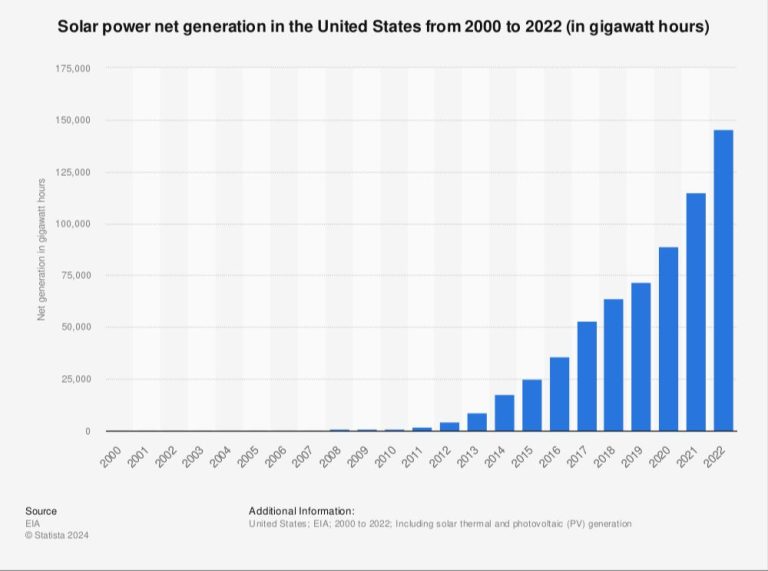
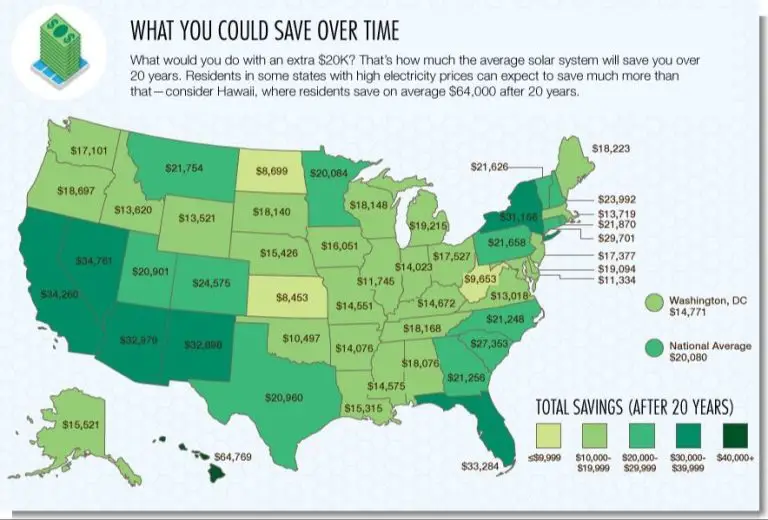
What Are 3 Uses Of Solar?
Solar energy is rapidly becoming an essential part of our global energy system. The sun provides an abundant and renewable source of power that can generate electricity, provide heating and cooling, and enable innovative new technologies. As solar technology improves and costs continue to fall, solar is poised to play a major role in reducing fossil fuel consumption and combating climate change.
Solar Electricity Generation
Solar photovoltaic (PV) panels are one of the most common ways to utilize the sun’s energy. PV cells convert sunlight directly into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. An array of PV modules/panels can be installed on rooftops, ground-mounted fixtures, or integrated into building materials to generate renewable electricity.
Grid-tied solar PV systems feed excess electricity back to the utility grid. This allows homes and businesses with PV panels to earn credit for the electricity they generate but don’t use. Solar PV systems can also be stand-alone off-grid systems, commonly used for remote power and in developing regions without existing grid infrastructure.
Solar PV capacity has expanded rapidly in recent years thanks to falling costs and supportive policies. With no fuel costs and minimal maintenance, solar PV provides a clean, renewable source of electricity at a predictable cost once installed. Advancements in energy storage technologies are helping address solar intermittency concerns as well.
Overall, solar PV electricity generation offers homeowners, businesses, and utilities a sustainable energy solution. It reduces reliance on fossil fuels, lowers carbon emissions, and takes advantage of an abundant free resource – the sun’s rays.
Solar Heating
Solar thermal systems harness heat from the sun to provide hot water and space heating in homes, businesses, and industry. Solar collectors, often mounted on rooftops, absorb sunlight and transfer the heat to a fluid which is circulated through the building’s water system. Solar thermal is one of the most widespread uses of solar energy.
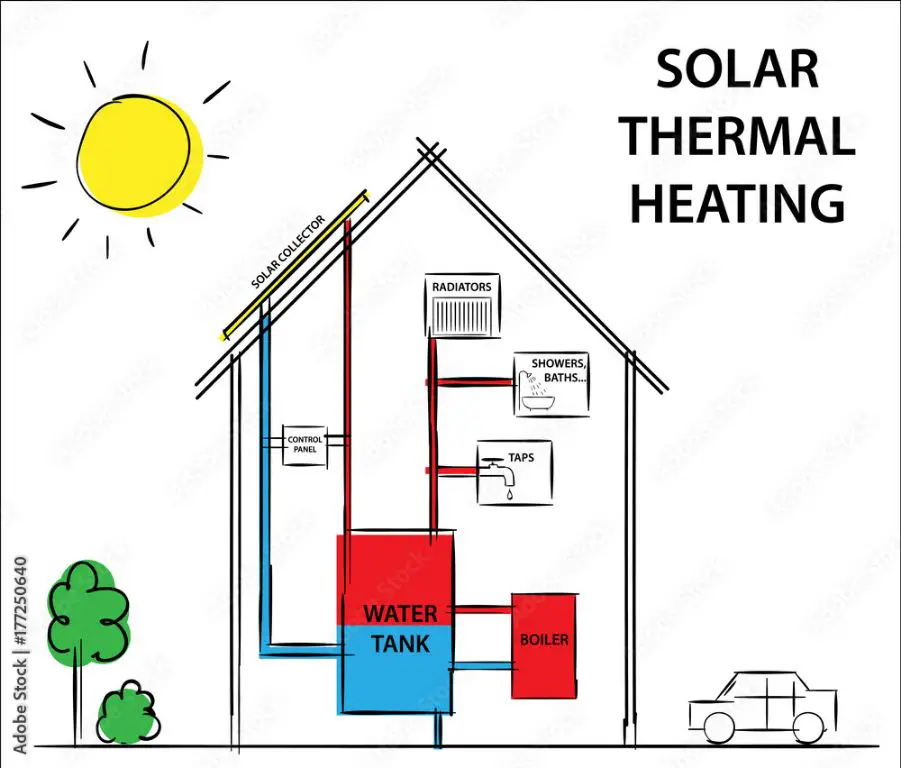
The two main types of solar collectors used for heating are flat plate collectors and evacuated tube collectors. Flat plate collectors, the most common type, are insulated, weatherproof boxes that contain a dark absorber plate under a glass or plastic cover. Evacuated tube collectors contain parallel rows of transparent glass tubes, each containing a glass outer tube and metal absorber attached to a fin. The vacuum between the two glass layers significantly improves efficiency.
Solar water heating systems can lower energy bills and reduce a building’s carbon footprint. Solar space heating is less common but can meet some or all of a structure’s space heating demand. In warmer climates, solar pool heating is popular for residential pools and water parks. The upfront costs of solar heating systems can be high, but the long-term savings and environmental benefits make it an increasingly attractive option.
Solar Cooking
Solar cookers and ovens harness the sun’s energy to cook food without the need for electricity or fuel. This makes them a sustainable, low-cost option for cooking in areas with abundant sunlight. Here are some key ways solar cooking is used:
Cooking meals: Solar cookers can be used to cook everyday meals ranging from rice, potatoes, and baked goods to stews, soups, and meats. Food is placed inside a solar cooker or oven and the sun’s rays heat it to cooking temperatures. Many solar oven designs reach over 300°F, sufficient for baking and roasting.
Sterilizing water: Solar cookers can heat water hot enough to sterilize it and make it safe to drink. Boiling water is an effective way to kill bacteria, viruses, and parasites. This makes solar cookers useful for producing clean drinking water in developing regions.
Pasteurizing milk: Heating milk to at least 145°F for 30 minutes pasteurizes it by killing harmful bacteria. Solar cookers can pasteurize milk to make it safer for drinking. This helps prevent foodborne illnesses.
Preserving foods: Solar drying is a traditional method of food preservation that extends shelf life. Solar ovens rapidly dry fruits, vegetables, meats, and herbs by evaporating moisture. Dried foods keep longer and can be reconstituted later by adding water.
Supporting healthy diets: In sunny and fuel-scarce regions, solar cooking grants access to hot meals that might otherwise be difficult to prepare. The availability of cooked food supports better nutrition and health.
Solar Desalination
One important use of solar energy is for desalination, which is the process of removing salt and other minerals from seawater to produce fresh, potable water. Areas with limited natural freshwater supplies can use solar desalination to create clean drinking water.
Solar desalination takes advantage of the sun’s heat to evaporate and purify water. Seawater or brackish water is contained in shallow ponds and exposed to sunlight. As the water heats up and evaporates, the condensation collects on clear plastic sheets as fresh water, leaving the salt behind. This basic solar still design can produce clean water for drinking and cooking.
More advanced solar desalination systems concentrate sunlight with mirrors to achieve the high temperatures needed to boil seawater. The steam is then captured and condensed into fresh water. These concentrated solar power systems can produce larger volumes of fresh water efficiently.
Solar desalination provides a sustainable solution for freshwater in areas with limited natural supplies. The renewable power of the sun can be harnessed to transform seawater into safe drinking water through evaporation and condensation.
Solar Vehicles
Solar vehicles use solar panels to convert sunlight into electricity to power electric motors. This allows vehicles like cars, boats, buses, and even planes to operate on solar energy rather than traditional fossil fuels like gasoline or diesel.
Solar vehicles first emerged in the 1980s and 1990s but have become increasingly popular and technologically advanced in recent years. The solar car industry has rapidly innovated and improved solar panel efficiency, battery technology, electric motors, and aerodynamic design to maximize the capture and use of solar energy.
Some of the main types of solar vehicles include:
- Solar cars – Solar cars use photovoltaic solar panels mounted on the vehicle to generate electricity that powers electric motors. Most solar cars are designed for racing competitions like the World Solar Challenge across Australia’s outback. Production models of solar cars for commercial use are now also emerging.
- Solar boats – Solar power is well suited for boats, with panels mounted on roofs or sails to capture sun and convert it to electricity to power propellers. Solar boats like PlanetSolar have even circumnavigated the globe using only solar power.
- Solar planes – Solar Impulse 2 was the first solar plane to fly around the world without any fuel, only powered by 17,000 solar cells. More solar planes are in development for cargo and even passenger use.
Solar vehicles are emission-free and environmentally sustainable forms of transportation. As solar technology continues to develop, solar-powered cars, boats, buses, and planes have the potential to significantly reduce fossil fuel consumption and pollution.
Solar Architecture
One of the most innovative uses of solar energy is in architectural design to maximize solar heat gain. This passive solar design takes advantage of the sun’s energy through building orientation, materials, and components. By optimizing the building’s interaction with the sun, solar architecture can significantly reduce energy costs for heating and lighting.
When designing a solar building, a key focus is orienting and shaping the structure to capture winter sun while rejecting summer sun. South-facing walls and windows collect heat from low-angle winter sunlight. Overhangs, awnings, and shade trees block high-angle summer sunshine to prevent overheating. Strategic landscaping also provides shade in summer and sunlight in winter.
Another important element is thermal mass – materials like concrete, stone, and tile that absorb and slowly release solar heat. Thermal mass installed on interior south-facing walls stores warmth when the sun shines and radiates it back into rooms at night. Operable vents, windows, and skylights maximize natural ventilation and daylighting.
Solar architecture utilizes passive systems only, without mechanical controls or external power sources. When thoughtfully integrated into construction and operations, buildings designed this way can reduce heating and cooling costs by up to 85%. With energy-efficient technologies and renewable materials, solar architecture offers a sustainable, cost-effective means of harnessing the sun’s abundant energy.
Agricultural Applications
Solar energy has become an important tool for farmers and the agricultural industry. Solar-powered equipment is being used in innovative ways to improve agricultural practices and increase yields.
One key application is solar crop drying. Solar dryers utilize passive solar heating to dry fruits, vegetables, grains, spices, and other crops for storage and preservation. The dry, hot air created by the solar collectors removes moisture gently and naturally without use of fossil fuels.
Solar-powered irrigation is another important agricultural use. Solar photovoltaic panels can power water pumps to irrigate fields and greenhouses. Solar-powered drip irrigation systems help distribute water efficiently to crops. Solar irrigation is extremely useful in remote areas without access to an electric grid.
Solar-powered lighting has also emerged as an important agricultural tool. Specialized solar lamps and light fixtures can provide artificial sunlight and extend daylight hours in greenhouses, livestock barns, and other farm buildings. This can help improve plant growth and animal health.
The many uses of solar energy are helping the agriculture industry reduce fossil fuel consumption, increase sustainability, and improve productivity.
Solar Products
Solar technology has led to the development of a wide variety of consumer products that utilize the sun’s energy. From small gadgets to larger systems, solar products provide clean power without the need for batteries or electricity.
One of the most common solar products are solar-powered calculators. These use tiny solar cells to convert light into electricity that powers the calculator. Solar chargers for small electronics like phones and tablets are also very popular. These portable chargers collect solar energy during the day so you can charge your devices anywhere.
For outdoor enthusiasts, solar-powered lanterns, fans, and phone chargers allow you to stay powered up without plugging in. Solar bags and backpacks have built-in solar panels to charge your gear on the go. Solar cookstoves provide an eco-friendly way to cook meals using the sun’s thermal energy.
For the home, solar-powered lighting fixtures, pool heaters and pumps provide green energy savings. Solar water heaters are a cost-effective way to heat water using the sun. Even solar-powered garden decor, like fountains and string lights, allow you to accessorize your outdoor space using just the power of the sun.
With solar product options continuing to expand, harnessing the sun’s energy for everyday use has never been easier or more convenient.
Conclusion
In summary, solar energy has many diverse applications that demonstrate its versatility and potential. From generating electricity to heating water, cooking food, and powering vehicles, solar provides a renewable and clean alternative to fossil fuels.
The future outlook for solar energy is very promising. With solar technology costs continuing to fall and efficiency improving, solar is becoming cost competitive with conventional power. Solar energy capacity and adoption is expected to grow rapidly in the coming decades. New innovative applications of solar energy are also likely to emerge. With solar energy’s environmental benefits, there is strong motivation worldwide to move towards a solar-powered future.