What Are The Top 3 Most Used Renewable Energy Sources?
Renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal and biomass are becoming increasingly important as countries around the world work to reduce their dependence on fossil fuels and transition to cleaner energy sources. Renewable energy provides a sustainable alternative to burning finite supplies of coal, oil and gas, which not only emit greenhouse gases responsible for climate change, but also contribute to air and water pollution.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), renewable energy accounted for over 26% of global electricity generation in 2018, with hydropower making up almost 50% of renewables used for electricity generation. The share of renewables continues to grow each year, as many governments provide incentives and targets to accelerate the transition away from coal and other fossil fuels.
Using renewable energy sources can help reduce carbon emissions, improve public health by cutting air pollution, boost energy security by relying on domestic resources, provide access to electricity in remote areas through decentralized energy, create jobs in the clean energy sector and allow businesses to gain a competitive edge by going green.
This article discusses the top three most widely used renewable energy sources today to provide an overview of this growing sector and why it has become so important for our future.
#1 – Hydroelectric Power
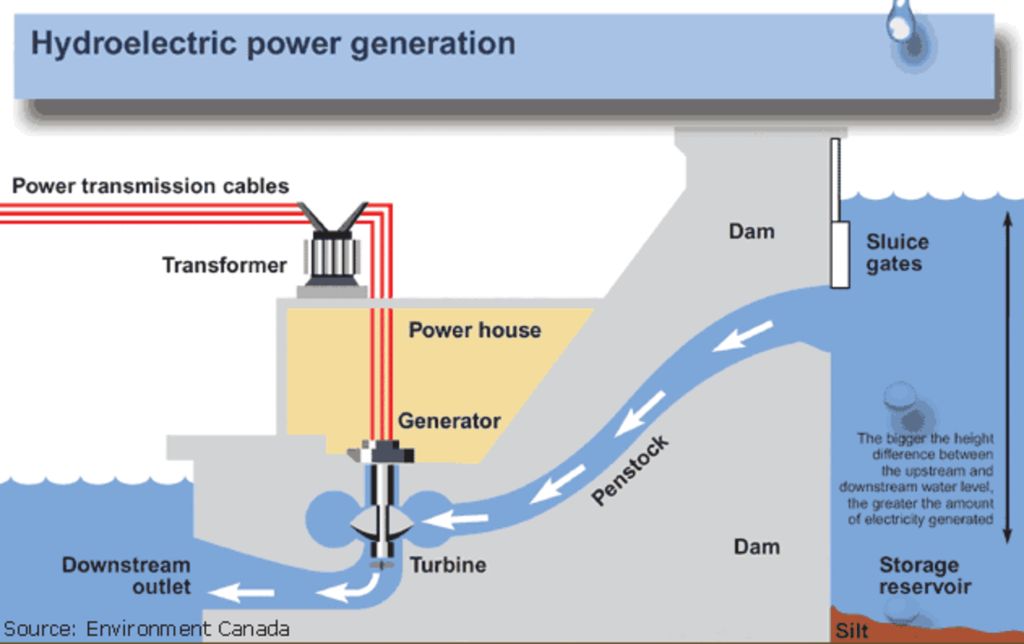
Hydroelectric power refers to the production of electricity by utilizing the power of flowing or falling water. It is one of the oldest and most widely used renewable energy sources in the world. Hydroelectricity is generated by directing water from a high elevation through turbines, which then spin and activate a generator to produce electricity.
Most hydroelectric power comes from dams, which control water flow and provide pressure. Large scale hydroelectric plants are built on rivers and often use a reservoir or artificial lake to hold water and control its flow. The water behind the dam flows through an intake and pushes blades in a turbine, causing them to turn. The turbine spins a generator to produce electricity. Major components in hydroelectric plants include the dam, reservoir, penstock, turbine, generator, and transformer.
Some of the top countries utilizing hydroelectric power are China, Brazil, Canada, United States, and Russia. China leads the world in hydroelectricity usage and capacity. In 2018, hydroelectric power accounted for 28% of China’s electricity generation. Major hydroelectric projects and dams can be found scattered across the country, especially along the Yangtze River. Some of the largest hydroelectric dams in the world are the Three Gorges Dam and Xiluodu Dam in China.
#2 – Wind Power
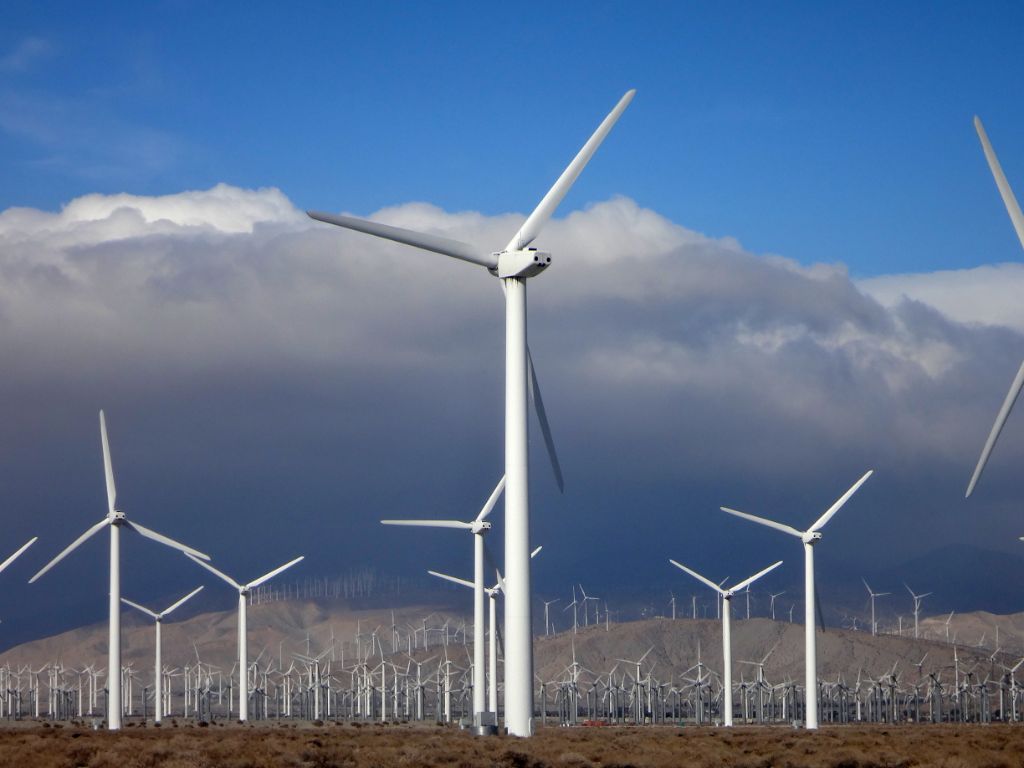

Wind power is the conversion of wind energy into electricity using wind turbines. Wind turbines convert kinetic energy from the wind into mechanical power, which is then converted into electricity.
Wind turbines are usually grouped together into wind farms, which are clusters of wind turbines that generate bulk electrical power. There are both onshore and offshore wind farms. Some of the largest wind farms can have hundreds of wind turbines.
Some of the top countries for wind power generation include China, the United States, and Germany. China currently leads the world in wind power capacity, with over 282 gigawatts as of 2019. The United States has over 100 gigawatts of wind power capacity. Other major producers are India, Spain, the UK, and France.
#3 – Solar Power
Solar power is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV), indirectly using concentrated solar power, or a combination.
Photovoltaic panels, known as solar panels, are a popular way to directly convert sunlight into electricity. When sunlight hits the panels, electrons are knocked loose from the atoms of the solar cell material, creating an electric current that can be captured and used as electricity. Some of the top solar photovoltaic panel producing countries include China, Japan, and Germany.
China is the world’s largest producer of solar photovoltaic power, with over 305 GW of installed capacity as of 2021. Japan and Germany had installed capacities of 71 GW and 59 GW respectively in 2021 (Source). The growth of solar PV is being driven by falling costs and supportive government policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions and increasing renewable energy generation.

Growth Trends
Renewable energy has experienced rapid growth in recent years. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global renewable power capacity is expected to grow by 2,400 gigawatts between 2022-2027, equal to the entire power capacity of China today (IEA, 2022). In 2023 alone, renewable capacity additions are projected to increase by 107 gigawatts, the largest absolute increase ever, to over 440 gigawatts (IEA, 2023). This growth is driven by rising investment and capacity as countries seek to improve energy security and meet climate goals.
Benefits
Renewable energy sources provide substantial benefits related to sustainability, energy independence, and cost savings. According to the EPA, renewable energy results in no greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuels, which helps mitigate climate change.[1] Shifting to domestic renewable resources reduces dependence on imported fuels and exposure to global price volatility.[2] The fuels for renewable energy are naturally replenished, unlike fossil fuels which are finite. Renewables can satisfy energy needs for the long term if resources are properly managed.
Once installed, the ‘fuel’ for renewables is free. This helps provide a hedge against electricity and fuel price increases. The cost of renewable technologies has dropped substantially in recent years, making them more affordable and cost-competitive with conventional power. Lifetime costs for renewables continue to decline, while fuel costs for fossil fuels remain volatile. Renewables can help stabilize energy costs for homeowners and businesses.
Challenges
While renewable energy is growing rapidly, it faces some key challenges. One major challenge is intermittency – many renewable sources like solar and wind are variable and don’t provide power consistently throughout the day. This requires utilities to have ways to store and dispatch power when needed. Storage options like batteries can be expensive and not yet viable at large scale (IEA).
Another challenge is transmission capacity and infrastructure. Renewable sources are often located far from population centers and require major investments in transmission lines to transport the electricity. Upgrading transmission is complex with multiple stakeholders and can take a long time (Sustainable Review).

Despite rapid gains, renewables still face challenges around continued cost declines, integrating high shares into grids, transmission infrastructure, and inconsistent government policies. However overcoming these hurdles can allow renewables to become the dominant source of new power generation globally.
Policies
Governments around the world have implemented policies to promote the growth of renewable energy. For example, the US Energy Policy Act of 2005 introduced tax incentives for energy efficiency and renewable energy production (https://www.energy.gov/scep/slsc/policies-and-programs). The US Environmental Protection Agency has a database tracking state policies that encourage renewable energy use through rebates, tax credits, and renewable portfolio standards (https://www.epa.gov/statelocalenergy/state-renewable-energy-policies). Many governments have set renewable energy targets, such as the US aiming for 30% of its electricity generation to come from renewable sources by 2030.
Future Outlook
The future potential for renewable energy is enormous as costs continue to fall and technology improves. According to the UN, renewable energy has the potential to provide up to 80% of total global energy demand by 2050. Investment and deployment of renewable energy is growing rapidly, with solar and wind expanding at double digit rates annually.
The NY Times reports that the transition to clean energy is happening faster than anticipated, with renewables projected to overtake coal as the world’s largest electricity source by 2025. Many experts predict renewables will make up 50-70% of global electricity by 2050. Lower costs, improved efficiency and energy storage solutions will enable greater integration of renewables into energy systems.
Governments, corporations and individuals worldwide are increasingly supporting renewable energy development. Over 130 countries have adopted renewable energy targets and policies to accelerate growth. Major companies like Google, Apple and Amazon have pledged to fully power operations with renewables. Further technological innovations, infrastructure build-out, and enabling policies can unlock the full potential of renewables this century.
Conclusion
In summary, the top three most used renewable energy sources are hydroelectric power, wind power, and solar power. Hydroelectric power harnesses the energy from flowing water and is used to generate electricity around the world. Wind power utilizes large wind turbines to capture kinetic energy from the wind and convert it into electricity. Finally, solar power makes use of photovoltaic panels to absorb energy from the sun and transform it into usable electrical power.
As we look to transition away from fossil fuels, expanding the use of renewable energy sources like these will be critical. Renewable energy has numerous benefits – it produces no greenhouse gas emissions, diversifies and secures our energy supply, and reduces dependence on finite fossil fuel reserves. There are still challenges to overcome, such as intermittency and high upfront costs, but continued innovation and supportive policies can help renewables become an increasingly cost-competitive and reliable contributor to our energy system. With the right strategies in place, renewable energy can play a leading role in building a sustainable energy future.