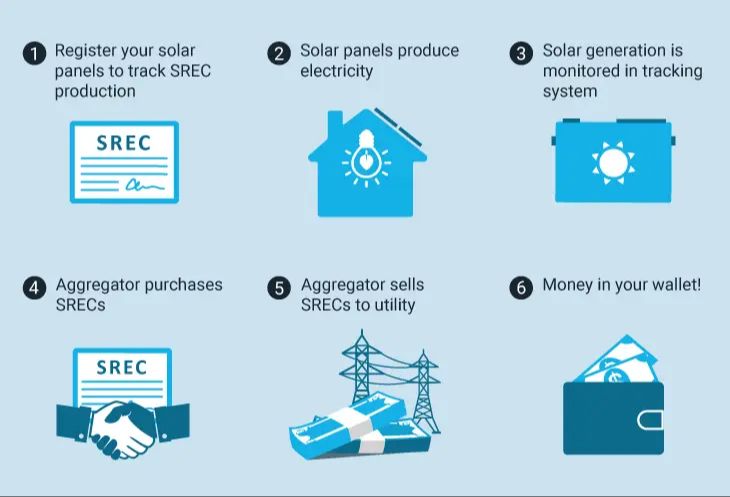
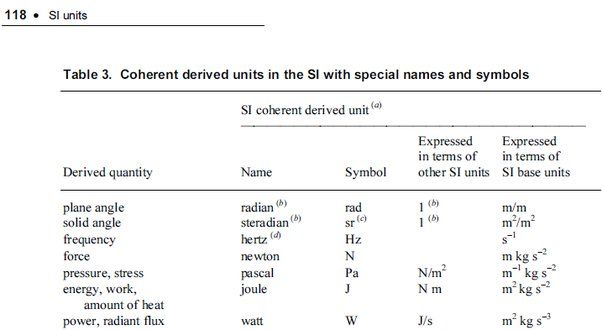
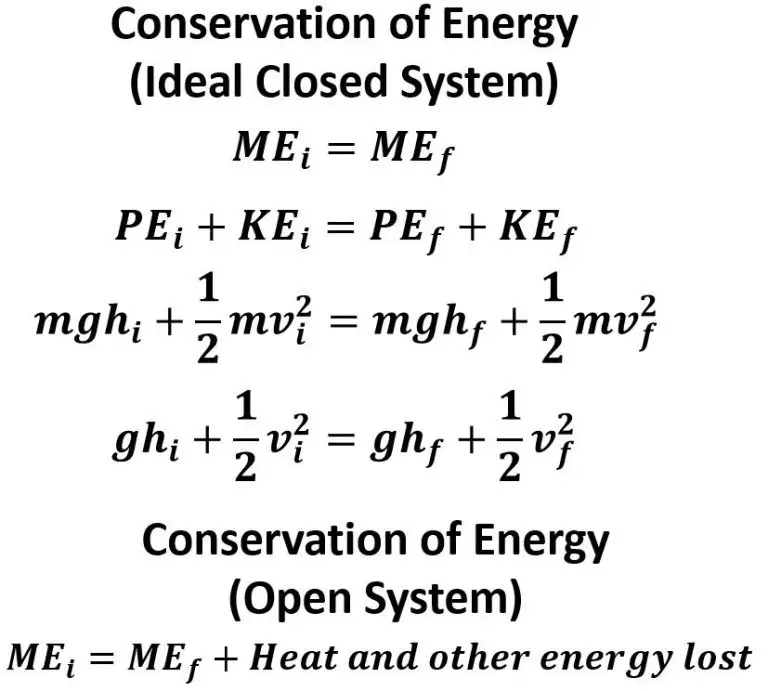
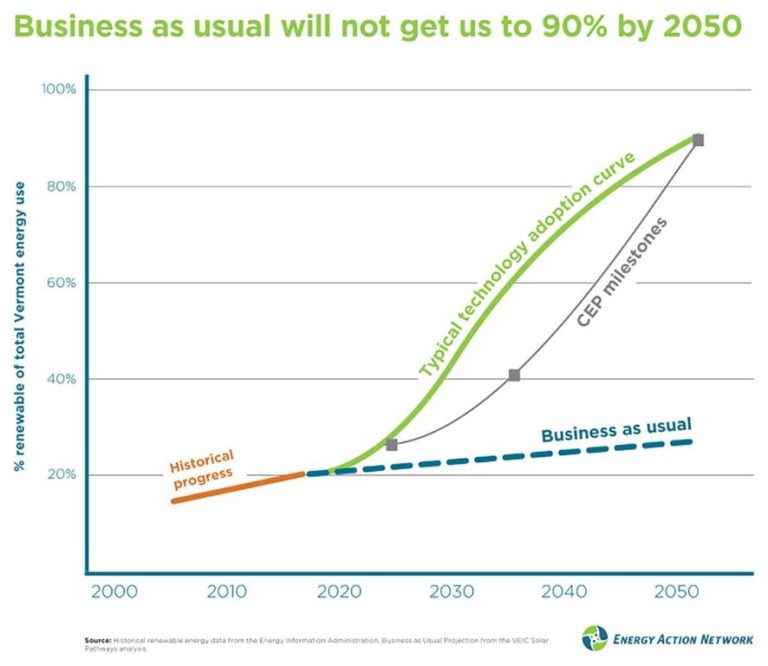
What Is A Good Sentence For Sustainable?
Definition of Sustainable
Sustainable refers to practices, processes or ways of life that are maintained indefinitely without depleting key resources or causing major ecological damage. The core idea is that current and future human needs can and should be met without compromising the health and functioning of the planet’s ecosystems.
More specifically, sustainability seeks to improve human well-being by preserving natural resources, reducing waste and pollution, using energy efficiently, and protecting human health and the environment. It requires taking a holistic, long-term view to find balanced solutions across economic, social, and ecological dimensions.
The concept of sustainability rose to prominence after 1987 with the publication of the Brundtland Report by the United Nations. This landmark report defined sustainable development as “development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.”
Why Sustainability Matters
Sustainability has become increasingly important in recent years as we recognize the immense strain our modern lifestyles put on the planet. Sustainability aims to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs. By living sustainably, we can maintain natural resources and healthy ecosystems for the future.
There are many benefits to adopting more sustainable practices:
- Protecting the environment – Sustainable practices like reducing waste, energy conservation, and green transportation help protect ecosystems and biodiversity.
- Combating climate change – Sustainability helps mitigate greenhouse gas emissions that drive climate change by promoting renewable energy, energy efficiency, and climate-friendly agriculture and transportation.
- Economic savings – Sustainable businesses often save money over the long-term by reducing resource and energy usage.
- Public health – Sustainability promotes practices like clean air and water that provide direct public health benefits.
- Social equity – Sustainable development aims to meet the basic needs of all people for a better quality of life.
- Thriving future – By preserving natural resources and protecting the planet, sustainability helps ensure the well-being of future generations.
In summary, living sustainably delivers environmental, economic, and social benefits that allow current and future generations to prosper.
Key Principles
Sustainability is grounded in several core principles that define its goals and approaches. The most common framework involves three pillars – environmental, social and economic sustainability.
Environmental sustainability focuses on preserving natural resources and protecting ecosystems. This involves using renewable energy, reducing pollution and waste, conserving water, and mitigating climate change. The goal is to meet current needs without compromising the health and function of ecological systems for the future.
Social sustainability emphasizes human wellbeing and equality. It means ensuring all people have access to basic needs like food, water, healthcare, education, and housing. Communities should be inclusive, connected, and provide a good quality of life. Human rights, labor rights, and community empowerment are key concerns.
Economic sustainability revolves around generating prosperity through responsible production and consumption. Businesses and growth should occur within ecological limits. Smart resource use, circular production models, and fair trade help ensure long-term economic viability.
These three pillars are interdependent – progress in one area requires support in the others. A holistic systems perspective is needed, along with cooperation among governments, businesses and civil society to advance integrated sustainable development.
Sustainable Development Goals
In 2015, the United Nations General Assembly set the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The SDGs are a collection of 17 interlinked global goals designed to be a blueprint to achieve a better and more sustainable future for all. They address the global challenges we face related to poverty, inequality, climate change, environmental degradation, peace and justice. The 17 SDGs are:
- No Poverty
- Zero Hunger
- Good Health and Well-being
- Quality Education
- Gender Equality
- Clean Water and Sanitation
- Affordable and Clean Energy
- Decent Work and Economic Growth
- Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
- Reduced Inequality
- Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Responsible Consumption and Production
- Climate Action
- Life Below Water
- Life on Land
- Peace and Justice Strong Institutions
- Partnerships to achieve the Goal
The SDGs provide a shared blueprint for peace and prosperity for people and the planet, now and into the future. They recognize that ending poverty must go hand-in-hand with strategies that build economic growth and addresses a range of social needs including education, health, social protection, and job opportunities, while also tackling climate change and environmental protection. The SDGs are designed to bring the world to several life-changing “zeros”, including zero poverty, hunger, AIDS and discrimination against women and girls.
Challenges
Achieving true sustainability is an immense challenge that requires overcoming many obstacles. Here are some of the main challenges to creating a sustainable world:
Overconsumption – Our consumerist culture promotes endless economic growth at the expense of the planet. Reducing overconsumption of goods, energy, and resources is critical but difficult to achieve.
Short-term thinking – Our political and economic systems often prioritize short-term profits over long-term sustainability. Shifting to more long-range planning is an obstacle.
Vested interests – Powerful industries like fossil fuels undermine sustainability reforms that threaten their bottom line. Overcoming their influence is an uphill battle.
Habits and behaviors – People are used to unsustainable lifestyles. Changing habits like driving, meat consumption, and waste is hard without systemic change.
Costs – Transitioning to renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, green infrastructure, etc. requires major upfront investments that can be prohibitive.
Complexity – Sustainability is an intricate issue involving climate, economics, social equity, and more. Coordinating comprehensive solutions is difficult.
Politics – Lack of political will, partisanship, insufficient global cooperation, and policies that promote unsustainability impede progress.
Overcoming these and other challenges will require unprecedented levels of commitment, resources, and cooperation locally and globally. But it’s a necessary struggle – our future depends on transitioning to a sustainable world.
Sustainable Technologies
New and emerging technologies are enabling greater sustainability across many sectors and industries. Here are some examples:
Renewable energy: Solar, wind, geothermal, and other renewable sources allow clean energy production with minimal environmental impact. Solar panels and wind turbines are becoming widespread.
Electric vehicles: EVs powered by renewable electricity produce no direct emissions, improving local air quality. Advances in batteries are making EVs more affordable and practical.
Energy efficiency: Smart thermostats, LED lighting, insulation materials, and efficient appliances cut energy waste in homes and businesses.
Water conservation: Low-flow faucets and showerheads, smart irrigation systems, greywater recycling, and improved infrastructure reduce water usage.
Sustainable materials: Green chemistry produces plastics, fabrics, and other materials from renewable feedstocks instead of fossil fuels. Biodegradable or recyclable materials also support circular economies.
Precision agriculture: Data collection, sensors, and digital tools optimize water and nutrient usage for crop yields while minimizing environmental impacts.
Food technologies: Innovations like vertical farming, hydroponics, and meat alternatives help produce more food sustainably.
Sustainable Business Practices
Businesses play a crucial role in supporting sustainability through their daily operations and long-term strategies. There are many ways companies can incorporate sustainability into their business models and practices.
Some examples of sustainable business practices include:
- Sourcing sustainable raw materials and supplies
- Using renewable energy to power operations
- Reducing waste production and enabling recycling/reuse
- Limiting water usage and treating wastewater
- Providing sustainable transportation options for employees
- Designing products that are durable, repairable and recyclable
- Offering sustainable goods and services to customers
- Using sustainable packaging and shipping solutions
- Engaging in carbon offsetting programs
- Investing in environmentally and socially responsible funds
- Promoting sustainability throughout the supply chain
- Developing a corporate sustainability strategy with goals
- Reporting on sustainability efforts and progress

By integrating these and other sustainable solutions into their operations and culture, businesses can significantly reduce their environmental footprint and enable more responsible consumption. This positively impacts the environment and society while strengthening the company for the future.
Sustainable Lifestyle
An eco-friendly lifestyle can go a long way towards preserving our planet. Here are some tips that individuals can follow in their daily lives to live more sustainably:
Reduce, reuse, recycle – The three R’s are an easy principle to implement. Reduce your consumption and waste, reuse products when possible, and recycle everything you can. This helps conserve resources and divert waste from landfills.
Conserve energy and water – Simple habits like turning off lights and electronics when not in use, taking shorter showers, and using energy-efficient appliances can reduce your environmental footprint. Installing low-flow faucets and toilets also decreases water usage.
Eat sustainably – Choosing locally-grown, organic foods reduces your carbon footprint. Limiting meat consumption, avoiding food waste, and growing your own produce are also great options.
Green your transportation – Walk, bike, carpool or take public transport to lower emissions. If driving, maintain your vehicle and use eco-friendly fuels to increase efficiency. Consider electric or hybrid models when buying a car.
Be mindful of purchases – Evaluate if you really need new items. When shopping, choose eco-friendly, reusable, recycled or upcycled products. Support green businesses and boycott unsustainable brands.
Advocate for change – Spread awareness by talking to family and friends about sustainability. Write to government and business leaders urging eco-friendly policies and practices.
With some mindful effort, we can all adopt habits that preserve the planet for future generations. Small sustainable steps by individuals add up to make a big difference.
Success Stories that demonstrate the impact of sustainable practices
Reforestation in Tanzania
In Tanzania, local communities have undertaken major reforestation efforts, planting over 2 million trees to restore depleted forests. This reforestation helps retain water, prevent soil erosion, sequester carbon, and provide habitat for native wildlife. Community-led efforts have been crucial for the success and longevity of the reforestation programs.
Renewable Energy in Texas
Texas leads the United States in wind energy, producing nearly 30% of the nation’s wind power. Massive wind farms with thousands of turbines now dot the Texas landscape. This surge in renewable wind energy has created over 25,000 jobs in Texas while also providing clean electricity. Wind helped generate nearly 20% of Texas’ electrical needs in 2019.
LEED Platinum Airport in India
The Cochin International Airport in India is the first airport worldwide to be fully powered by solar energy. Covering 45 acres, the airport’s solar plant generates enough clean electricity to meet all of its energy needs. It achieved LEED Platinum certification – the highest level of green building certification. This solar airport showcases India’s commitment to clean energy.
The Future of Sustainability
The future of sustainability looks bright, but there is still much work to be done. Key areas for improvement include transitioning to renewable energy on a global scale, promoting regenerative agriculture, creating circular economies, and inspiring sustainable lifestyles.
Renewable energy capacity will need to greatly expand to reduce reliance on fossil fuels. This transition remains a priority, as energy production and consumption comprise the largest portion of greenhouse gas emissions worldwide. While solar and wind have seen exponential growth, we need sustained policy commitments and infrastructure changes to reach full decarbonization of the power sector.
Regenerative agriculture has incredible potential to capture carbon in soils while greatly reducing environmental impacts. But practices like no-till farming, cover cropping, and rotational grazing need to become widespread across farms. Consumer demand and food companies’ sustainability commitments can accelerate the transition to a regenerative food system.
Moving from linear to circular economic models will be vital for reducing waste and unnecessary resource use. This entails designing for durability, reuse, and recycling across products, buildings, and infrastructure. It requires innovation and strategic partnerships between businesses, governments, and communities. Early progress demonstrates the promise of circularity.
Lastly, inspiring sustainable lifestyles remains crucial. Already, we see growing demand for ethical products, plant-based diets, and low-impact living. Peer influence and youth activism play key roles in spreading sustainable habits. With the right social conditions and incentives, sustainable living can become the new normal.
In summary, the sustainability transformation calls for breakthroughs across sectors, supported by favorable public policies and shifting social norms. The task is immense but within reach if we ramp up efforts now. The rewards will be immense — from stabilizing the climate and reviving ecosystems to building more just and resilient societies.