What Is It Called When The Sun Produces Energy?
Solar energy is the radiant light and heat that comes from the sun. It is produced by the nuclear fusion reactions that occur inside stars like our sun. The sun radiates an enormous amount of energy, totaling around 3.8×10^26 watts. About 1.7×10^17 watts of solar power reaches the Earth’s atmosphere. This solar energy can be harnessed in various ways and converted into other forms of energy like heat and electricity. The conversion and use of the sun’s energy is often referred to as solar power or solar energy.
The sun produces solar energy through thermonuclear fusion reactions. Inside the core of the sun, hydrogen atoms fuse together under immense pressure and temperatures to create helium. This fusion process releases photons in the form of solar energy. These photons originate from the core of the sun and slowly make their way outward over a period of thousands to millions of years before reaching the sun’s surface. Once they emerge from the sun’s outer layer or photosphere, the photons stream through space at the speed of light until some reach Earth about 8 minutes later. This solar radiation that reaches our planet is the direct origin of nearly all energy sources and life here on Earth.
The Science Behind Solar Energy
The sun produces energy through the process of nuclear fusion. At the core of the sun, extremely high temperatures and pressures cause hydrogen atoms to come together and fuse into helium. This nuclear fusion process releases an enormous amount of energy in the form of heat and light.
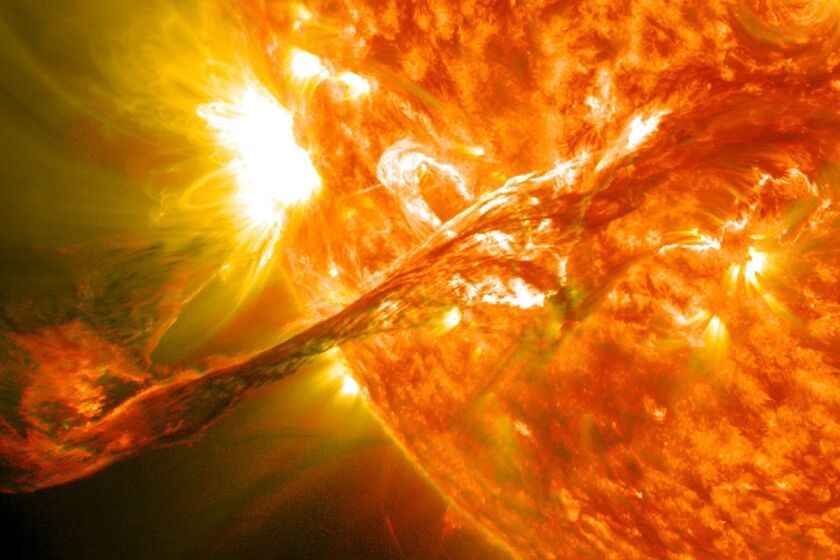

Specifically, when four hydrogen atoms fuse together, a helium atom is created, along with photons and neutrinos. Photons are packets of light energy, while neutrinos are nearly massless particles. The photons carry the light energy from the core of the sun to its surface, in a process that takes about 100,000 years. From the sun’s surface, the light then travels through space to reach Earth in about 8 minutes.
The light that arrives at Earth contains UV rays, visible light, and infrared energy. This broad spectrum light provides a tremendous amount of energy – about 1,000 watts per square meter at the upper regions of the Earth’s atmosphere. Solar panel technology allows us to convert the sun’s light energy into usable electricity for our homes, businesses, and infrastructure.
History of Utilizing Solar Energy
Humans have harnessed solar energy for thousands of years in passive ways like orienting buildings to maximize light and warmth from the sun. Ancient Greek and Roman architecture often incorporated south-facing windows to let in sunlight for illumination and heating. Solar energy was also used to heat water for bathing and cooking food.
The earliest known use of a “solar collector” to capture energy from the sun dates back to the 7th century B.C.E. People oriented mirrors to focus sunlight on a centralized location to heat objects. Similar technology was used in the 1700s to cook food and heat homes.
In the 1860s, Auguste Mouchout pioneered early solar-powered engines. He displayed a working model at the 1878 Universal Exhibition in Paris that used a parabolic trough concentrator to power a printing press and ice-making machine.
Throughout the late 19th and early 20th centuries, scientists continued experimenting with solar-powered devices. Innovations like photovoltaic solar cells emerged, leading to new applications for harnessing the abundant and renewable power of the sun.
Modern Solar Power Technology
The two main types of modern solar power technology are photovoltaic (PV) cells and solar thermal systems. PV cells, often referred to as solar panels, are made from materials like silicon that convert sunlight directly into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. Arrays of PV cells are installed on rooftops, vehicles, and large-scale solar farms to generate clean renewable electricity.
Solar thermal systems, also called concentrated solar power (CSP), use mirrors to focus sunlight and convert it into high temperatures that can be used to spin a turbine to generate electricity. There are different CSP technologies like parabolic troughs, solar towers, and solar dishes that concentrate solar radiation in various ways. CSP plants allow solar energy to be stored as heat and used to generate electricity even when the sun isn’t shining.
Solar Power Generation
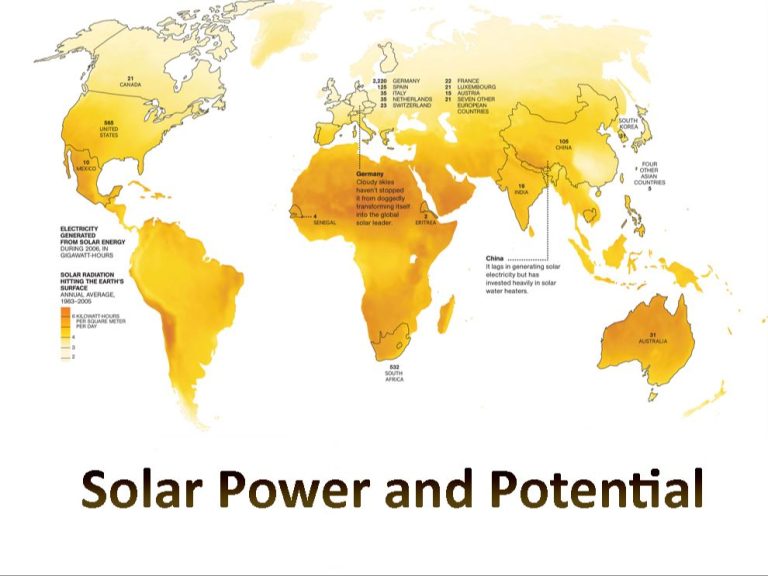
Solar power generation has grown dramatically in recent years as the costs of solar panels and associated technologies have declined. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the global solar PV capacity reached over 627 gigawatts (GW) by the end of 2019, with an estimated increase of 17% from 2018. This accounts for over 2.6% of global electricity demand. The countries with the most solar PV capacity are China, the United States, Japan, Germany and India. The IEA projects that solar PV capacity could reach over 4,500 GW globally by 2040, accounting for 16% of global electricity generation.
The amount of solar energy that can be generated depends on several factors such as the number and size of solar panels installed, the efficiency of the solar cells, the amount of direct sunlight received, and the presence of any shading. On average, current solar panels on homes have capacities between 3-8 kilowatts (kW), while large-scale solar farms can have capacities in the megawatts (MW) or even gigawatts. Assuming full sun conditions, a 5 kW solar array could generate around 20 kilowatt-hours of electricity per day, enough to power the average U.S. home.
Solar power generation provides clean, renewable electricity without any fuel costs or carbon emissions during operation. The modular nature of solar PV also allows generation capacity to be scaled as needed. Nevertheless, the intermittency of solar irradiation and the need for energy storage remains a challenge. Overall, solar power has proven itself as a rapidly scalable source of renewable energy with enormous potential to continue growing globally.
Benefits of Solar Energy
Solar energy offers numerous benefits that make it an attractive renewable energy source. Here are some of the main advantages of solar power:
It’s renewable – Solar energy comes from the sun, which will continue shining for billions of years. This makes solar a clean, renewable source of energy unlike finite fossil fuels.
It reduces carbon emissions – Generating electricity from solar panels produces no greenhouse gas emissions. Widespread adoption of solar power can significantly lower a country’s carbon footprint.
It lowers utility bills – Putting solar panels on your roof allows you to generate your own electricity during the day. This can reduce your dependence on the grid and lower your monthly utility bills.
It requires little maintenance – Unlike other power sources, solar panels have no moving parts and require almost no maintenance once installed. The panels will produce electricity for decades with minimal upkeep.
It creates jobs – The solar industry employs hundreds of thousands of people in manufacturing, installation, maintenance and other roles. Growth in solar power brings economic benefits.
Limitations of Solar Power
While solar power has many benefits, it also has some limitations that need to be considered:
Intermittency
Solar energy production depends on the amount of sunlight, which varies throughout the day and year. Solar panels do not generate electricity at night, and output can be reduced on cloudy days. This intermittency means solar often needs to be combined with energy storage or a supplemental power source.
Higher Upfront Costs
The initial purchase and installation cost of a solar system is still higher than fossil fuel alternatives. However, once installed solar has very low maintenance and fuel costs. The overall lifetime cost of solar is competitive, but the upfront investment can deter some users.
Land Use
Utility-scale solar farms require significant land area. This could compete with agriculture, wildlife habitats or residential areas. However rooftop solar on homes and businesses maximizes existing structures without using additional land.
Improving Efficiency and Storage
Significant research and development efforts are focused on improving the efficiency and storage capacity of solar power systems. Some key areas of focus include:
New materials – Scientists are developing advanced solar cell materials like perovskites that can convert sunlight to electricity more efficiently than traditional silicon cells. Organic solar cells made from carbon-based materials also show promise as a low-cost, flexible option.
Solar tracking – Systems that dynamically move solar panels to follow the sun’s path across the sky can increase energy capture by 20-30%. Single and dual-axis trackers are becoming more prevalent in large-scale solar farms.
Batteries – Storing solar energy for use when the sun isn’t shining is key to making solar power more practical and grid-friendly. Lithium-ion batteries have advanced tremendously, and new battery chemistries like flow batteries are being researched to find safer, cheaper, longer-lasting storage.
Hybrid systems – Pairing solar power with other technologies like diesel generators or battery storage can provide more consistent, around-the-clock energy production.
Improved manufacturing – New fabrication techniques for solar cells can reduce costs and increase efficiency. Automated assembly and streamlined processes are helping scale up production.
With ongoing progress, solar power systems are only going to get more capable and cost-effective over time.
Future Outlook
The future looks bright for solar energy. Most experts predict substantial growth in solar power generation over the next several decades. Here are some projections for the future of solar energy:
Growth in installations: According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), total solar photovoltaic capacity is forecast to reach over 4,500 gigawatts by 2050, a 14-fold increase from 2020 levels. This is enough to power entire countries. The IEA predicts solar will dominate renewable energy growth and become the new king of electricity markets.
Declining costs: Solar panel costs have already dropped 90% over the last decade. Experts predict costs will continue falling as technology improves and solar power scales up. According to Lazard’s annual energy cost analysis, utility-scale solar costs could be as low as $0.01 per kWh within the next two decades, undercutting fossil fuels.
Grid integration: As solar and wind gain share, managing their variability will be critical for grid stability. Building out transmission networks, implementing smart inverters, and advancing energy storage solutions will enable greater penetration of solar power onto the grid. Widespread electrification and “vehicle-to-grid” technologies using EV batteries as storage will also help integrate solar and wind onto the grid.
With solar already among the cheapest sources of electricity in many markets, ongoing innovations and enabling technologies will allow solar power to continue its rapid growth in the decades ahead.
Conclusion
In summary, the process by which the sun produces energy is called solar power. The sun naturally generates energy through nuclear fusion in its core, releasing photons that travel outwards and reach Earth. When these photons interact with certain materials like silicon, they can dislodge electrons and create an electric current that we capture as electricity. Humans have harnessed solar power for centuries in simple ways like heating homes and water. But in modern times, we now have advanced photovoltaic panels and concentrated solar plants that convert sunlight into electricity on a massive scale. Solar power provides clean, renewable energy without producing greenhouse gases. It has huge potential to provide a substantial portion of the world’s electricity needs. While solar currently accounts for only about 2% of global energy production, it is the fastest growing renewable source. With improving technology and energy storage solutions, along with supportive policies and decreasing costs, solar energy can continue its rapid growth. Widespread adoption of solar power will be an important part of building a sustainable future and mitigating climate change.