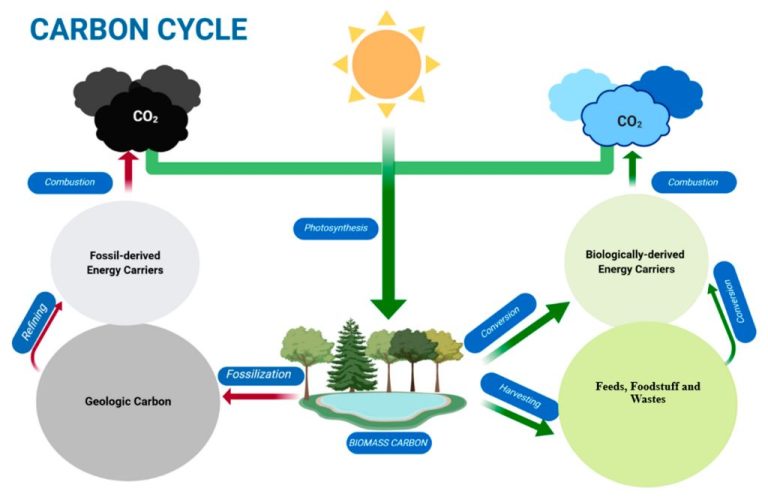
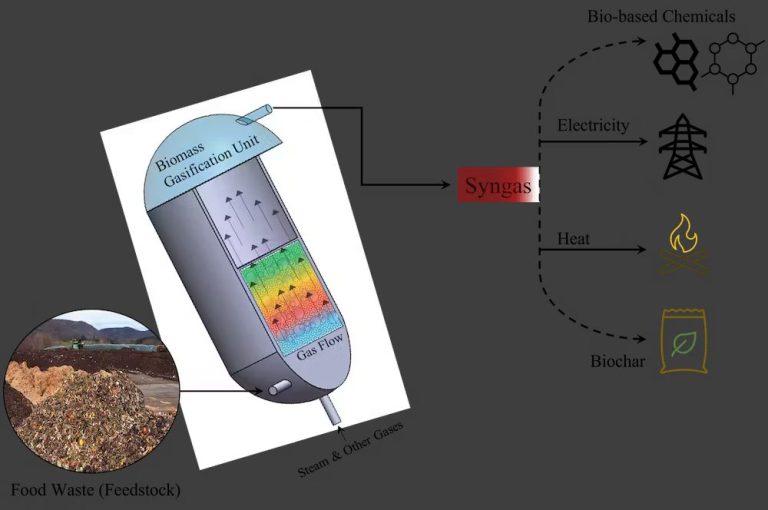
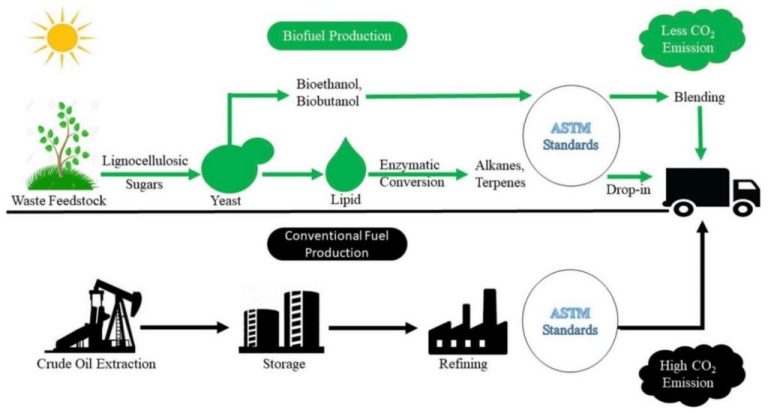
What Do Biofuel Engineers Do?
Biofuel engineering is an interdisciplinary field focused on the research, development, and implementation of biofuels as sources of renewable energy. Biofuels are fuels derived from biomass such as plants, algae, agricultural crops, and organic waste (1). Biofuel engineers work to design, optimize, and scale up processes for efficiently producing transportation fuels like ethanol, biodiesel, and jet fuel from these renewable biological feedstocks.
The goal of biofuel engineering is to create sustainable, low-carbon alternatives to fossil fuels that have less environmental impact. Biofuel engineering combines principles of chemical engineering, biotechnology, agriculture, chemistry, and more to convert biomass sources into usable, high-energy liquid fuels (2).
Key focus areas for biofuel engineers include developing high-yield feedstocks, designing biorefineries for fuel production, creating enzymes to break down cellulose, modeling biofuel processes, analyzing life cycle impacts, and more. Their work aims to increase the viability of biofuels as part of the global energy mix.
Sources:
(1) https://www.britannica.com/technology/biofuel
(2) https://www.energy.gov/science/doe-explainsbiofuels
Typical Background
To become a biofuel engineer, a bachelor’s degree in biochemical engineering, chemical engineering, or a related field is usually required (https://www.careerexplorer.com/careers/biofuel-engineer/how-to-become/). These programs provide the necessary foundation in math, physics, biology, chemistry, and engineering principles. Coursework typically covers areas like fluid mechanics, thermodynamics, process design, and biological engineering.
Engineers may also have a bachelor’s, master’s, or doctoral degree in electrical, electronics, industrial, mechanical, or civil engineering (https://vault.com/professions/bioenergy-biofuels-workers/requirements). Advanced degrees in a specialized engineering field or biochemistry are often needed for research roles or advanced positions.
In addition to an engineering degree, licensing or certification may be required in some states and for certain roles. Biofuel engineers often gain work experience through internships while pursuing their degree.
Day-to-Day Responsibilities
Biofuel engineers spend much of their time researching, designing, and developing new biofuel technologies. They conduct laboratory experiments and computer simulations to test new biofuel production methods involving enzymes, microorganisms, and chemical catalysts. Their goal is to find ways to efficiently convert biomass feedstocks like corn, sugarcane, or algae into usable biofuels like ethanol or biodiesel.
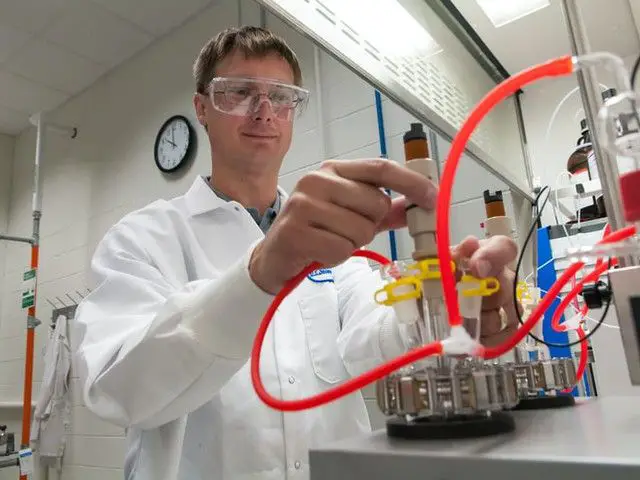

According to one biofuel engineer’s account, a typical day involves analyzing data, troubleshooting any issues in the biofuel production process, and brainstorming ways to optimize the technology. They may use advanced software to model chemical reactions and design bioreactor systems. Collaboration with other engineers, scientists, and business professionals is common as they work to scale up biofuel technologies for commercial implementation.
Throughout their work, biofuel engineers adhere to safety, testing, and documentation procedures. They aim to develop affordable, sustainable biofuel production methods that have minimal environmental impact.
Focus Areas
Biofuel engineers focus on researching and developing various types of biofuels, improving production methods, and testing performance. Some of the key focus areas include:
Types of biofuels – Biofuel engineers work with different feedstocks like corn, sugarcane, palm oil, algae etc to produce bioethanol, biodiesel, biogas, green diesel, and more. They aim to optimize biofuel production from various sources.
Production methods – Optimizing biofuel production processes and yields is a major focus. This involves developing better catalysts, bioreactors, fermentation techniques, and recovery methods. Engineers also work to reduce water and energy usage in production.
Testing and performance – Engineers rigorously test biofuel performance and emissions in engines and vehicles. They aim to improve fuel properties like combustion, stability, cold flow, and more. Extensive lab work is done to test and improve biofuel formulations.
Skills Needed
To be successful as a biofuel engineer, certain technical skills are required. According to LinkedIn, a solid background in science, engineering, or technology is essential. Specific technical expertise in areas like chemical engineering, mechanical engineering, biochemistry, microbiology, and genetics allows biofuel engineers to develop and improve biofuel production methods.
Strong research skills are also critical, as biofuel engineers must stay up to date on the latest biofuel technologies and innovations. They rely on scientific research to identify new feedstocks, enzymes, and production processes. According to Mentoria, biofuel engineers require excellent research abilities to gather and analyze complex data.
Project management skills enable biofuel engineers to oversee facility operations and coordinate teams. Per Vault, biofuel engineers must have strong communication and management capabilities to direct staff, delegate tasks, and ensure timelines and targets are met.
Career Development
According to the Career Explorer (https://www.careerexplorer.com/careers/biofuel-engineer/) website, the career path for biofuel engineers typically begins with an entry-level position as a research assistant or associate biofuel engineer after completing a bachelor’s degree. In these roles, they support senior biofuel engineers and gain hands-on experience in areas like conducting laboratory tests, collecting and analyzing data, troubleshooting processes, and optimizing biofuel production.
With 2-5 years of experience, biofuel engineers may progress to mid-level roles with titles like biofuel engineer or biofuel plant engineer. Their responsibilities expand to include supervising teams, designing testing protocols, reviewing project plans, monitoring safety and environmental regulations, and streamlining production. Some may begin specializing in areas like feedstock, conversion processes, plant operations, or quality control.
After 5-10 years of experience, biofuel engineers can achieve senior positions such as lead biofuel engineer, biofuel production manager, or head of biofuel R&D. They take on leadership duties like managing teams of engineers, overseeing multiple projects, coordinating with clients and stakeholders, evaluating technological advances, and spearheading process improvements. Those interested in research can become principal scientists directing laboratory work and discoveries.
Ongoing professional development is important for biofuel engineers to stay current with the latest technologies and advance their expertise. Many pursue a master’s degree or Ph.D. in bioengineering, chemical engineering, biochemistry, or a related scientific field. Attending conferences, workshops, and biofuel industry events allows networking and exposure to new innovations. Certifications such as the Certified Energy Manager (CEM) credential offered by the Association of Energy Engineers demonstrate updated technical knowledge as well.
Job Outlook
The job outlook for biofuel engineers is strong. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment of biofuels engineers is projected to grow 8 percent from 2016 to 2026, about as fast as the average for all occupations. As demand for sustainable energy continues to rise, more employers will seek qualified biofuels engineers.
Some of the top employers of biofuel engineers include ethanol and biodiesel companies, research organizations, alternative energy companies, chemical manufacturers, and the federal government. Major employers include DuPont, POET, Abengoa Bioenergy, Archer Daniels Midland Company, and Pacific Ethanol.
Salary Range
The salary range for biofuel engineers can vary greatly depending on experience and geographical region. According to ZipRecruiter, the average annual salary for a biofuel engineer in the United States is $115,864 as of February 2024. The pay scale tends to follow experience levels, with entry-level biofuel engineers starting around $75,000 per year, mid-career making $115,000, and highly experienced engineers earning over $150,000 annually.
Region also impacts salaries. Biofuel engineers in Texas earn an average of $128,000 per year according to ZipRecruiter data, with a range from $90,000 – $150,000. Other high paying states include California, Washington, Oklahoma, and Louisiana. Rural areas tend to be on the lower end of the pay scale while major metro areas like Houston and Los Angeles are on the higher end for biofuel engineering salaries.
Satisfaction
Biofuel engineers tend to have good job satisfaction, according to studies of people working in renewable energy fields. One survey showed above average rates of work-life balance and enjoyment of the role among biofuel engineers and related occupations [1]. Factors contributing to satisfaction include doing meaningful work to develop alternative energy solutions, intellectual challenge, variety of responsibilities, and good salaries. Many biofuel engineers appreciate being part of a growing field focused on innovation and reducing dependence on fossil fuels. Work settings at biorefineries and research labs also facilitate collaboration and flexibility.
However, the work can involve frustration at times. Projects may encounter setbacks and funding uncertainties. Some engineers dislike the paperwork and regulations involved with new technologies. Working with agricultural feedstocks introduces variability and challenges. Occasional travel to facilities may be required. But overall, biofuel engineering rates well for work-life balance and providing an interesting career path.
Related Careers
Biofuel engineers can leverage their background to pursue careers in other engineering fields like chemical, mechanical, or environmental engineering. Their expertise in renewable energy and sustainability is also applicable to roles focused on advancing green technology and sustainable practices.
Some related careers biofuel engineers may consider include:
- Chemical engineer – Design and oversee chemical manufacturing processes and production.
- Mechanical engineer – Design, build, and test mechanical devices and systems.
- Environmental engineer – Develop solutions for environmental issues like pollution and waste.
- Sustainability manager – Lead organizational initiatives to reduce environmental impact.
- Renewable energy engineer – Design and implement renewable energy systems like solar, wind, or geothermal.
With their broad engineering skills and knowledge of biofuels and sustainability, biofuel engineers have versatile careers paths to explore in growing fields focused on energy, technology, and the environment.