What Is Bee India?
bee India is a nonprofit organization dedicated to protecting bees and other pollinators in India. The organization was founded in 2015 by a group of scientists, conservationists, and citizens concerned about the decline in bee populations.
The mission of bee India is to conserve bees and other pollinators through research, education, outreach, and on-the-ground conservation efforts. Pollinators like bees play a crucial role in food production and the health of ecosystems, but they face threats from habitat loss, pesticides, diseases, and climate change. bee India aims to address these threats and create a sustainable future for bees and people in India.
Through partnerships and community engagement, bee India works to study pollinator populations, educate the public, support pollinator-friendly practices, and protect critical bee habitats across India. The organization strives to involve citizens in efforts to sustain pollinators which are essential for food security, biodiversity and environmental health in the country.
History of bee India
Beekeeping in India has a long history dating back thousands of years. Bees and honey are mentioned in ancient Hindu texts like the Vedas and Buddhist scriptures. Rock paintings from the Mesolithic era found in Madhya Pradesh show honey collection and beekeeping scenes.
Bees held an important place in mythology and symbolism in ancient India. Hindu gods like Krishna and Vishnu were associated with bees and called “Madhava” meaning “born of honey”. The sacred texts Rig Veda written between 2000-3000 BCE contains many references to bees and honey.
The practice of keeping and cultivating bees in India was widespread since ancient times. Traditional methods like log hives and clay hives were used. Beekeeping was done for both honey production and crop pollination. India has a diversity of native honey bee species like the giant honey bee, Apis dorsata, which have been harvested for centuries.
Modern techniques of beekeeping were introduced in India during the late 19th century under British colonial rule. Italian honey bees were brought to India in the 1960s and crossbred with native bees to create high-yielding hybrids for commercial beekeeping.
The need for organized research and training in beekeeping was recognized in the early 20th century, leading to the establishment of centers like the Indian Agricultural Research Institute’s National Centre for Integrated Pest Management. In more recent years, organizations like Bee India have emerged to promote beekeeping as a means of sustainable livelihood and conserve native bees.
Goals and Activities
The Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) has several main goals and activities focused on promoting energy conservation and efficiency in India. Some of the key goals outlined on the BEE’s website (https://beeindia.gov.in/en) include:
- Developing policies and strategies to reduce the energy intensity of the Indian economy
- Leading the implementation of the Energy Conservation Act, which includes initiatives like energy labeling of appliances, the Perform, Achieve and Trade scheme, and energy conservation building codes
- Developing testing protocols and certification programs for energy-efficient appliances and equipment
- Raising awareness and promoting energy efficiency and conservation through initiatives like the National Energy Conservation Awards, painting competitions, and educational campaigns
- Conducting training programs and developing educational materials related to energy efficiency and conservation
- Undertaking demonstration projects to showcase energy efficient technologies and practices
- Supporting research and development of new energy efficient technologies
Overall, the BEE aims to reduce energy intensity in India by promoting energy efficiency across sectors like industry, buildings, appliances, transport, and agriculture (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bureau_of_Energy_Efficiency). Its activities span policy, implementation, education, awareness, and technology development.
Bee conservation efforts
Bee conservation has become a major focus for Bee City India. Bees play a critical role as pollinators in agricultural systems and ecosystems. However, bee populations have been declining due to habitat loss, pesticides, diseases, and climate change.
Bee City India has launched multiple programs focused on protecting bees and other pollinators in India. Some key efforts include:
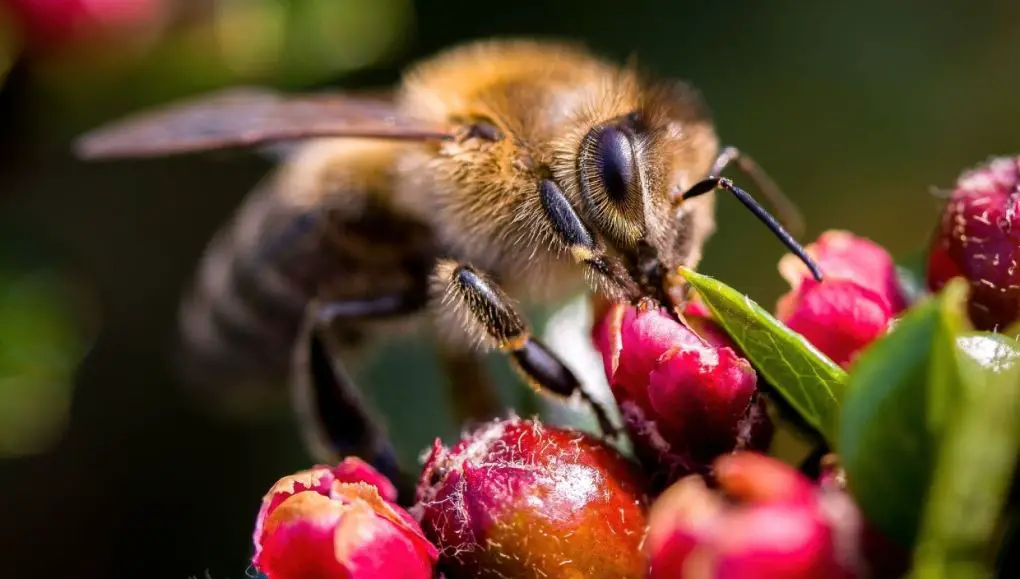

– Promoting organic and sustainable agriculture practices that avoid pesticide use linked to bee deaths.
– Creating pollinator habitats and food sources by planting native flowers, trees, and shrubs.
– Educating farmers, schools, businesses, and the public about the importance of pollinators.
– Training beekeepers on proper hive management to maintain healthy bee colonies.
– Researching issues impacting bee health and population declines.
– Advocating for policies and regulations that support pollinators.
– Forming partnerships with government agencies, NGOs, corporations, and local communities to expand pollinator protection.
By undertaking focused bee conservation programs, Bee City India aims to stabilize and grow bee populations which are essential for agriculture, biodiversity, and healthy ecosystems in India.
Education and outreach
Bee India has extensive education and outreach programs to promote energy efficiency across India. Some key initiatives include:
Bee India partners with schools and universities across India to educate students about energy conservation through initiatives like the National Children’s Painting Competition on Energy Conservation and the National Energy Conservation Awards for Schools. Over 15,000 schools have participated in these programs.[1]
Outreach to rural communities is a priority. Bee India trains farmers on efficient irrigation techniques and provides cooking stoves that reduce fuel use to rural households. Over 5 million rural households have benefited from energy efficiency improvements.[2]
Public awareness campaigns like Energy Conservation Week and the National Energy Conservation awards engage citizens across India on saving energy.
Research initiatives
Bee India supports and conducts scientific research on bees and beekeeping in India. Some of the key research initiatives include:
Studying the climatic impacts on bee behavior and colony health across different agro-climatic zones of India (Bee India research report). This helps identify optimal beekeeping practices for specific regions.
Researching integrated beekeeping models for small and marginal farmers to enhance pollination services and livelihood opportunities (AICRP honeybee report). This focuses on sustainable models for supporting beekeepers.
Developing protocols for bee disease identification and control to improve colony health and honey production (Bee India overview). This provides scientific guidance on disease prevention and treatment.
Evaluating the role of bees in increasing yields of hive-dependent crops through targeted pollination studies (AICRP honeybee). This quantifies the benefits of beekeeping for crop productivity.
Partnerships
Bee India collaborates with various organizations to further its mission of protecting bees and promoting bee research. Some of Bee India’s key partnerships include:
Project Pollinator with Syngenta – This partnership launched in 2008 aims to improve biodiversity on farmlands by creating pollinator-friendly habitats. As part of this, wildflower seeds are provided to farmers to sow on non-crop land.
Centre for Pollination Studies at University of Calicut – Bee India partners with the university by supporting research projects on bee diversity and pollination. Researchers from the center have conducted studies on bees across different agro-climatic zones in India.
Nature Forever Society – This non-profit focuses on protecting biodiversity and Bee India partners with them on awareness campaigns about bees and other pollinators.
Beekeeping associations – Bee India works with state and national level beekeeping associations to promote best practices in beekeeping and train beekeepers across India.
Funding and supporters
BEE India receives funding from a variety of sources to support its energy efficiency initiatives and programs. Some of the key funding sources include:
– Government of India – As an organization under the Ministry of Power, a significant portion of BEE’s budget comes from government funding. This allows BEE to administer national programs on energy efficiency and conservation (EEFP).
– International organizations – BEE has partnered with and received funding support from organizations like the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), Global Environment Facility (GEF), and Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) to run special energy efficiency programs and schemes (FEEED).
– Private sector – BEE works closely with financial institutions like Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) to create innovative financing platforms that provide funding for energy efficiency projects in industries and MSMEs.
– State agencies – Some state governments also provide budgetary support to implement BEE’s programs and initiatives within their jurisdiction.
Challenges
Bee India faces several challenges in achieving its goals of bee conservation and sustainable beekeeping. One major challenge is the declining bee population. According to India’s bees are dying out and only its farmers know why, the use of pesticides is believed to be a key threat to bee colonies in India. Since 2002, farmers have noticed fewer bees in agricultural areas where pesticides are heavily used.
Another obstacle is the lack of a stable honey market. As described in Beekeeping for Sustainable Economic Development of India, pricing of honey is a major issue because there is no fixed minimum support price. This results in large unsold stocks as beekeepers refuse to sell below production costs. Adverse weather events like droughts also periodically affect honey production, as noted in India’s Honey Production and Beekeeping Industry Face Challenges Due to Adverse Weather in 2023.
Furthermore, lack of education and awareness poses a challenge. Many farmers lack proper training in beekeeping methods and best practices. Overcoming these obstacles will be key for Bee India to achieve its mission of supporting beekeepers and conserving bees.
Impact
The Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) has made significant impacts through its various initiatives and programs since its inception in 2002. Some key successes and measurable impact include:
Under the Standards & Labeling program, BEE has covered 26 appliances and equipment resulting in an estimated annual savings of 167 billion units of electricity and 11.6 MTOE by 2020-21, leading to avoided capacity of 66 GW. As per a recent impact assessment report, the program has been successful in transforming the market, with over 95% of BEE star labeled products in some categories.
The Perform, Achieve and Trade (PAT) scheme, covering 13 energy-intensive sectors, has resulted in an energy savings of 31 MTOE in PAT Cycle I which concluded in 2015 and is estimated to lead to savings of 83 MTOE in PAT Cycle II ending in 2019-20. The savings translate to avoided capacity addition of around 19 GW and actual monetary savings of INR 24,000 crores.
Through the Energy Conservation Building Code, adoption has expanded from less than 20 million sq.ft in 2007 to over 2.7 billion sq.ft by 2019 leading to 30 million tonnes of annual CO2 emission reduction. ECBC has been crucial in mainstreaming energy efficiency in the buildings sector.
Overall, BEE’s efforts have transformed energy efficiency as a resource and led to avoided capacity addition of over 100 GW by 2020-21. The accumulated electricity savings of 325 billion units have resulted in cost savings of INR 35,000 crores and 250 million tonnes of CO2 emission reduction.