels produces no greenhouse gases or air pollution. Widespread adoption of solar power can significantly lower a region’s carbon footprint.
Solar panels can lower electricity bills. Once the system is installed, the “fuel” is free. This allows homeowners and businesses to reduce their monthly utility bills and electricity costs.
Solar provides energy independence. Producing your own renewable electricity allows you to reduce reliance on the traditional electric grid.
Solar Energy Cons
While solar energy has become more affordable and widespread in recent years, it still has some drawbacks that need to be considered. Here are some of the main disadvantages of solar energy:
High Upfront Costs
The biggest downside of solar panels is that they require a high upfront investment. The cost of purchasing and installing solar panels for a home averages around $20,000 according to Constellation (source). This high upfront cost can deter some homeowners from choosing solar.
Intermittent Power
Solar panels do not produce electricity at night, and their efficiency depends on the amount of unblocked sunlight during the day. Cloudy weather and seasons with limited daylight reduce solar energy generation, making it an intermittent power source. Battery storage systems can help mitigate this issue but add to the upfront costs (source).
Land Usage
Utility-scale solar farms require significant land area. The average solar farm takes up between 4 and 10 acres per megawatt of energy capacity produced. This land usage can disrupt natural habitats and take agricultural land out of production.
Toxic Materials
The manufacturing process of solar panels uses some toxic materials like arsenic and cadmium. Improper disposal of damaged solar panels can leach these chemicals into the environment. However, solar panel recycling programs are becoming more common.
Solar Energy Costs
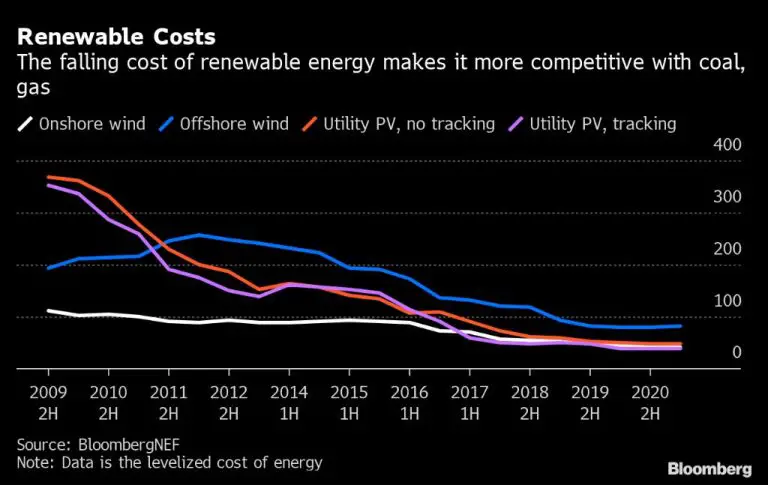
The cost of installing solar panels has dropped dramatically in recent years. According to Our World In Data, solar panel prices have fallen by over 90% since 1977 [1]. The average cost to install solar panels on a home in the U.S. is now around $16,000 for an average-sized residential solar panel system, according to Forbes [2]. However, costs can range from $4,500 to $36,000 depending on system size, location, panels, inverters and installation costs.
There are several incentives and tax credits available to help lower the upfront costs of solar panel installation. The federal solar tax credit offers a 26% tax credit for systems installed in 2022-2023, and 22% after 2023. Many local and state governments also offer additional rebates and incentives. When accounting for these credits and incentives, the payback period for solar panels is typically 6-12 years.
While solar panels do require an upfront investment, most homeowners see a return on their investment in under 10 years through lower electricity bills. In the long run, switching to solar can save homeowners tens of thousands of dollars in energy costs over the 25+ year lifespan of a solar panel system.
Top Countries Using Solar
Solar energy is being rapidly adopted around the world. According to Solar power by country, some of the top countries leading in solar power utilization include:
China has by far the most total installed solar PV capacity at over 306,973 MW, accounting for 35.8% of global solar capacity as of 2021. China has invested heavily in renewable energy, with solar being a major focus. The country has vast solar resources, especially in regions like the Gobi Desert.
The United States ranks second in total solar PV capacity at 95,209 MW as of 2021, accounting for 11.1% of the global share. Solar power has expanded rapidly in the US due to falling costs and supportive policies. Sunny states like California, Texas, and Florida lead in installed capacity. The US has tremendous untapped solar potential.
Japan comes in third with 74,191 MW of solar capacity installed as of 2021, making up 8.7% of the global market share. Japan’s solar growth has been driven by incentives for residential solar adoption. The country aims to continue increasing its renewable energy mix after the Fukushima nuclear disaster.
Germany takes fourth place with 58,461 MW of solar capacity. Despite having less sunny weather, Germany has promoted renewable energy heavily, with solar being a major focus. The country aims to phase out nuclear power and continue increasing solar and other renewables.
Future of Solar Energy
The future of solar energy looks very bright. According to research from MIT, solar could provide up to 69% of electricity generation by 2050 if new technologies and scaled production can reduce costs (The Future of Solar Energy). Key factors influencing growth include:
Projected growth – Solar power capacity is expected to grow exponentially in the coming decades. The U.S. Department of Energy found that solar energy could make up over 40% of the nation’s electricity by 2035 and 45% by 2050 with supportive policies (NREL).
New technologies – Continued improvements in solar cell efficiency and new applications like building-integrated photovoltaics will further reduce costs. Emerging technologies like perovskite solar cells and solar thermophotovoltaics offer potential breakthroughs.
Clean energy transition – As nations move away from fossil fuels, solar is poised to be a major component in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and fighting climate change.
However, obstacles remain such as intermittent power generation, land use constraints, and costs of energy storage and transmission infrastructure upgrades. Overall though, solar energy is expected to play a central role in the global shift to renewable energy.