What Is Radiant Energy For Kids?
What is energy?
Energy is what makes things happen or change. It is the ability to do work. Energy allows things to move, change, grow, and more. Without energy, nothing would happen at all!
There are different forms of energy around us every day. The food we eat gives us energy to play and move. The sun’s light provides energy that plants use to grow. Batteries store energy that can power toys and games. Energy is all around us and allows us to do everything we do.
Energy comes in different types like light, heat, motion, and more. But they all have something in common – they allow work to be done. So whether it’s the sun warming your skin, the wind blowing a windmill, or a battery powering a flashlight, it’s all energy at work!
Forms of energy
Energy comes in many different forms that we encounter in our everyday lives. Some of the main forms of energy include:
- Mechanical energy – the energy of motion and position. Examples are a ball rolling down a hill or a spring that is compressed.
- Chemical energy – the energy stored in the bonds between atoms and molecules. Batteries and food are examples of stored chemical energy.
- Electrical energy – the movement of electrons. Lightning and electricity from wall outlets are examples.
- Thermal energy – the energy that comes from the temperature of matter. The higher the temperature, the more thermal energy something has.
- Radiant energy – energy that travels as waves or particles, like light from the sun or x-rays.
- Nuclear energy – the energy stored in the nucleus of an atom. Nuclear power plants split atoms to release this energy.
- Sound energy – energy that travels in waves that our ears can detect as sound. Musical instruments create vibrations that turn into sound energy.
Energy is never created or destroyed – it just changes from one form into another. Like when a light bulb changes electrical energy into light and heat energy.
What is radiant energy?
Radiant energy is a form of energy that travels as waves. It includes visible light, ultraviolet light, infrared radiation, radio waves, X-rays, and gamma rays. These different types of radiant energy have different wavelengths and frequencies.
Radiant energy is created when atoms or molecules emit electromagnetic waves. The atoms can release energy as light or heat. For example, the radiant energy from the Sun is created by nuclear fusion reactions inside the Sun. The released energy travels to Earth in the form of electromagnetic radiation.
Unlike heat energy that is transferred by convection or conduction, radiant energy can travel through empty space. The waves do not require a medium to travel through. This means radiant energy from the Sun can travel through the vacuum of space before reaching Earth’s atmosphere.
Radiant energy travels very fast. Visible light from the Sun reaches Earth in just over 8 minutes. Because it does not need a medium like air or water, radiant energy can cover long distances quickly.
Types of radiant energy
There are different types of radiant energy including:
- Light – The visible light that our eyes can see is a type of radiant energy. Light allows us to see the world around us.
- Infrared – Infrared waves have longer wavelengths than visible light. Infrared allows us to feel heat from sources like the sun or a fire.
- Ultraviolet – Ultraviolet light has shorter wavelengths than visible light. Ultraviolet rays from the sun help provide vitamin D but too much exposure can cause sunburn.
- Radio waves – Radio waves have very long wavelengths and are used for radio, television, and wireless technology like WiFi and Bluetooth.
- Microwaves – Microwaves have medium wavelength and are commonly used for microwave ovens, radars, and wireless internet.
- X-rays – X-rays have very short wavelengths and can penetrate many materials. In medicine, x-rays allow us to see inside the human body.
All these types of waves are forms of radiant energy that travel through space or matter at the speed of light.
How does radiant energy travel?
Radiant energy travels in waves from one place to another. These waves are called electromagnetic waves. Electromagnetic waves can travel through substances like air, water or even the vacuum of outer space!
The waves spread out as they move. Think of throwing a pebble in a pond. The waves created by the pebble will spread out in circles that get bigger and bigger. Radiant energy waves spread out in a similar way as they travel.
Electromagnetic waves have different wavelengths. Some have very short wavelengths, like x-rays and gamma rays. Others have longer wavelengths, like radio waves. Visible light that we can see with our eyes has wavelengths in between. The wavelength affects how much energy the electromagnetic wave carries. Shorter wavelengths carry more energy.
Radiant energy from the sun
The sun is the biggest natural source of radiant energy in our solar system. The light and heat that travels from the sun to Earth is a form of radiant energy. This energy starts out in the center of the sun where atoms combine in nuclear fusion reactions that give off tremendous amounts of energy. This energy then radiates outward through the different layers of the sun and into the space surrounding it.
It takes about 8 minutes for the radiant energy from the sun’s surface to reach Earth, which is 93 million miles away. This radiant energy travels at the speed of light, which is about 186,000 miles per second! When the radiant light and heat from the sun reaches Earth, it provides the energy that powers almost all life on our planet. Plants use the sun’s radiant energy to grow. The food chain depends on plants capturing radiant energy. Radiant energy from the sun also warms Earth’s air, land, and water, creating our climate and weather patterns.
Sunlight and heat are critical forms of radiant energy for life on Earth. Without the constant stream of solar radiant energy, our planet would be dark and cold. The sun’s radiant energy makes life on Earth possible.
Uses of radiant energy
Radiant energy has many practical uses in our everyday lives. Here are some of the main ways we utilize radiant energy:
Heating – The warmth from sunlight or fires is an example of radiant energy that we use for heating homes, water, and even food.
Lighting – Light bulbs, candles, and firelight give off visible radiant energy that allows us to see.
Cooking – Using the radiant heat from stoves, grills, campfires, and the sun to cook food.
Vision – Our eyes detect the visible radiant energy bouncing off people and objects to see the world around us.
Communications – Radios, cell phones, televisions, and wifi rely on radiant energy waves transmitted through the air to communication information.
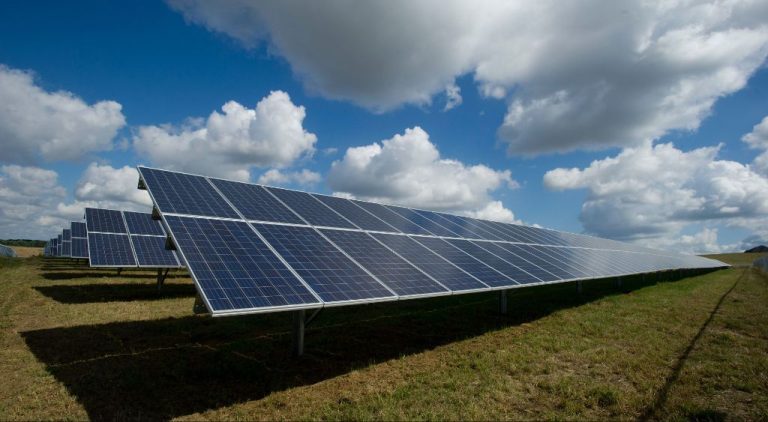
Solar power – Solar panels convert radiant light energy from the sun into electricity that powers homes and devices.
Medical imaging – X-rays, MRIs, and other imaging technologies use different forms of radiant energy to see inside the human body.
Examples of Radiant Energy
There are many common examples of radiant energy that kids experience every day:
- Sunlight – The warmth and light from the sun that we can see and feel is a form of radiant energy. Sunlight allows plants to grow and provides light so we can see.
- Microwaves – The microwave oven in your kitchen uses radiant energy in the form of microwaves to cook food. Microwaves are good at heating up food and drinks very quickly.
- Radio Waves – Radios and wireless internet work using radio waves, a type of radiant energy. Radio waves can travel over long distances and don’t need wires to work.
- Infrared Heaters – Some space heaters use infrared light, a type of radiant energy that we cannot see but can feel as warmth. Infrared heaters warm up people and objects instead of just heating the air.
So radiant energy is all around us! It allows us to see, feel warmth, cook food, listen to music, and more.
Radiant energy conversion
Radiant energy can be converted into other useful forms of energy like heat, electricity, and mechanical motion. For example, solar panels convert radiant light energy from the sun into electrical energy. The solar cells in the panels absorb photons from sunlight and cause electrons to move, creating an electric current. This current is captured and turned into electricity that we can use to power things like lights, appliances, and electric vehicles.
Another example is a solar cooker, which uses sunlight to heat food directly instead of using electricity or gas. The dark pots or surfaces convert the radiant energy into heat energy that cooks the food. Solar water heaters also work this way to heat water for use in homes and swimming pools.
One more way radiant energy is converted is through wind turbines. As sunlight hits the Earth, it warms the atmosphere unevenly creating wind. The kinetic energy of the moving air molecules is captured by the wind turbines and converted into rotational mechanical energy. This spins a generator to produce electricity.
Understanding radiant energy conversion allows us to harness the power of the sun in many useful ways, from generating electricity to cooking food! Converting radiant energy into other forms lets us utilize this abundant renewable resource.
Fun facts about radiant energy
Radiant energy is a fascinating form of energy that moves at incredible speeds. One of the coolest facts about radiant energy for kids to know is that it travels at the speed of light – a whopping 186,000 miles per second! That means in just one second, radiant energy can travel around the Earth over 7 times. Light from the sun, heat from a fire, and radiation from stars are all examples of radiant energy zipping around us. Understanding how quickly radiant energy moves helps explain why we can feel the warmth of the sun and see the light from stars that are very far away almost instantly. The speed of radiant energy is one of the many cool and fun facts for kids to learn about this unique form of energy.