What Are Benefits Of Geothermal?
Geothermal energy is heat derived from the Earth. It is a renewable and sustainable energy source that offers numerous benefits. This article will provide an overview of the key advantages of using geothermal energy.
Renewable and Sustainable
Geothermal energy is considered renewable because heat is continuously produced inside the earth. The heat originates from radioactive decay of minerals, as well as residual heat from the planet’s formation. Geothermal energy is therefore constantly replenished and will be available for the foreseeable future.
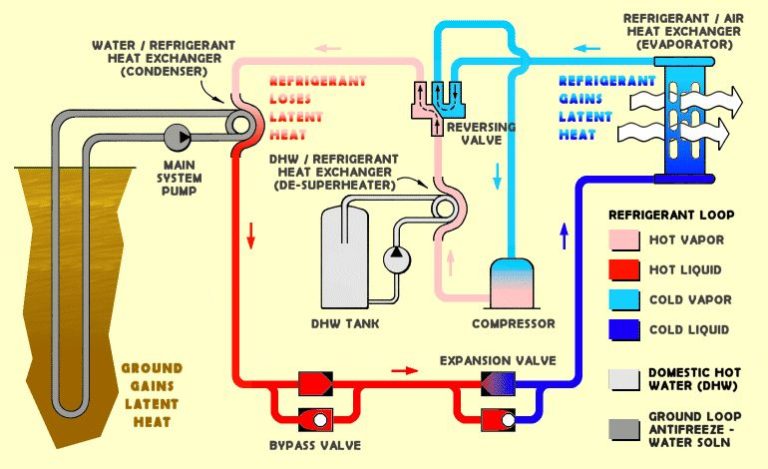
Geothermal is also sustainable if properly managed. Sustainability comes from replacing the water extracted from geothermal reservoirs. By injecting wastewater back underground, the water supply can be conserved. Geothermal plants with subsurface heat exchangers that don’t require water extraction are even more sustainable.
Unlike fossil fuels which take millions of years to form and are depleted with use, geothermal energy is available indefinitely. This makes geothermal a reliable long-term energy solution compared to finite resources.
Reduces Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Geothermal power plants produce significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional fossil fuel power plants. While fossil fuels like coal, oil and natural gas emit high levels of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases when burned, geothermal utilizes heat already present below the earth’s surface and does not require combustion. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, geothermal power plants emit on average just 5% of the carbon dioxide of a coal-fired plant per megawatt-hour of electricity produced. They also emit 5% of the nitrous oxide and less than 1% of the sulfur dioxide compared to conventional coal plants. This minimal greenhouse gas footprint makes geothermal an environmentally friendly option for power generation as countries and organizations look for ways to transition to low carbon energy sources.
Provides Reliable Base Load Power
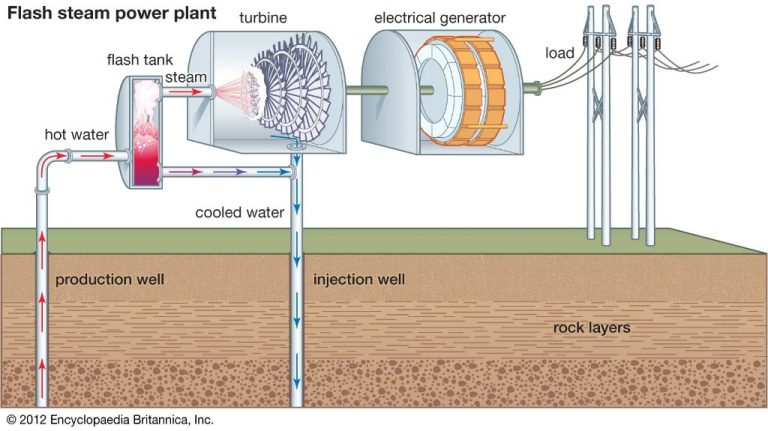
Geothermal energy is able to provide consistent base load power capability unlike some other renewable energy sources like wind and solar that are intermittent and weather dependent. The geothermal resource under the earth’s surface is available 24/7 regardless of weather conditions on the surface. Geothermal plants have capacity factors of 90-95%, meaning they can generate nearly full power all day every day.
This reliable base load capacity is important for grid stability and security, ensuring that demand can be met at all times. Geothermal helps complement other renewables like wind and solar that may have variable output. The baseload geothermal power can fill in when variable resources are offline.
Geothermal’s reliability also provides energy security. With on-site fuel availability, geothermal plants are not subject to potential fuel delivery disruptions. The consistent power supply protects against grid instability and blackouts.
In regions where geothermal resources are available, geothermal power plants can form the backbone of a resilient, renewable electricity system alongside solar, wind and other renewables.
Cost Competitive
Geothermal energy is cost competitive with conventional energy sources like coal and nuclear when analyzing the full lifecycle costs. The levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) for geothermal power plants is estimated to be around $0.04 to $0.07 per kWh, making it comparable to natural gas and coal.
While the initial drilling and exploration costs for geothermal plants can be high, the plants have a long lifespan of 20-30 years with very low maintenance costs. This makes the levelized costs over the full lifespan competitive. There are also no fuel costs for geothermal since the earth’s internal heat is used directly for power generation. This provides price stability without exposure to fluctuating fuel markets.
When subsidies and tax incentives are factored in, geothermal can be even more cost effective. Many countries provide financial incentives to accelerate geothermal development and adoption. Overall, geothermal provides a cost-stable, competitively priced solution over the long term when compared to conventional fuel sources.
Widely Available
Geothermal energy is widely available in many countries around the world thanks to the heat beneath the Earth’s surface. The Earth’s core is over 6,000°C, and this heat conducts to shallower depths that we can access for geothermal power and heating. Only a small fraction of this enormous amount of heat is needed to supply the world’s energy needs.
Geothermal resources are available on every continent and traditionally have been utilized in countries with obvious surface manifestations like geysers and hot springs. However, with recent advances in technology, countries are increasingly accessing the ubiquitous geothermal heat available everywhere by drilling to deeper depths. Unlike solar or wind which depend on weather and time of day, the heat beneath the surface is constantly available 24/7.

Experts estimate geothermal power potential to be over 200 gigawatts just within the western United States alone. With enhanced geothermal systems, there is enough accessible geothermal energy to provide 10% of U.S. electricity generation. The geothermal electricity generation market is still underdeveloped relative to its vast potential.
Energy Security
Geothermal energy enhances national and energy security by reducing our dependence on imported fossil fuels. Geothermal plants can operate continuously, unaffected by changing weather conditions or fuel prices, providing a reliable and secure baseload power source. Developing geothermal resources utilizes domestic energy sources, often in rural communities, keeping energy spending within the local economy. With over 30 countries currently using geothermal power, and a vast global resource potential, there is opportunity for many nations to increase energy independence through geothermal development.
Job Creation
Geothermal energy provides substantial domestic job creation opportunities. According to the Geothermal Energy Association, the geothermal industry employed an estimated 25,000 Americans across geothermal project development, power plant construction, operation and maintenance in 2018. This represented a 4% increase in geothermal jobs from the previous year. The geothermal workforce spans a wide range of professions including drilling rig crews, engineers, geologists, technicians, construction workers, electricians, and more. Most of these jobs are local, supporting communities near geothermal plants and cannot be outsourced.
With over 3.5 gigawatts of geothermal power plants currently under development in the U.S., thousands of new well-paying jobs are expected in the coming years as these projects come online. The Department of Energy estimates that reaching the Biden Administration’s goal of 100 GW of geothermal capacity by 2050 would support approximately 150,000 new jobs nationwide. Realizing the immense geothermal resource potential across the Western U.S. can become an economic engine, creating new employment opportunities in rural communities near untapped geothermal reservoirs.
Versatile Applications
In addition to generating power, geothermal resources can be used for a variety of applications thanks to their inherent qualities as a baseload renewable energy source. Here are some of the main ways geothermal is being utilized today:
Direct Heating: Geothermal reservoirs located near the earth’s surface provide water or steam that can be used directly for heating buildings, greenhouses, fish farms and other facilities. This direct use of geothermal is estimated to meet the heating and cooling needs for over 120 million square feet worldwide.
District Heating: Geothermal district heating systems distribute hot water from a central geothermal source to multiple buildings in a community via a network of underground pipes. These systems provide climate-friendly heating for homes, businesses, schools and other facilities.
Food Drying: The heat from geothermal resources can be used in food processing and drying. It is a clean, renewable source of low-temperature heat ideal for drying fruits, vegetables and meats.
Aquaculture: Geothermal fluids provide consistent warm water temperatures that are perfect for raising fish and shellfish in aquaculture facilities. Geothermal aquaculture is being used for tropical fish, alligators and more.
Industrial Processing: A number of industrial processes require very precise temperature control and clean heat sources, which geothermal can provide. Examples include milk pasteurization, gold mining, laundering, chemical extraction and more.
Absorption Cooling: Geothermal power plants produce excess heat that can be used to drive absorption chillers for air conditioning. This provides cooling without the greenhouse gas emissions of conventional systems.
Conclusion
In summary, geothermal energy provides numerous important benefits as part of the global energy transition. As a renewable and sustainable energy source available 24/7, geothermal can deliver reliable base load power to electric grids while dramatically reducing greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels. The geothermal energy resource is widely available across the planet and can be harnessed locally, improving energy security. While geothermal power plants require high upfront investments, their operating costs are competitive with conventional fuels. Geothermal energy also enables job creation and versatile direct use applications for heating buildings, greenhouses and industrial processes. With all of these advantages, geothermal has a crucial role to play in building a clean energy future.