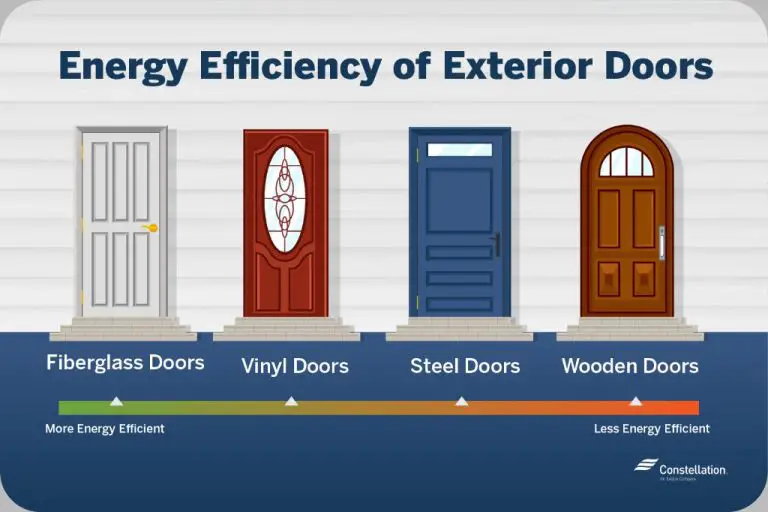
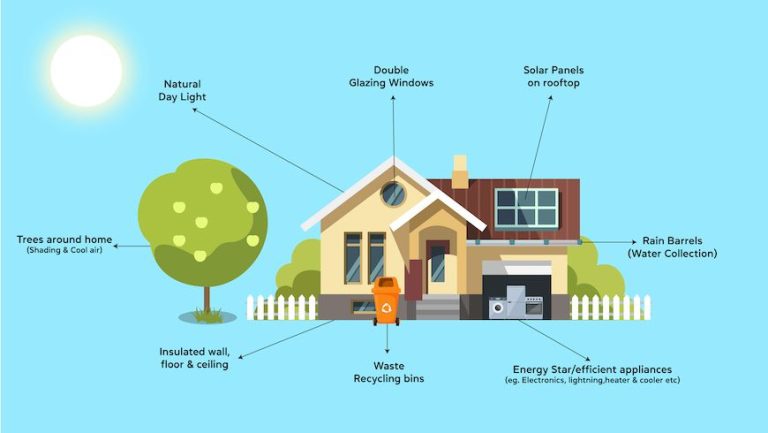
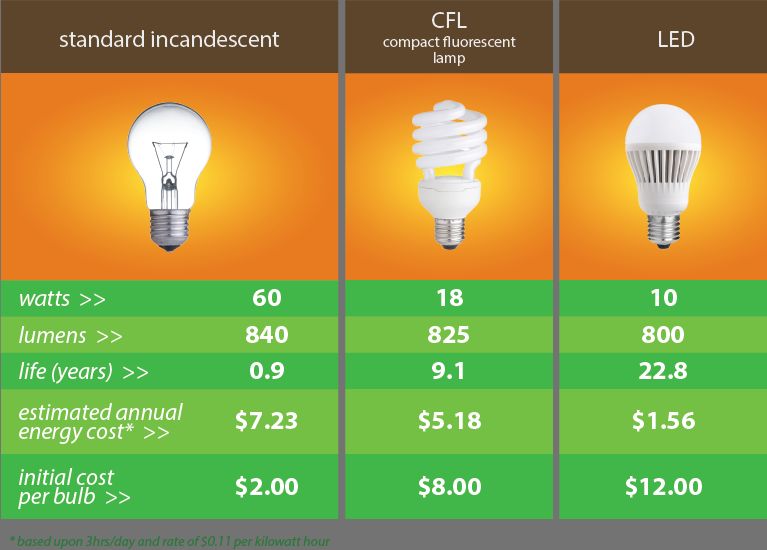
What Does It Mean To Be Energy Star Certified?
What is ENERGY STAR certification?

ENERGY STAR is a voluntary certification program from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) that helps businesses and individuals save money and protect the environment through superior energy efficiency. Products that earn the ENERGY STAR label meet strict energy efficiency guidelines set by the EPA, meaning they use less energy while maintaining or exceeding performance compared to standard models (Source: https://www.tuvsud.com/en/services/product-certification/energy-star).
The EPA introduced ENERGY STAR in 1992 as a voluntary labeling program designed to identify and promote energy-efficient products to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Products that earn the ENERGY STAR certification have been independently certified to meet EPA efficiency standards, which are based on verified test methods and defined product specifications (Source: https://pegasusenergysolutions.com/energy-benchmarking/what-is-energy-star-certification). The ENERGY STAR label makes it easy for consumers to identify products that offer significant savings in energy consumption while delivering the same or better performance as comparable models.
History of the ENERGY STAR Program
The ENERGY STAR program was created in 1992 by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) as a voluntary labeling program designed to identify and promote energy-efficient products in order to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. According to the EPA’s website, “ENERGY STAR was established to introduce energy efficiency into the marketplace.” (EPA)
The program was born out of increased national awareness about environmental issues in the late 1980s. In 1988, the EPA and other federal agencies partnered to study the “greenhouse effect” and determine solutions to reduce pollution and other factors contributing to climate change. Based on this study, the EPA determined that energy efficiency was the “lowest cost option for addressing climate change and air pollution.” (EPA)
In launching ENERGY STAR in 1992, the EPA partnered with manufacturers, retailers, building owners, and utilities to voluntarily introduce energy efficient options into the marketplace. Companies could have their products certified as ENERGY STAR if they met strict energy efficiency guidelines set by the EPA. The blue ENERGY STAR label was designed to help consumers easily identify more efficient options when shopping.
Benefits of ENERGY STAR certified products
There are many benefits to choosing ENERGY STAR certified products, both for consumers and the environment. According to the EPA, products that earn the ENERGY STAR label save energy and money without sacrificing quality or performance. Some key benefits include:
Energy savings – ENERGY STAR certified products meet strict energy efficiency guidelines set by the EPA and Department of Energy. For example, an ENERGY STAR certified refrigerator is estimated to use 10% less energy than a standard model (https://www.energystar.gov/products/what_makes_product_energy_star). This results in lower energy bills for consumers.
Cost savings – The energy efficiency of ENERGY STAR products translates into direct dollar savings on utility bills. It’s estimated that from 1992-2021, ENERGY STAR helped families and businesses save over $500 billion in energy costs (https://www.energystar.gov/about/impacts). Consumers can expect to save about $75 per year by using ENERGY STAR certified appliances.
Environmental benefits – By using less energy, ENERGY STAR certified products reduce greenhouse gas emissions that contribute to climate change. According to the EPA, people using ENERGY STAR certified products helped keep over 500 million metric tons of greenhouse gases out of the atmosphere in 2021 alone, equivalent to the annual emissions of over 70% of U.S. homes (https://www.energystar.gov/about/impacts).
Types of products that can be ENERGY STAR certified
The ENERGY STAR program certifies products across over 70 categories. The major categories include:
Appliances
Many common household appliances can be ENERGY STAR certified, such as refrigerators, dishwashers, washing machines, and dryers. ENERGY STAR certified appliances incorporate energy efficient features like improved insulation, sensors, and motors.
Heating & Cooling
Heating and cooling equipment like furnaces, air conditioners, and heat pumps can earn the ENERGY STAR certification by meeting strict energy efficiency requirements. This can reduce energy usage and utility bills.
Electronics
Televisions, audio equipment, computers, monitors, and other electronics can be ENERGY STAR certified. Features like efficient power management and low standby power help certified electronics save energy.
Lighting
From screw-based bulbs to decorative fixtures, ENERGY STAR certified lighting products produce the same or better light quality while using less energy. Most use LED or other high efficiency lighting technology.
Many other product categories like roofing, windows, office equipment, and more can also earn ENERGY STAR certification. Overall, the program covers most major household and business energy uses.
ENERGY STAR Certification Process
For a product to be certified as ENERGY STAR, the manufacturer must follow these key steps:
1. Ensure the product meets the ENERGY STAR efficiency criteria set for that product category. For example, refrigerators must be at least 10% more energy efficient than the federal minimum standard.
2. Complete third-party testing at an EPA-recognized laboratory to verify the product’s energy performance. This ensures accurate measurements.
3. Register the product with the EPA and complete the ENERGY STAR partnership agreement. This allows the company to use the ENERGY STAR certification mark.
4. Submit certified test results and other product data to the EPA for approval. The EPA reviews submissions to ensure requirements are met.
5. Once approved, market and label the product as ENERGY STAR certified. The certification is valid for a set number of years based on product type.
Companies must annually provide the EPA updated information and verify ongoing conformance. The EPA also conducts periodic off-the-shelf product testing to ensure certified products continue meeting efficiency levels.
By completing this rigorous certification process, companies show their products meet strict energy efficiency guidelines designed to save energy and money (source).
How to identify ENERGY STAR certified products
The easiest way to identify ENERGY STAR certified products is to look for the ENERGY STAR label. This label was introduced by EPA in the early 1990s and has become the simple choice for energy efficiency.
The ENERGY STAR label will typically be blue with the words “ENERGY STAR” written in white in the center. There will also be a small leaf design above the letter “A” in “STAR.” Underneath the logo, you may see the specific type of product it is certified for, such as “Clothes Washer” or “Refrigerator.”
This label can be found directly on certified products like appliances, electronics, and lighting. For items like windows or insulation that are certified as part of a full home, you should look for the label on the packaging or product specification sheet.
You can also look for the ENERGY STAR certification logo and language on retailer websites when shopping online. Retailers are allowed to use the ENERGY STAR name and label only on certified products.
Checking for the label is the simplest way to ensure you are getting an energy efficient product that meets strict certification guidelines. Learn more about ENERGY STAR certified product criteria at https://www.energystar.gov/products/ask-the-experts/what-makes-a-product-energy-star-certified
ENERGY STAR certification around the world
The ENERGY STAR program originated in the United States as a voluntary labeling program designed to identify and promote energy-efficient products. Over time, ENERGY STAR has expanded internationally with partnerships in Canada, Europe, Japan, New Zealand, Taiwan, and other countries.
While the core principles of ENERGY STAR remain the same globally, there are some differences in implementation between countries. For example, in Canada, Natural Resources Canada (NRCan) administers an independent ENERGY STAR certified homes program with unique requirements that differ from the US EPA program. In Europe, the European Union has adopted the ENERGY STAR label under the EU Ecolabel program. Products seeking ENERGY STAR certification in Europe must meet EU-specific efficiency requirements.
Other international partners, such as Japan, New Zealand, and Taiwan have signed agreements to generally align their local programs with the US EPA’s ENERGY STAR specifications. However, there is still flexibility to account for local energy factors, market conditions, and product testing standards.
Overall, while criteria and administrative details vary between different countries, the fundamental goal of ENERGY STAR remains the same globally – to help consumers identify the most energy efficient products on the market through credible third-party certification.
Criticisms and controversies
There have been some criticisms regarding the effectiveness of the ENERGY STAR program. One area of controversy is around the verification process for certifying homes. To receive ENERGY STAR certification, a third-party verifier must review the data and inspect the home. However, some have argued this verification process is not rigorous enough to ensure proper certification.
For example, according to a 2015 EPA report, some stakeholders recommended expanding the pool of eligible verifiers beyond just certified professionals, citing concerns about inconsistencies in the verification process (source). There were calls for more oversight and standardized procedures to ensure the verification steps were followed properly in all cases.
Additionally, some homeowners have complained when they believed their ENERGY STAR certified home did not meet the program’s efficiency standards. Though these cases are a minority, it points to potential gaps in enforcement (source).
Overall, while the ENERGY STAR program has rigorous guidelines in place, some have questioned if there is sufficient oversight and consistency in the verification process across the many certified homes. However, the EPA contends these issues are limited in scope and that the program delivers significant energy savings overall.
The future of ENERGY STAR
Going forward, the ENERGY STAR program aims to continue expanding and improving in several key areas. According to the EPA’s report “New Product Development: The Pipeline For Future ENERGY STAR Growth,” the program plans to focus on bringing new product categories into the program, strengthening specifications, and exploring third-party certification globally.
Some products the EPA is looking into adding to the ENERGY STAR program in the future include commercial food service equipment, gaming consoles, pool pumps, and smart home devices and apps [1]. By expanding the range of certified products, the program can save even more energy across numerous aspects of daily life.
The EPA also aims to continuously strengthen its efficiency criteria over time as technology improves. This will ensure ENERGY STAR products maintain a high standard of energy savings as more advanced options become available. The EPA coordinates with industry partners to determine feasible levels to push efficiency forward.
There are also efforts to increase third-party certification of ENERGY STAR products internationally. Currently used in the U.S. and Canada, third-party certification could help verify energy savings claims and prevent false use of the ENERGY STAR label in global markets.
Key takeaways
ENERGY STAR certification means that a product meets strict energy efficiency guidelines set by the EPA. Certified products are proven to use less energy, save money on utility bills, and help protect the environment.
The main points to know about ENERGY STAR certification are:
- It was created by the EPA in 1992 to identify energy efficient products and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Certified products meet technical specifications for energy performance set by the EPA.
- Products are independently certified – manufacturers cannot just claim the label.
- ENERGY STAR is recognized worldwide as the premier mark of energy efficiency.
- Thousands of product models across 70+ categories can be certified.
- The blue ENERGY STAR logo makes it easy to identify certified products.
- Using ENERGY STAR products can lead to significant energy and cost savings.
- The program helps consumers, businesses, and organizations save money and protect the climate.
In summary, ENERGY STAR certification signifies that a product performs its intended function using less energy than comparable models. It provides a trusted guideline for finding energy efficient products that save money and reduce environmental impact.