What Is Energy Efficiency Environmental Science?
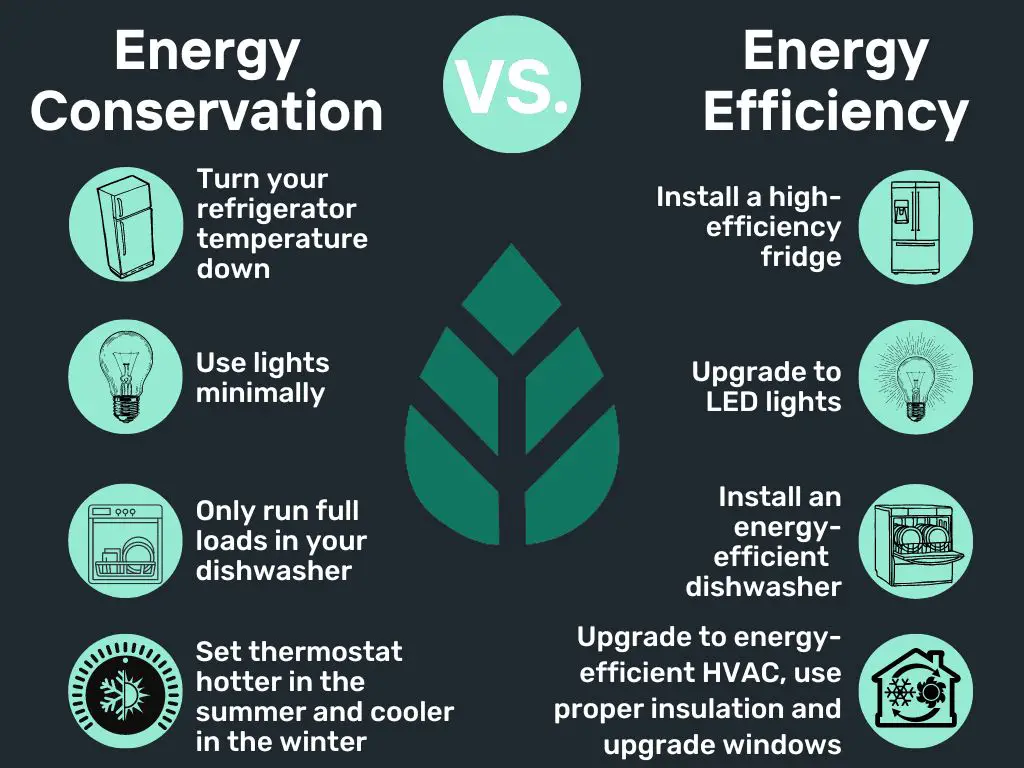
Energy efficiency refers to the practice of optimizing energy use to reduce energy demands and consumption (https://utilitiesone.com/importance-of-energy-efficiency-in-developing-world-construction). Energy efficiency is important because it helps conserve finite resources, reduces pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, lowers energy costs, and promotes sustainable development.
Energy efficient practices aim to reduce the amount of energy required to provide energy services like heating, cooling, lighting, transportation, and manufacturing. This is achieved through more efficient energy use, conversion, and distribution. Some common examples include installing insulation, using LED lighting, utilizing renewable energy sources, and choosing energy efficient appliances and electronics.
This content will provide an in-depth overview of energy efficiency topics related to environmental science. We will explore ways to increase efficiency in buildings, transportation, industry, and more. The importance of energy policy and future directions for efficiency will also be discussed.
Reducing Energy Consumption
There are many strategies that can be implemented to reduce energy consumption in homes, businesses, and transportation. Simple behavioral changes like turning off lights and appliances when not in use can make a difference. Homeowners can also invest in energy efficient appliances, heating and cooling systems, insulation, windows, and lighting to reduce energy waste (EPA).
Businesses can install energy management systems, upgrade equipment, and implement sustainability practices. Shutting down equipment when not in use, enabling power management settings on computers, and encouraging employees to be mindful of their energy use are impactful steps. Companies can also optimize heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) through regular maintenance, smart thermostats, and upgraded insulation (NHSaves).
In transportation, using public transit, walking, biking, carpooling, and driving electric vehicles are ways to conserve energy. Proper vehicle maintenance such as checking tire pressure can also improve fuel efficiency. Reducing idling, removing extra weight from vehicles, and avoiding rapid acceleration and braking while driving can help save gasoline.
Increasing Efficiency of Appliances
One impactful way to improve energy efficiency is by utilizing more efficient household appliances and electronics. According to the EPA, appliances and electronics account for up to 30% of the average home’s energy use [1]. Upgrading to ENERGY STAR certified models can reduce appliance energy use by 10-50% [2].
ENERGY STAR is an EPA program that rates appliances based on their energy performance. Appliances like refrigerators, dishwashers, clothes washers and dryers that earn the ENERGY STAR label use less energy and water than standard models. Replacing an old appliance with an ENERGY STAR model can save on monthly utility bills. For example, replacing a 10-year-old refrigerator with a new ENERGY STAR certified one can save a household $270 over the life of the appliance [3].
Upgrading older appliances, even if they are still functioning, to more efficient models is one of the most effective ways households can reduce their energy consumption and costs. Energy efficient appliances also help conserve resources and reduce carbon emissions from power plants.
Building Design and Materials
Energy efficient building design focuses on maximizing efficiency through passive solar techniques, proper insulation, weatherization, and green materials Efficient Home Design. Passive solar design incorporates large south-facing windows to allow sunlight to heat the building naturally. Strategic landscaping features like deciduous trees can provide shade in summer and sunlight in winter. Insulation in walls, attics, and foundations prevent heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer. Weather stripping, caulking, and proper ventilation regulate air flow. Green building materials like sustainable lumber, recycled content insulation, and non-toxic paints promote energy efficiency.
Key features of an energy efficient building include high R-value insulation, insulated windows with low-emissivity coatings, passive solar orientation, cool roofing materials, and careful air sealing 23 Key Features of an Energy Efficient Building. Proper insulation levels and air tight construction prevent drafts and regulate temperature. Smart thermostats and zoned heating/cooling systems maximize efficiency. Energy efficient lighting like LEDs reduce electricity use. Renewable energy systems like solar panels or geothermal heat pumps can help make buildings net-zero.
Following green building standards like LEED can help architects and builders construct high-performance, sustainable buildings with energy efficiency at the forefront Energy efficient building design. Attention to siting, materials, and design is crucial for minimizing a building’s energy demands and environmental footprint over its lifetime.
Heating and Cooling Systems
HVAC systems account for a significant portion of a building’s energy use. By upgrading to high efficiency systems, substantial energy savings can be achieved. The most efficient HVAC systems have a SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) rating of 16 or higher for air conditioning and AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) of 90% or more for heating systems.
One of the most energy efficient technologies are geothermal heat pumps. These systems take advantage of relatively constant ground temperatures to provide heating and cooling. According to Energy Star, geothermal heat pumps can reduce energy use for heating by 44-72% and for cooling by 25-50% compared to conventional systems.
Zoning your HVAC system is another way to improve efficiency. Zoning divides your home into different zones each with its own thermostat and HVAC equipment. This allows you to heat or cool only occupied spaces saving energy compared to conditioning the whole home.
Lighting
In commercial and residential buildings, lighting accounts for roughly 12% of energy usage in the United States (LRC, 2022). Energy-efficient lighting can significantly reduce electricity consumption, lower emissions from power plants, and reduce environmental impact.
Using natural lighting during daytime hours through proper building orientation, window placement, solar tubes, skylights and light shelves is an effective way to reduce the need for artificial lighting (LRC, 2022).
When artificial lighting is required, LED and CFL bulbs are up to 80% more efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs (SEPCO Solar Lighting, 2022). The energy efficiency of LED lights reduces electricity demand and greenhouse gas emissions from power plants.
Advanced lighting controls like occupancy sensors, daylight harvesting systems, and dimmers help optimize lighting usage. By reducing unnecessary lighting, controls can achieve additional electricity savings beyond efficient bulbs alone (Utilities One, 2022).
Overall, energy-efficient lighting through natural light, LED and CFL bulbs, and lighting controls provides significant environmental benefits by lowering electricity consumption and mitigating climate change.
Renewable Energy
Renewable energy comes from natural sources that are constantly replenished, such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves, and geothermal heat. Some of the most common forms of renewable energy are solar, wind, hydroelectric, and biofuels.
Solar power harnesses energy from the sun to generate electricity and provide lighting, heating, and hot water for homes, businesses, and industry. Solar energy can be captured through photovoltaic cells or used to heat fluids to run a turbine and generate electricity (https://www.energy.gov/eere/solar/solar-energy-technologies-office).
Wind power uses large wind turbines, usually grouped together in wind farms, to generate electricity. As wind blows past the turbine blades, they turn a rotor which spins a generator to create electricity (https://www.nrdc.org/issues/renewable-energy).
Hydroelectric power converts the energy of flowing or falling water into electricity. Hydropower plants capture water as it flows through dams or pipelines to spin turbines connected to generators (https://www.energy.gov/eere/water/hydropower-technologies).
Biofuels are fuels derived from biomass or biological material, including plant materials and animal waste. Common biofuels include ethanol produced from corn and sugarcane, and biodiesel from vegetable oils and animal fats. Biofuels can power vehicles and generate electricity (https://www.nrdc.org/issues/renewable-energy).
Transportation
Transportation accounts for a significant portion of energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions globally. Improving transportation efficiency through fuel efficient vehicles, mass transit, and telecommuting can dramatically reduce environmental impacts.
Fuel efficient vehicles like hybrids and electric cars can greatly reduce petroleum consumption and emissions compared to conventional internal combustion engines, according to the U.S. Department of Energy’s Sustainable Transportation and Fuels program. Widespread adoption of fuel efficient vehicles has helped lower transportation energy usage in countries like the United States.
Investing in mass transit systems like buses, trains, and light rail can also promote efficiency by moving more people with less energy compared to single occupancy vehicles, as noted by the UN’s Sustainable Energy for All initiative. Effective mass transit reduces congestion and pollution in urban areas.
Finally, telecommuting and remote work arrangements can eliminate commuting trips entirely. The US Department of Energy found telecommuting even 1-2 days per week can substantially reduce transportation energy usage when adopted widely.
Industry and Manufacturing
Industry accounts for a significant portion of energy consumption, approximately 32% in the United States according to the National Academy of Sciences (Energy Efficiency, Industrial Efficiency). Therefore, improving efficiency in this sector can yield major energy savings and reductions in greenhouse gas emissions. There are various ways industrial facilities can improve their energy efficiency.
One major area is increasing the efficiency of motors, which account for about two-thirds of electricity used in the industrial sector. Using variable speed drives, upgrading to premium efficiency motors, and performing regular maintenance can significantly reduce motor energy usage (Energy Efficiency Technologies).
Optimizing manufacturing reactors is another strategy, as chemical reactions are often very energy-intensive. Recovering waste heat from reactors to generate electricity is one effective approach. Proper insulation, modifying reaction parameters, and using more efficient reactors can also decrease energy needs.
In general, reducing waste in processes through techniques like lean manufacturing increases efficiency and saves energy. Recycling and reusing waste materials further lowers resource consumption. Overall, taking a systemic approach to minimize energy use across industrial facilities can yield major efficiency gains.
Policy and Future Directions
Governments around the world are implementing policies and regulations to improve energy efficiency and reduce energy consumption. According to the Stanford News article “Future of energy: Efficiency” https://news.stanford.edu/2017/10/05/future-energy-efficiency/, mandates for more efficient appliances, lighting, vehicles and buildings have played a major role in improving energy efficiency. Stricter building codes requiring better insulation, windows and HVAC systems have reduced energy needs in the building sector.
Governments also offer incentives like tax credits and rebates to consumers and businesses to upgrade to more efficient appliances, equipment and vehicles. The federal government in the U.S. offers tax credits for purchasing energy efficient windows, insulation, HVAC systems, water heaters and more through programs like Energy Star https://www.forbes.com/sites/feliciajackson/2023/11/09/energy-efficiency-its-time-to-get-next-level/. Many utility companies provide rebates on efficient appliances and equipment as well.
Investing in research and development for new energy efficient technologies will also help drive future improvements. Emerging technologies like smart grids, energy storage, and advanced building materials and systems can potentially deliver major gains in energy efficiency. Government and industry funding for R&D in these areas is key to advancing innovations in energy efficient technologies according to the Nature article “Clean energy can fuel the future” https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-023-02510-y.
Overall, a combination of regulations, incentives and new technology development will shape the future of energy efficiency and efforts to reduce energy consumption and emissions.