What Is Renewable Vs Green Vs Clean?
Defining Renewable Energy

Renewable energy comes from naturally replenishing sources that are not depleted when consumed (1). These include wind, sunlight, geothermal heat, tides, water, various forms of biomass, and more. Renewable energy can be derived from energy sources like the sun and wind, which will not run out for billions of years (2). The most common types of renewable energy include:
(1) https://www.un.org/en/climatechange/what-is-renewable-energy
(2) https://www.nrdc.org/stories/renewable-energy-clean-facts
Defining Green Energy
Green energy refers to energy generated from clean, renewable sources that have a minimal environmental impact. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) defines green power as “a subset of renewable energy” that provides the greatest environmental benefit. It comes primarily from solar, wind, geothermal, biogas, low-impact hydropower and wave/tidal energy sources.
Green power sources and technologies have much lower carbon footprints and less polluting emissions compared to conventional fossil fuel sources. Generating energy from these renewable sources helps conserve natural resources and reduces greenhouse gas emissions, which contribute to climate change. Wide adoption of green energy is a key strategy for building a sustainable future based on clean energy.
Defining Clean Energy
Clean energy refers to energy that comes from sources with little to minimal greenhouse gas emissions and pollution. Some of the most common sources of clean energy include solar, wind, and hydro power. Clean energy comes from natural sources or processes that do not produce carbon dioxide and other pollutants. This is in contrast to fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas, which do emit greenhouse gases when used for energy.
According to the US Department of Energy, clean energy includes renewable energy sources, technologies that improve energy efficiency, and energy storage. Examples of clean energy technologies include solar photovoltaics, wind turbines, hydropower facilities, geothermal power plants, and advanced batteries for energy storage. These technologies harness natural cycles and resources to generate electricity with minimal environmental impact.
The shift to clean energy is important to reduce air and water pollution, improve public health, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and mitigate climate change. Widespread adoption of clean energy can also enhance energy security by reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels.
Comparing Renewable, Green and Clean Energy
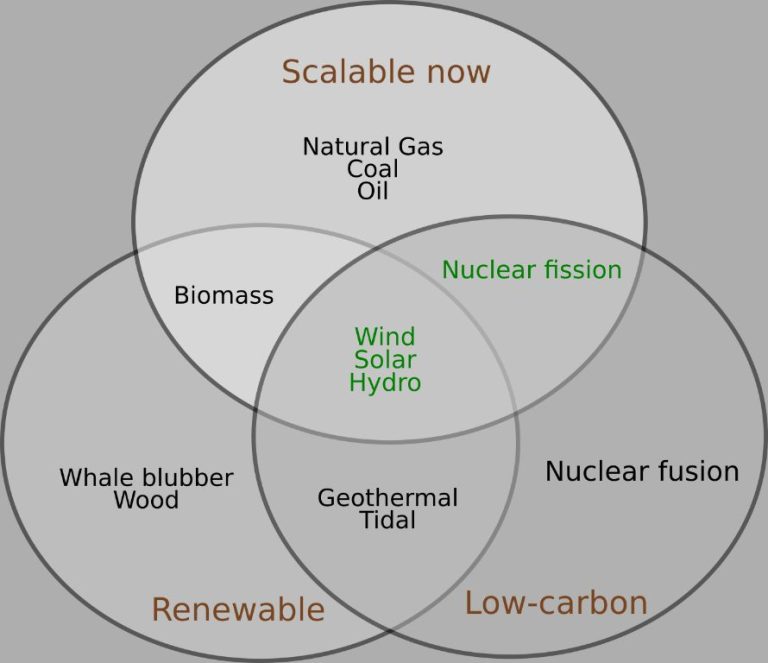
Renewable energy, green energy, and clean energy are related terms that often overlap but have some key differences. According to National Grid, green energy refers specifically to energy sources that are both renewable and have minimal environmental impact 1. Renewable energy includes sources that don’t deplete resources like fossil fuels, such as solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal, and biomass. However, some renewable sources can still have negative environmental impacts. Clean energy refers to energy sources that don’t pollute the air or environment when used. This includes some renewables like solar, wind, and hydropower, but also cleaner fossil fuels like natural gas 2.
In summary, green energy is a subset of renewable energy that has minimal environmental impact. Renewable energy overlaps with green and clean energy, but some renewables are not necessarily clean or green. Clean energy overlaps with some renewables but also includes cleaner fossil fuels.
Most Common Renewable Sources
Some of the most widely used renewable energy sources include:
- Solar Energy – Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity. Solar is one of the fastest growing renewable sources.[1]
- Wind Energy – Wind turbines use the wind to generate mechanical power which is converted into electricity. Wind power capacity has expanded rapidly in recent years.[2]
- Hydropower – Flowing water is used to spin turbines connected to generators. Hydropower is the largest renewable power source globally.[2]
- Geothermal Energy – Steam or hot water from underground is used to generate electricity. Geothermal capacity has grown steadily.
- Biomass – Organic matter like plants, wood, and waste are used to produce energy. Bioenergy covers around 10% of global energy supply.
Other renewable sources like wave and tidal power are not yet widely adopted but have potential for future growth.
[1] https://www.un.org/en/climatechange/what-is-renewable-energy
[2] https://www.power-technology.com/features/featurethe-worlds-most-used-renewable-power-sources-4160168/
Benefits of Renewable Energy
There are many key benefits to using renewable energy sources like wind, solar, hydroelectric, geothermal and biomass:
Less Pollution: Unlike fossil fuels, most renewable energy sources produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions or air pollutants, leading to cleaner air and water. This helps mitigate climate change and reduces health impacts. According to the EPA, renewable electricity standards could cut carbon dioxide emissions by 887 million metric tons by 2030.
Infinite Supply: Renewable energy sources are considered infinite and will not run out, unlike fossil fuels which are finite. The sun’s rays, wind, and heat from the earth’s core can be harnessed indefinitely when the proper technologies are in place. This provides long-term sustainability and energy security.
Price Stability: While fossil fuel prices are prone to volatility based on geopolitical events and availability, renewable energy is insulated from these supply shocks after installation. Locking in low renewable energy prices through power purchase agreements helps stabilize energy costs.
Energy Independence: Developing local renewable energy sources allows communities and countries to rely less on imported fuels. This reduces dependence on foreign oil and improves trade deficits. In 2020, 11% of U.S. energy consumption was from renewable sources.
Drawbacks of Renewable Energy
While renewable energy has many benefits, there are some drawbacks to be aware of as well. Some of the main disadvantages of renewable energy include:
High Upfront Costs
The technologies and infrastructure needed for renewable energy often require high upfront investments. According to the Union of Concerned Scientists, capital costs for renewable energy can be a barrier to increased adoption, as they can be more expensive than traditional fossil fuel plants and technologies initially [1]. However, over the long term, the lower operating costs and free fuel sources of renewables can provide economic advantages.
Intermittency
Many renewable energy sources like wind and solar are weather-dependent and provide intermittent power. The availability of the resource must be matched to demand, which can require storage systems and backup power to provide continuous electricity supply. Intermittency can also create challenges for grid integration and transmission infrastructure [2].
Location Constraints
Renewable energy systems are often location-dependent, with power generation limited to areas with ideal resource availability. Transmission infrastructure is needed to bring the power to end users, which can add costs and complexities. Siting and permitting of projects can also be an issue in less ideal areas [3].
Global Growth of Renewables
Renewable energy capacity has seen rapid growth globally over the past few decades. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), renewable energy sources accounted for over 42% of global electricity generation in 2028, with wind and solar PV doubling their share to 25% (IEA). The IEA also reports that renewable power is on course to shatter more records, as countries around the world speed up deployment. The world’s total renewable electricity capacity is projected to rise to 4,500 gigawatts (GW) in 2023, equal to the entire power capacity of China today (IEA).
According to Statista, electricity generation from renewable energy is projected to amount to 7,295 billion KWh in 2024, with an annual growth rate of 3.88% expected between 2024-2028 (Statista). This demonstrates the accelerating pace of renewable energy capacity and generation globally.
Future Outlook
The future looks bright for renewable energy. According to the UN, renewable energy has seen exponential growth in recent years and is expected to be the world’s main source of energy by 2050 (https://www.un.org/en/climatechange/raising-ambition/renewable-energy). The US Department of Interior states that renewable energy projects will help power communities across America in the future (https://www.doi.gov/priorities/clean-energy-future). The New York Times reports that wind and solar are breaking records, and are projected to surpass coal as the top source of electricity by 2025 (https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2023/08/12/climate/clean-energy-us-fossil-fuels.html).
With global investments and favorable policies, the potential for renewables is enormous. Solar and wind power are becoming more efficient and affordable. Emerging technologies like wave, tidal and geothermal energy are gaining traction. The transition to renewables is accelerating worldwide as countries target carbon neutrality and energy security.
Conclusion
Renewable, green, and clean energy sources all represent progress in the transition away from fossil fuels, but each term has some important distinctions:
- Renewable energy comes from naturally replenished sources like sunlight, wind, water flow, and geothermal heat. Key examples are solar, wind, hydroelectric, geothermal and biomass.
- Green energy refers more broadly to any energy generation or use that is sustainable and environmentally friendly. This includes renewables as well as cleaner natural gas and nuclear energy.
- Clean energy refers to energy sources that don’t pollute the atmosphere when used. Renewables and nuclear energy are considered clean, while fossil fuels are not.
While no energy source is perfect, the continued growth of renewables is critical for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change. Renewables are now the cheapest form of new electricity generation in most major markets, and costs continue to fall. Global renewable energy consumption is projected to grow 50% from 2022 to 2027.
The energy transition is well underway but more work remains to increase adoption of renewables across the heat, electricity and transportation sectors. With supportive policies and technological advances, renewable energy could realistically provide 50-90% of global electricity by 2050. This transition will bring major environmental and health benefits from cleaner air and lower carbon emissions.