What Company Owns Sunrun?
Sunrun is a leading residential solar, battery storage, and energy services company based in the United States. Founded in 2007, Sunrun aims to provide clean and affordable solar energy to homeowners across the country (https://www.sunrun.com/). The company operates a solar-as-a-service business model, where homeowners can install solar panel systems on their roofs with little to no upfront costs. Sunrun owns, installs, maintains, insures, and monitors the solar energy systems while homeowners pay a predictable monthly fee based on system size and energy production (https://www.sunrun.com/why-sunrun). This allows homeowners to access solar energy without large initial investments. As of 2022, Sunrun has around 600,000 customers and operates in over 22 states, Washington D.C. and Puerto Rico. The company is a leader in residential solar energy in the United States.
History of Sunrun
Sunrun was founded in 2007 in San Francisco, California by Lynn Jurich, Edward Fenster, and Nat Kreamer [1]. The company was started with the goal of making solar energy more accessible to homeowners across the United States. As a residential solar company, Sunrun aims to provide cleaner and more affordable energy through solar panel system leasing and solar power purchase agreements (PPAs).
The three co-founders brought together critical expertise to launch Sunrun’s innovative model. Lynn Jurich served as the CEO, bringing her background in clean energy and venture capital. Edward Fenster served as executive chairman, leveraging his experience as a corporate finance attorney. Nat Kreamer brought his experience in the solar industry to serve as the initial CEO before passing the reigns to Lynn Jurich.
With this leadership team in place, Sunrun set out to disrupt the residential solar market by allowing homeowners to avoid high upfront costs through leasing and PPAs. This made going solar affordable and accessible for more households across the country.
Sunrun Business Model
Sunrun pioneered the residential solar panel leasing and power purchase agreement (PPA) business model. Under this model, Sunrun owns, installs, and maintains the solar panels on a customer’s home, while the customer pays little to no upfront cost and agrees to purchase the power generated from the panels at a fixed rate over a long-term contract, usually 15-25 years [1]. This makes going solar affordable and accessible to homeowners who cannot afford the high upfront investment of purchasing and installing a solar system.
The leasing and PPA model was innovative in opening up the residential solar market beyond early adopters who could afford the steep initial investment. By removing that barrier, Sunrun was able to expand the potential market and drive rapid growth. Today, leasing and PPAs still account for the majority of Sunrun’s business.
While the model has risks, such as customers defaulting on payments, it allows Sunrun to capture the recurring revenue stream and tax incentives from each solar system over decades. Sunrun’s ability to scale this model drove its rise to become one of the leading residential solar companies in the U.S. [2]
However, the industry is evolving and shifting more toward direct purchase and loan options. In response, Sunrun aims to provide a mix of purchase, lease, and PPA options to meet diverse customer needs.
Growth and Expansion
Sunrun experienced rapid growth and expansion in its early years. After starting operations in 2007, the company expanded to 4 states by 2010. By 2014, Sunrun had grown to offer residential solar leases in 10 states1. This expansion was fueled by strong consumer demand for residential solar and Sunrun’s innovative solar lease business model.
Sunrun continued its rapid growth, expanding to 22 states by 20182. Some of the new markets added during this period included New York, New Mexico, and South Carolina. This geographic expansion allowed Sunrun to increase its customer base and establish itself as one of the leading residential solar companies in the United States.
Sunrun IPO
After experiencing rapid growth in the residential solar market, Sunrun went public with an initial public offering (IPO) in 2015. On August 5, 2015, Sunrun began trading on the NASDAQ exchange under the ticker symbol RUN [1]. The company offered 11 million shares at $14 per share, right in the middle of its expected range of $13 to $15 per share. The IPO raised $251 million in total proceeds for Sunrun [2]. Going public provided Sunrun with additional capital to fund its continued growth and expansion in the residential solar market.
Acquisition of Vivint Solar
In July 2020, Sunrun announced that it would acquire Vivint Solar in an all-stock transaction valued at $3.2 billion (Renewable Energy World). The deal closed in October 2020, making Sunrun the largest dedicated residential solar and storage company in the United States. Vivint had over 180,000 customers at the time of the acquisition.
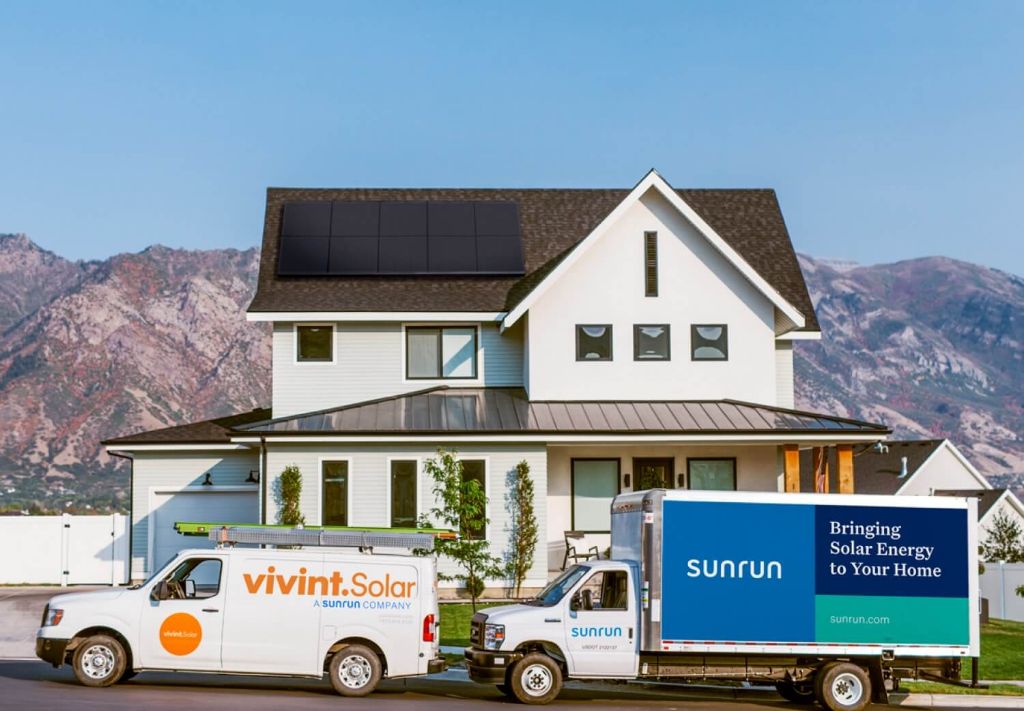

Current Ownership
Sunrun is primarily owned by institutional investors, with 97.95% of company shares held by institutions as of March 2022 according to Zippia. The company went public with an IPO in 2015, and its shares now trade on the NASDAQ exchange under the ticker symbol RUN.
Major institutional shareholders of Sunrun include:
- BlackRock Fund Advisors – 9.60% stake as of December 2021 (Wall Street Zen)
- FMR LLC – 7.73% stake as of December 2021
- Invesco Ltd. – 6.10% stake as of December 2021
These three investment managers hold over 20% of Sunrun’s shares combined. The remainder is held by various asset managers, hedge funds, and other institutional investors. Sunrun insiders, including executives and board members, hold around 3% of shares.
Leadership
Sunrun was co-founded in 2007 by Lynn Jurich and Edward Fenster, who currently serve as the company’s CEO and Executive Chairman, respectively. Under Jurich’s leadership, Sunrun has grown into the largest dedicated residential solar company in the United States.
According to Zippia, the Sunrun executive team is 42% female and 58% male, showing a commitment to diversity in leadership. The company’s leadership ranks highly in terms of employee satisfaction as well, with CEO Mary Powell and the executive team receiving an A+ rating on Comparably based on feedback from over 1200 employees.
As CEO, Jurich has focused on aggressive national expansion, utilizing partnerships and acquisitions to scale up Sunrun’s operations. Her vision has established the company as an industry leader in providing home solar power and battery storage solutions across the country.
Financial Performance
Sunrun has experienced significant growth in revenue over the past several years. According to a TipRanks financial report, Sunrun generated revenue of $922 million in 2020. This was an increase from $846 million in revenue in 2019. The company has continued to grow its customer base and expand operations, leading to increasing sales and revenue. In Q3 2023, Sunrun brought in $563.2 million in revenue, showing the company’s continued growth trajectory.
In addition to growing revenue, Sunrun has also been working to improve profitability. After posting a net loss of $151 million in 2019, the company reduced its losses to $79 million in 2020. While Sunrun is not yet consistently profitable, the shrinking net losses demonstrate the company’s path toward profitability as it scales up operations.
Overall, Sunrun’s financial performance shows an organization experiencing rapid growth. With rising revenue and improving profit margins, the company appears well-positioned to continue expanding its footprint in the residential solar market.
The Future of Sunrun
Sunrun is well-positioned for continued growth as the transition to renewable energy accelerates. With climate change driving policy shifts and cost reductions in solar technology, the residential solar market is expected to expand rapidly. According to one forecast, the global residential solar market could reach over $70 billion by 2028, up from $25 billion in 2021.
As the leading home solar and battery storage provider in the United States, Sunrun stands to benefit greatly from this continued growth. The company has significant economies of scale and an established national presence. Sunrun is projected to increase customers to over 600,000 by the end of 2023, up from 500,000 at the end of 2019.
Additionally, Sunrun’s acquisition of Vivint Solar in 2020 strengthened its market position and expanded its access to capital. The company is now able to provide solar energy and battery storage solutions to even more homeowners across the country. With renewable energy goals being set at both the state and federal level, the outlook for residential solar demand remains strong.
While the solar industry is competitive, Sunrun’s leadership position, expanding customer base, and innovative product offerings indicate a bright future. As homeowners increasingly switch to solar power, Sunrun is poised to continue as a dominant force in the residential solar marketplace for years to come.