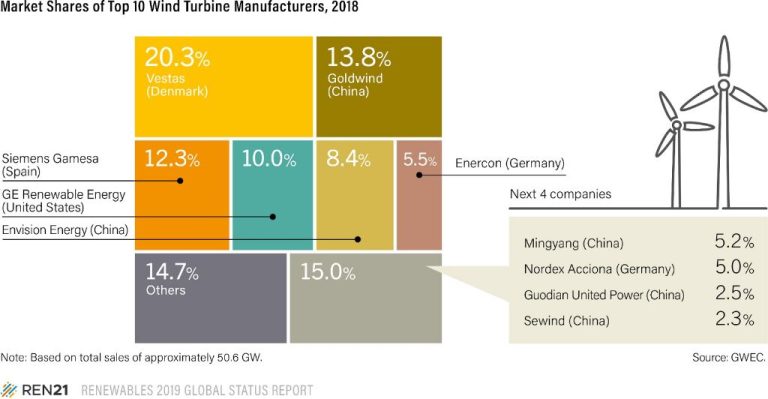
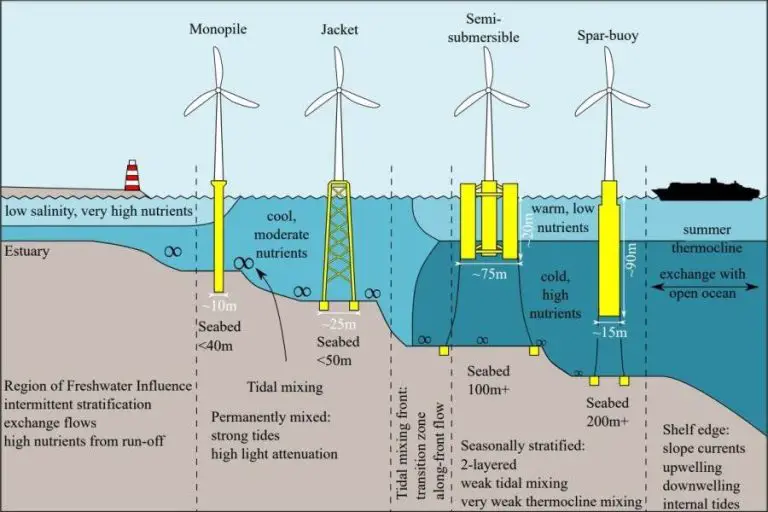
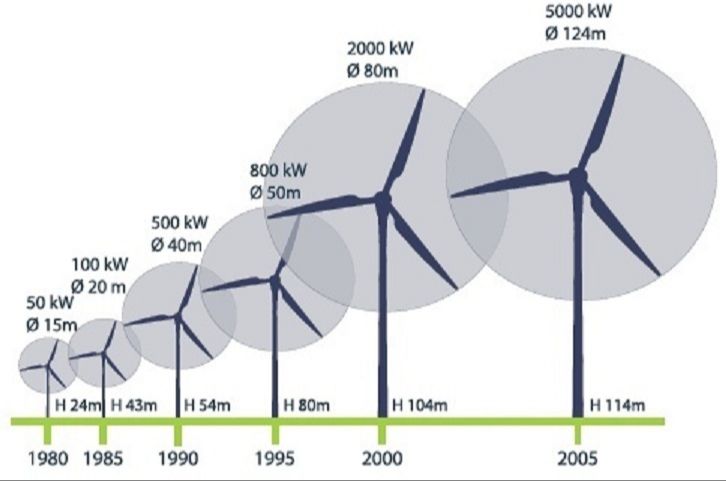
What Can Be Powered By Wind Power?
Wind power harnesses the wind to generate mechanical power or electricity (Kalmikov, 2017). It is one of the fastest growing renewable energy sources globally, with capacity doubling approximately every three years (CleanTechnica, 2022). Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy in wind into electrical power that can be used to power homes, schools, businesses, manufacturing facilities, farms, municipalities, military bases, islands, and remote locations.
Homes
Wind power can provide clean, renewable electricity to power homes across the country. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, the average U.S. home uses around 900 kilowatt-hours (kWh) per month[1]. A single 1.5 MW wind turbine operating at 33% capacity can generate over 5 million kWh per year, enough to power 415 average homes[2].
Using wind power to electrify homes provides environmental benefits by reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Homes powered by wind energy have a smaller carbon footprint. Wind power also provides energy security by using a free domestic resource not subject to global price volatility. With wind turbine costs decreasing, wind energy is becoming more affordable for homeowners seeking an eco-friendly way to power their houses.
Schools
Many schools around the United States and the world are powered at least in part by wind energy. According to a recent study, Minnesota ranks first in the nation for the number of schools utilizing wind power, with over 800 schools using it as an energy source (https://energy5.com/wind-energy-and-school-infrastructure-a-study-in-green-building). Iowa also has numerous schools that rely on wind turbines for electricity and heating needs (https://urbandsm.com/forum/viewtopic.php?t=3528).
The benefits of powering schools with wind energy are plentiful. Wind power provides a clean, renewable source of electricity that reduces a school’s carbon footprint. It also helps lower utility bills, allowing schools to allocate more funds toward education programs and resources. Utilizing wind energy enhances science and technology education, as schools can use on-site turbines to teach students about wind power. Many schools even offer wind technician training programs to prepare students for careers in the growing wind industry.
Businesses
Many businesses are turning to wind power as part of their sustainability initiatives. According to Crains New York, businesses like Bark Hot Dogs use wind power to complement their other green practices, like sourcing local ingredients. Large corporations are also embracing wind energy to power their operations and meet renewable energy targets.
For example, CNBC reported that Smucker’s signed a wind power purchase agreement to help achieve their goal of using 100% renewable energy. Many companies view investing in wind energy as an important part of their corporate sustainability initiatives and a way to reduce their carbon footprint.
Manufacturing
Wind power can significantly reduce electricity costs for manufacturing facilities. According to a report by CleanPower.org, at least 11 new wind power manufacturing facilities have been announced in the U.S. focused on producing components for the wind energy industry (Clean Energy Investing in America). For example, GE recently opened a new wind turbine blade manufacturing plant in Virginia powered entirely by renewable energy from a nearby wind farm (New Policy Blows New Life into Wind). This allows GE to manufacture wind turbine blades with very low overhead costs.
In addition to powering the manufacturing of wind energy components, wind power itself can provide inexpensive electricity to all types of manufacturing facilities. According to an analysis by Rystad Energy, rapidly expanding wind power generation capacity in Europe will require a massive increase in component manufacturing. New investments in wind turbine and blade factories are needed to meet demand (Offshore wind in Europe needs urgent factory aid to hit targets). Wind energy allows manufacturing facilities to lock in low electricity rates for years, reducing operating expenses.
Agriculture
Wind power can be used to run various agricultural operations and equipment on farms. According to a report by Just Agriculture, wind turbines can pump water for livestock, power electric fencing around fields, and provide electricity for lighting, heating and cooling systems (https://justagriculture.in/files/newsletter/2021/march/03.pdf). The mechanical power from wind turbines can also turn grinders to mill grain and drive irrigation pumps to water crops.
Irrigation is one of the main uses of wind power on farms. Wind pumps can draw water up from wells or rivers to irrigate crops and pastures. According to a review in the National Center for Biotechnology Information, wind-powered irrigation has become popular for watering crops and increasing agricultural productivity, especially in remote areas without easy grid access (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7926571/). Wind turbines provide a clean, renewable way to pump water without the need for diesel or electricity from the grid.
Municipalities
Many cities and towns are adopting wind power to meet their electricity needs and improve resiliency. According to Windustry, municipal wind power projects allow local governments to manage the regulatory process and arrange public meetings to educate and engage residents.[1]
Advantages of municipal wind projects include providing local, renewable energy, retaining energy expenditures in the community, securing a stable long-term energy price, and reducing exposure to volatile fossil fuel prices. Municipal utilities, rural electric co-ops, townships, and other government bodies are all developing wind power. [2]
Locally-owned wind helps municipalities be more self-reliant for their energy needs. It also keeps money spent on energy in the community. Towns across the Midwest and Great Plains are benefitting from municipal wind. The reliable and affordable power makes communities more resilient.
Military
The U.S. military has increasingly embraced wind power as a way to improve energy security and independence at bases and installations across the country. According to an article by Energy5, wind power provides “an excellent solution to address these challenges: Decreases the military’s reliance on fossil fuel imports” (1). By generating their own renewable electricity on-site, military bases can better withstand potential disruptions to the grid or fuel supply lines during natural disasters or attacks.
Many major military bases now have large wind farms helping power their operations. For example, Nellis Air Force Base in Nevada hosts a 140 megawatt wind farm with nearly 100 turbines (1). Renewable energy, including wind power, accounted for over 25% of electricity use across the Department of Defense in 2018 (1). The military cites energy security as a key reason for ramping up on-site power generation from clean sources like wind and solar. As the article notes, “wind energy allows bases to maintain critical operations during power outages by providing electricity generation on-site” (1).
Sources:
(1) https://energy5.com/wind-energy-independence-a-strategic-advantage-for-the-military

Islands
Many islands around the world are turning to wind power to provide electricity and reduce their reliance on expensive imported fossil fuels for power generation. For example, the Danish government is planning to build one of the world’s first energy islands in the North Sea (Energy Islands, n.d.). This artificial island will act as a hub for hundreds of surrounding offshore wind turbines and transmit power back to Denmark and other European countries. According to the Danish Energy Agency, the energy island will utilize Denmark’s abundant offshore wind resources and provide power for millions of households.
Another example is El Hierro, the smallest of Spain’s Canary Islands, which recently achieved a record of powering itself for 28 straight days using only wind and hydropower (Euronews, 2023). By investing in wind turbines and a pumped-storage hydropower plant, El Hierro has been able to dramatically cut its diesel fuel usage and become a model for sustainable island communities worldwide. Islands have abundant wind resources but often lack their own fossil fuel reserves, so switching to renewable energy helps improve energy security and insulation from global oil price volatility.
Remote locations
Wind power is an ideal solution for providing electricity to remote locations that are off the grid and not connected to centralized power infrastructure. Small, standalone wind turbines can generate clean, renewable power for various purposes in isolated areas. According to this article, “Remote wind power systems often incorporate additional generating systems such as diesel generators and solar arrays.”
Some key applications of wind power in remote locations include:
- Telecommunications towers – Wind turbines provide a green way to power remote cell towers, radio antennas, weather monitoring stations and other telecom infrastructure off the grid.
- Weather stations and scientific outposts – Wind power allows important weather and climate data collection to happen autonomously in distant places like Antarctica or remote islands.
- Rural homes and farms – Small wind turbines can provide electricity for off-grid homes, farms, ranches and other rural properties far from utility lines.
- Remote industrial sites – Mines, pipelines, oil rigs and other remote industrial facilities can use wind turbines as an onsite power source.
Wind power provides a reliable, emissions-free energy solution for locations beyond the reach of the electrical grid. With the right turbine system designed for harsh conditions, wind can supply continuous off-grid power even in some of the most isolated spots on the planet.